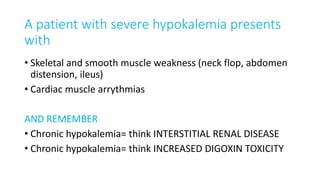
Hypokalemia is defined as a serum potassium level below 3.5 mEq/L, requiring tests like spot urine potassium and the trans tubular potassium gradient (TTKG) for diagnosis. Causes can be differentiated into renal and non-renal categories, with treatment tailored accordingly; oral potassium is preferred unless severe cases necessitate IV administration under ECG monitoring. Patients with hypokalemia may present with symptoms such as muscle weakness and cardiac arrhythmias, and chronic cases can lead to interstitial renal disease or increased digoxin toxicity.



![Spot urine potassium is
denoted by U[K+]
It maybe less than 20 or more than 20](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hypokalemia-200213191742/85/Hypokalemia-4-320.jpg)

![Trans Tubular Potassium
Gradient
TTKG= U[K+] times serum osmolality /
serum K+ times urine osmolality](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hypokalemia-200213191742/85/Hypokalemia-6-320.jpg)

![If U[K+] is less than 20mEq/L
TTKG will definitely be less than 4
AND
THINK “NON RENAL”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hypokalemia-200213191742/85/Hypokalemia-8-320.jpg)
![If U[K+] is more than 20mEq/L
TTKG will definitely be more than 4
AND
THINK “RENAL”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hypokalemia-200213191742/85/Hypokalemia-9-320.jpg)