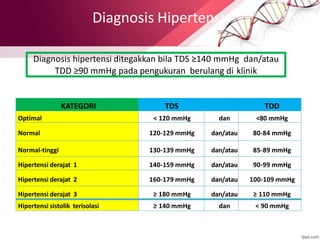
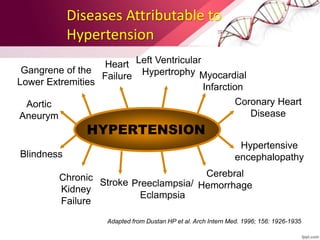
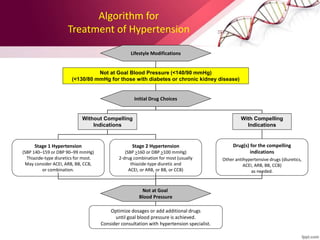
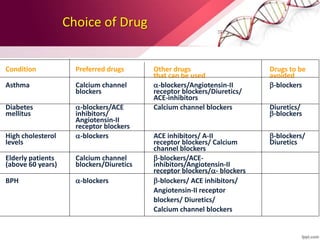
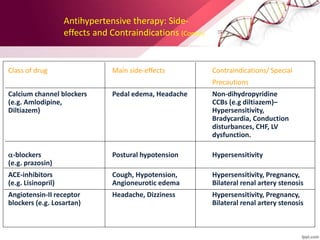
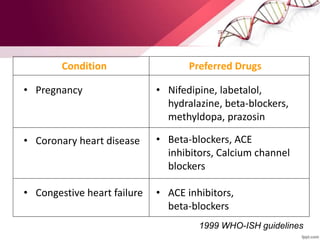
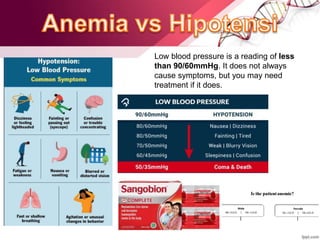
Hypertension is defined as blood pressure above 140/90 mmHg. It is classified as essential (95% of cases, no identifiable cause) or secondary (underlying cause such as renal or endocrine issues). Risk factors include age, family history, obesity, smoking, high salt diet, and sedentary lifestyle. If untreated, hypertension can lead to heart failure, stroke, kidney failure and other complications. Treatment involves lifestyle modifications like weight loss, exercise, diet changes and reducing alcohol/sodium intake, as well as pharmacologic treatments like diuretics, ACE inhibitors, calcium channel blockers and others. The goals of treatment are to prevent target organ damage and reduce cardiac and renal morbidity and mortality by achieving a