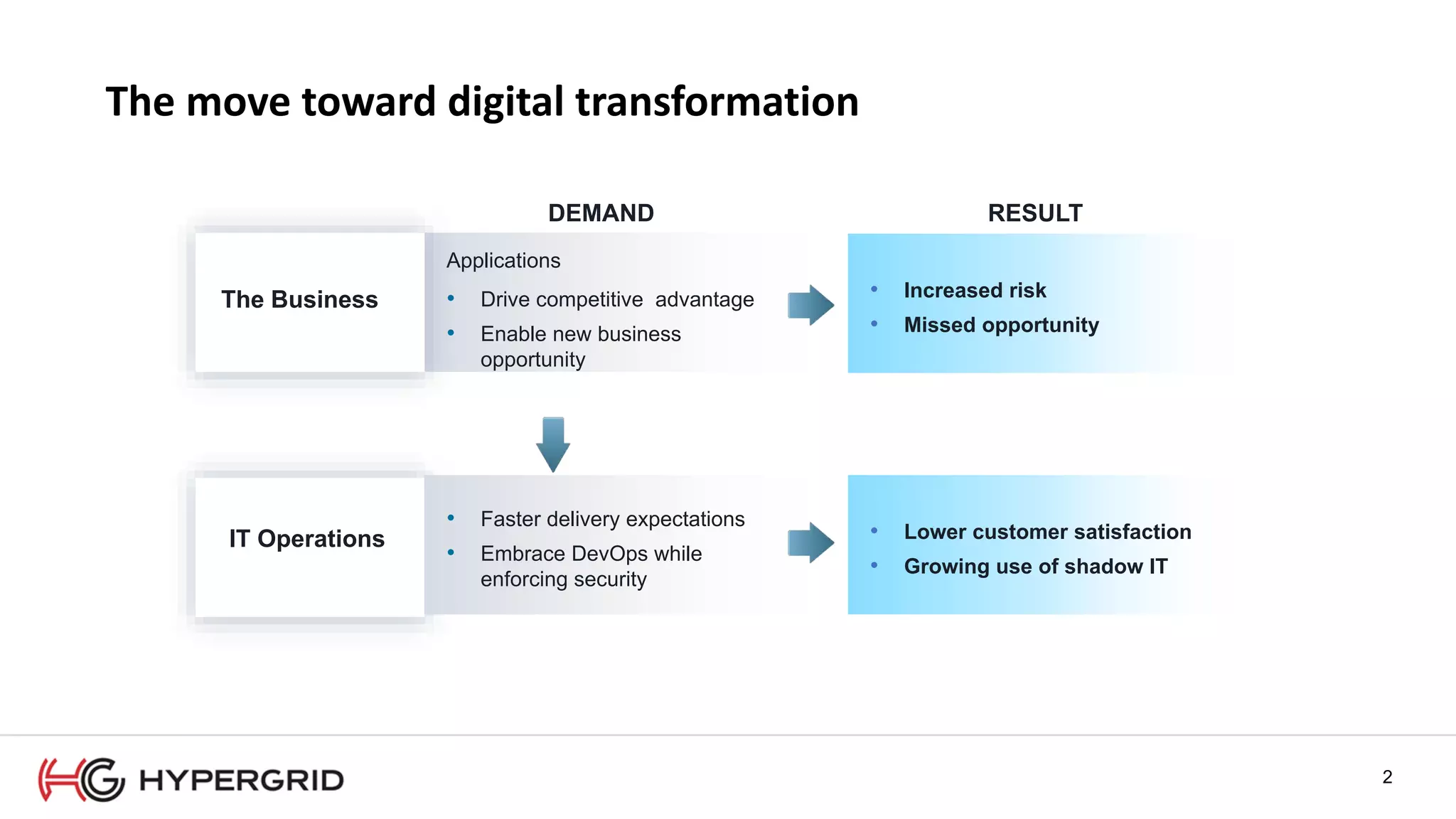
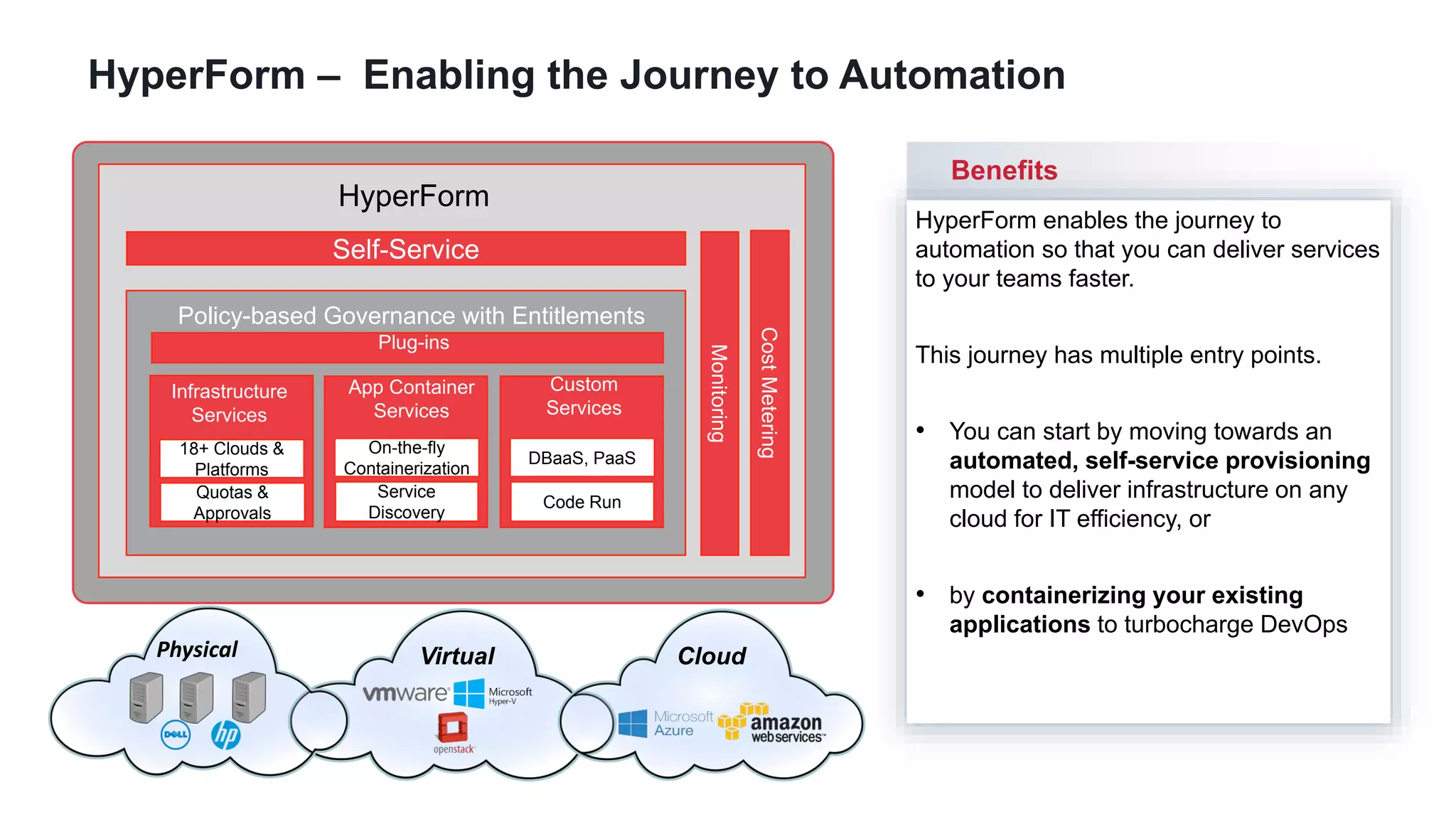
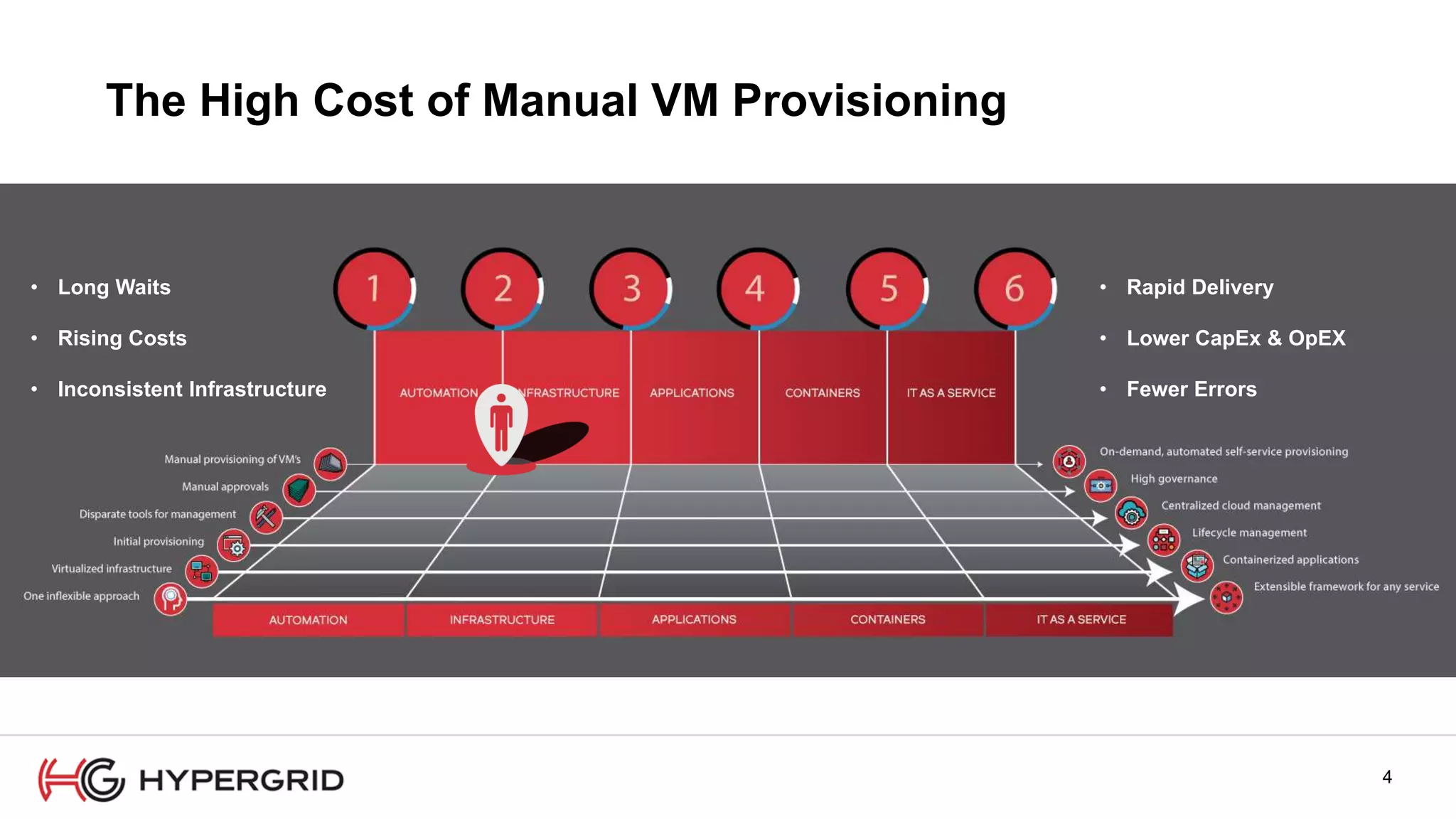
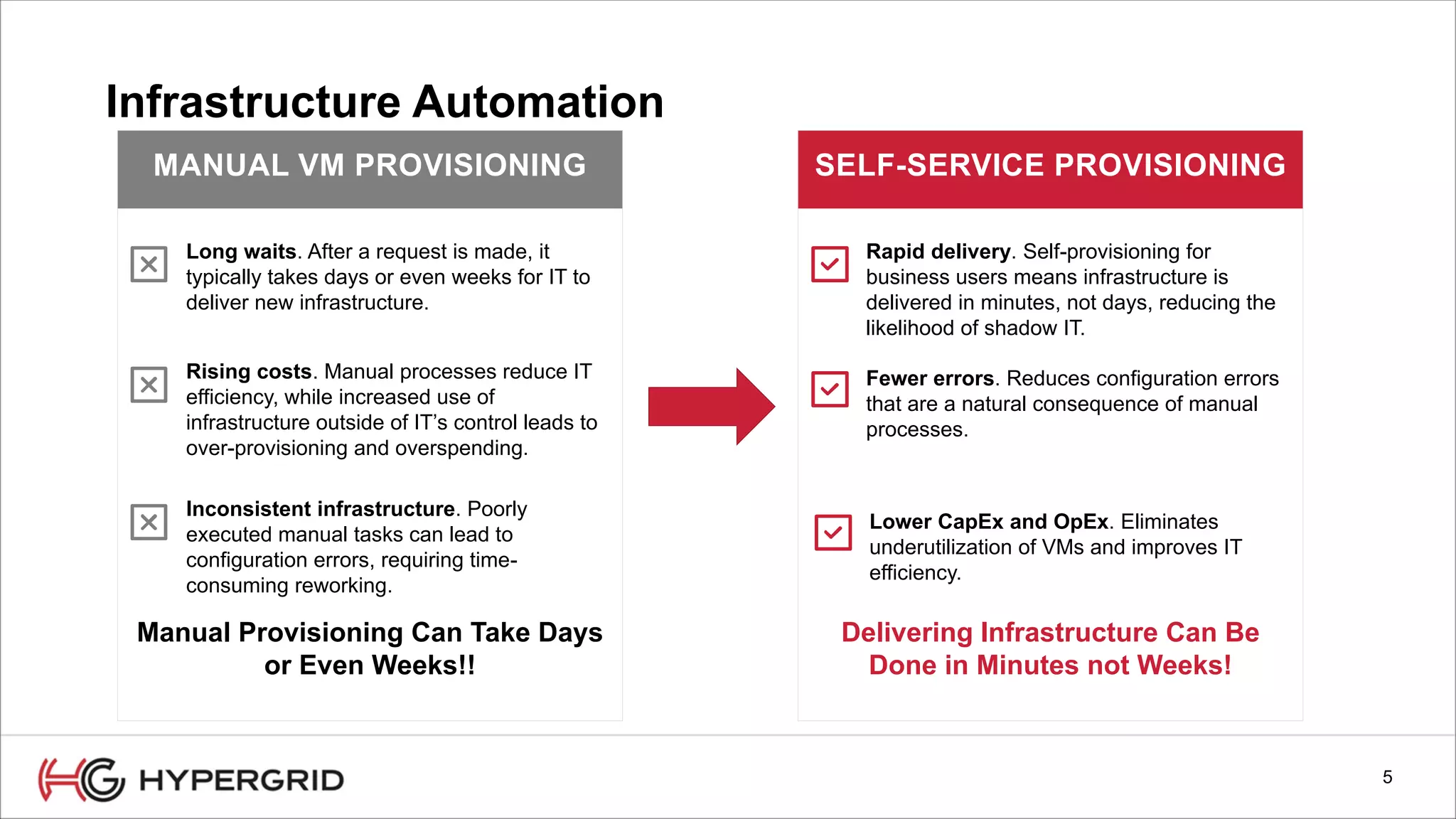
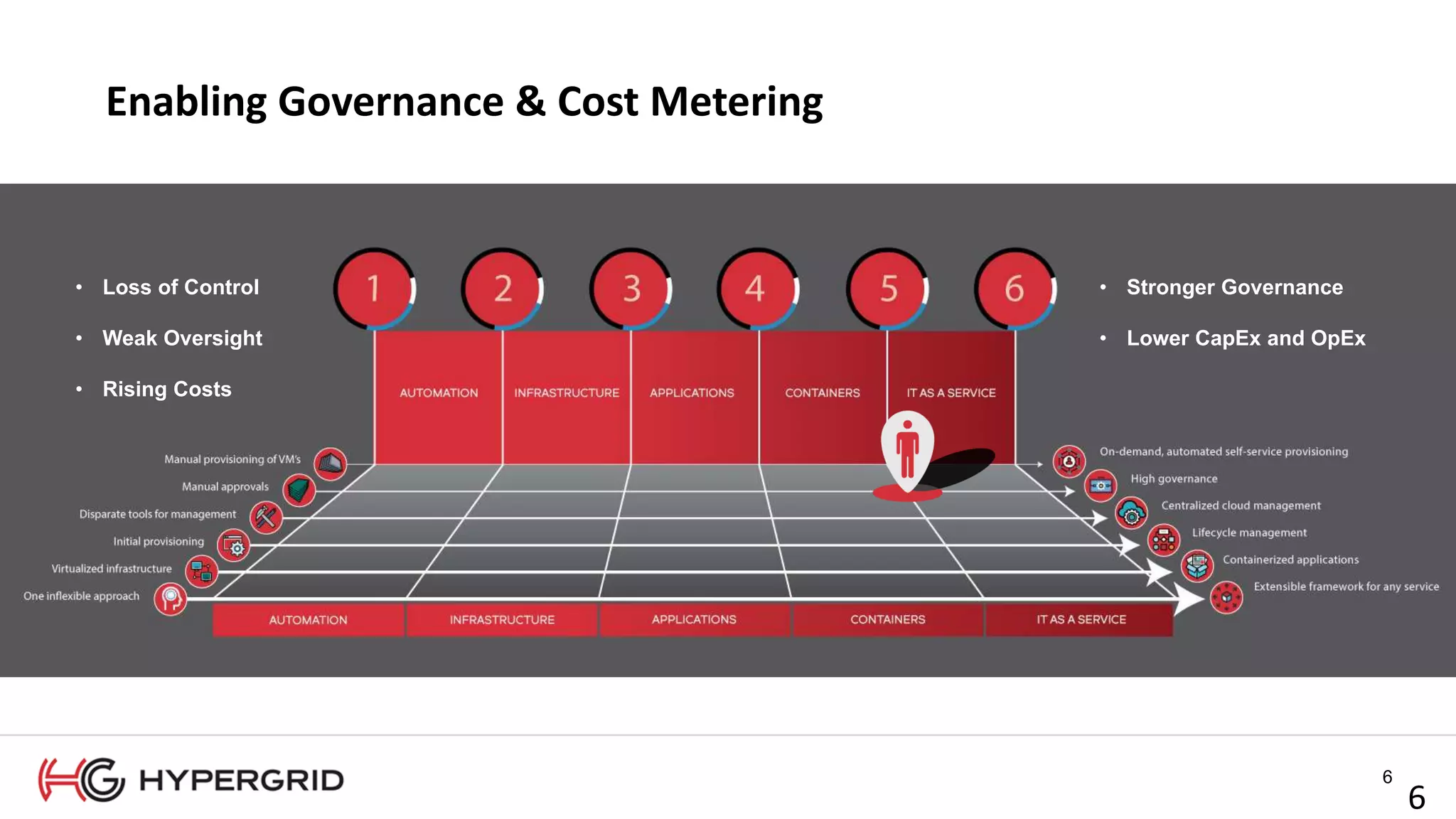
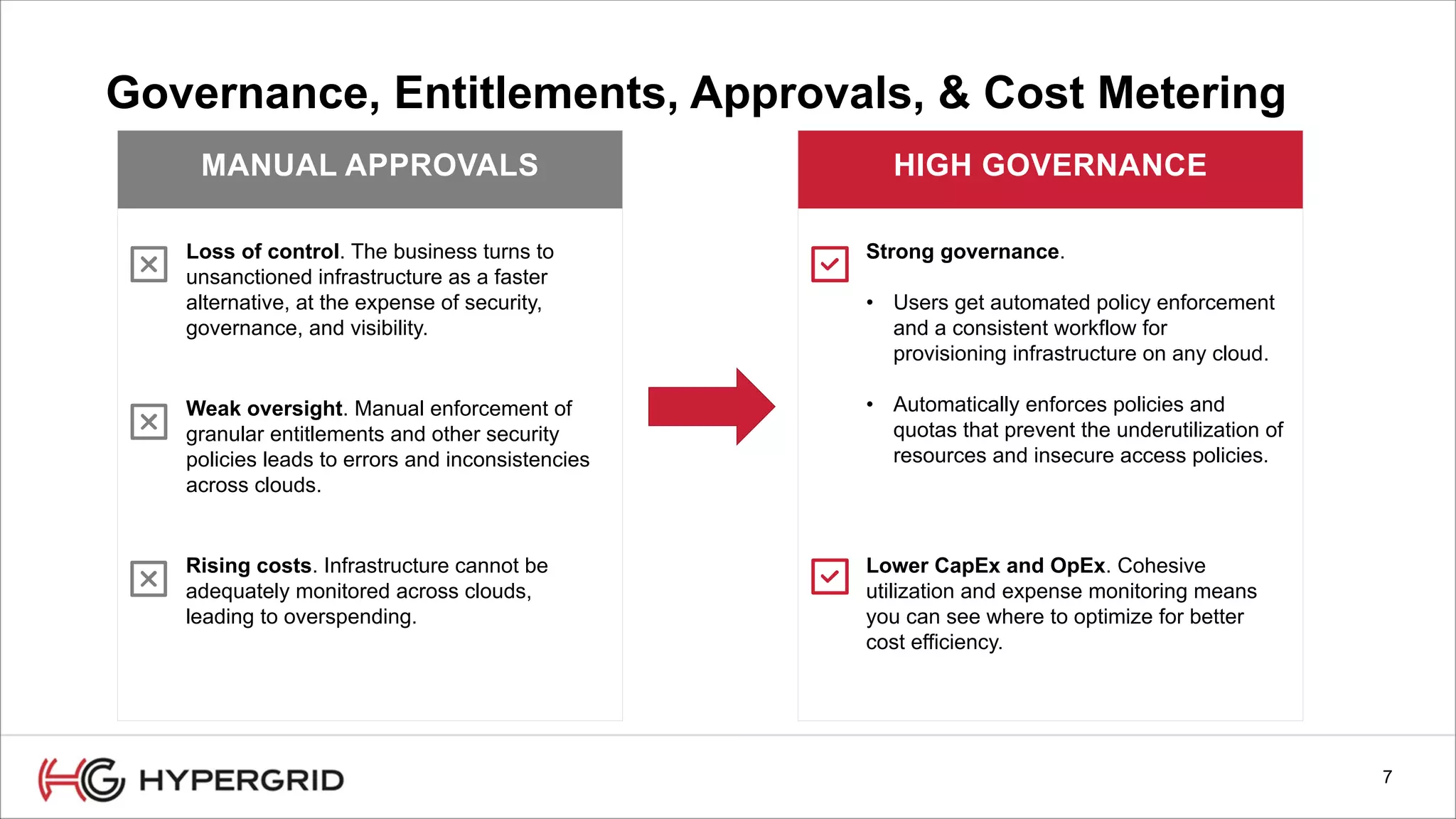
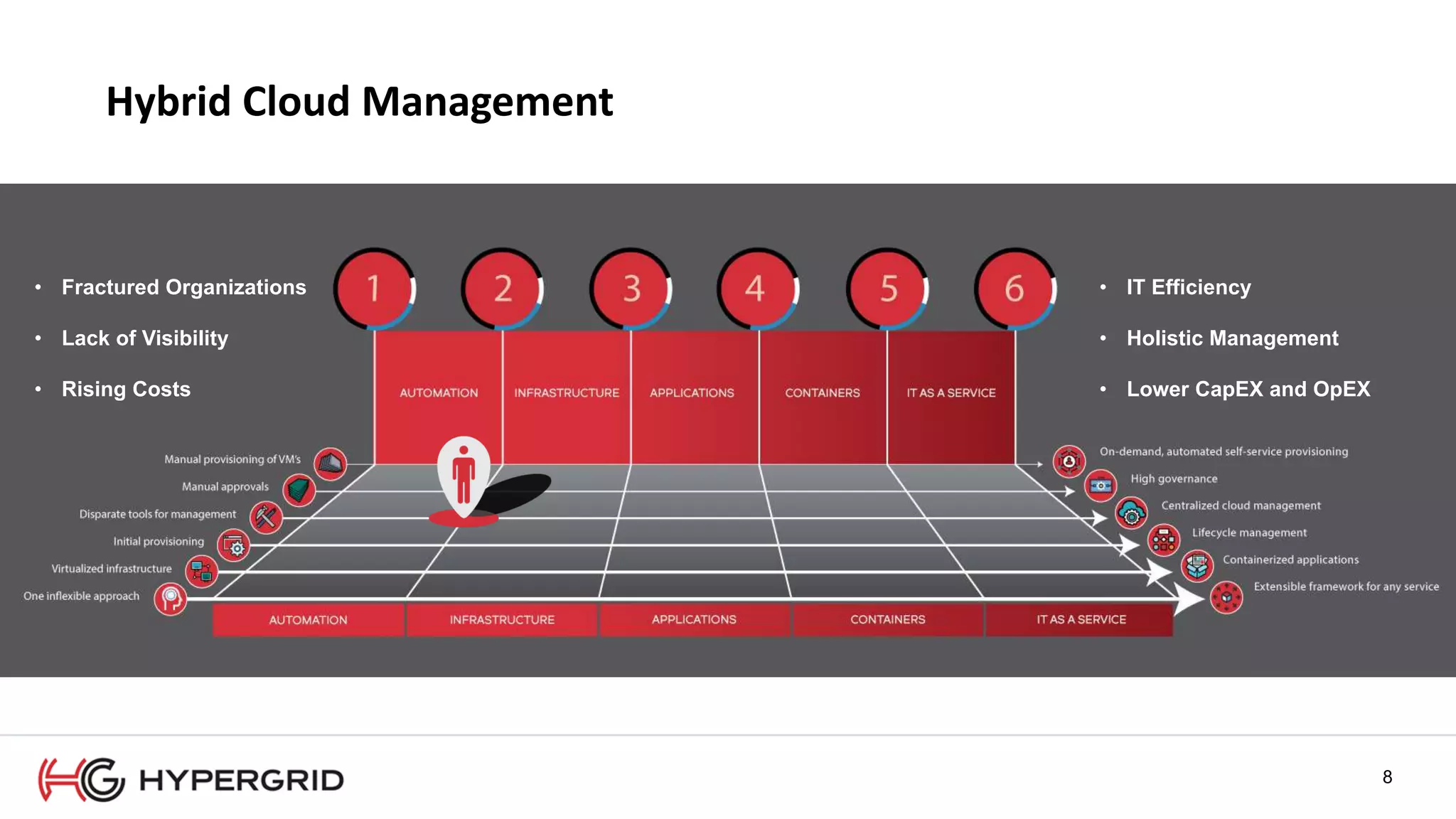
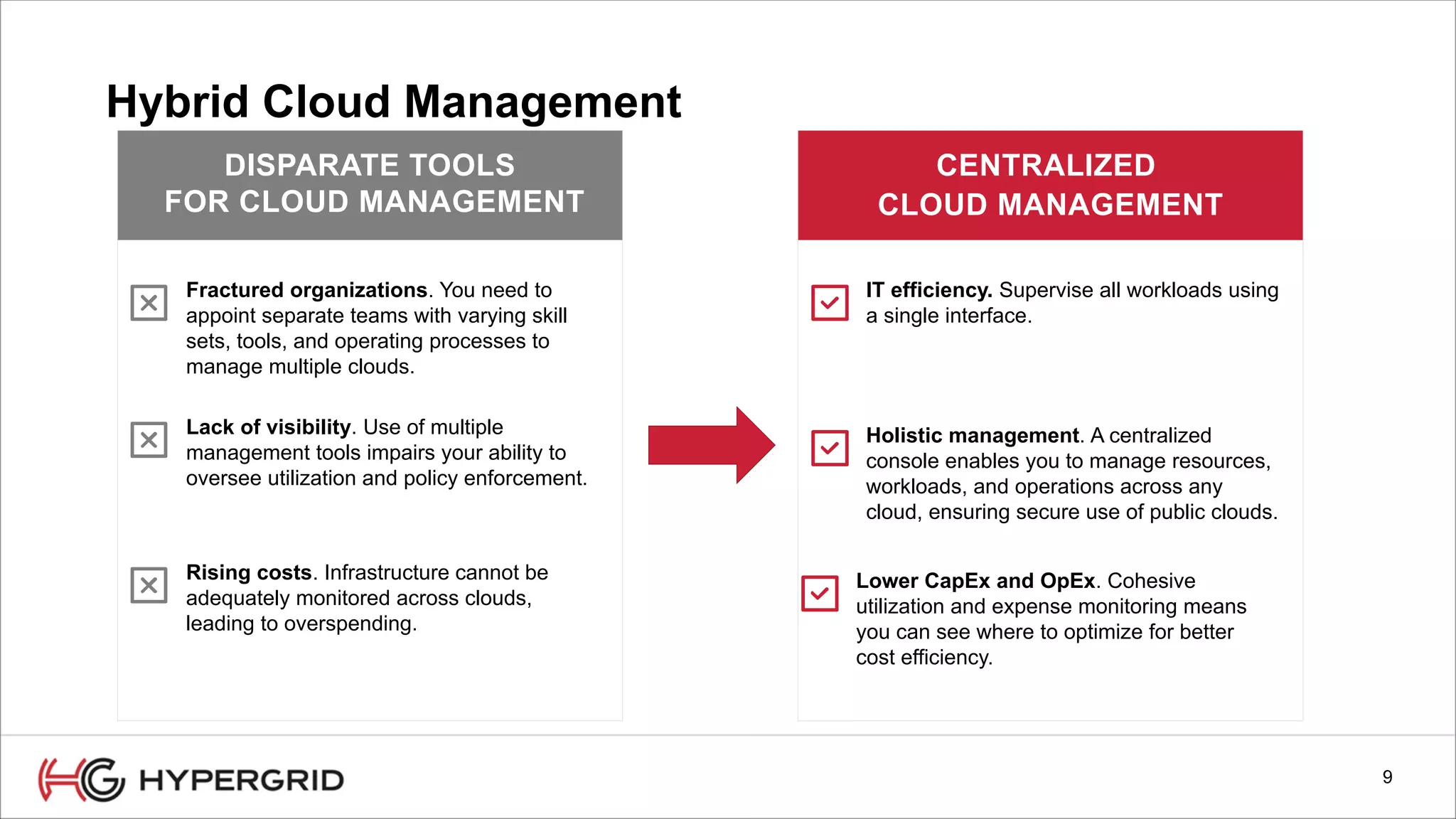
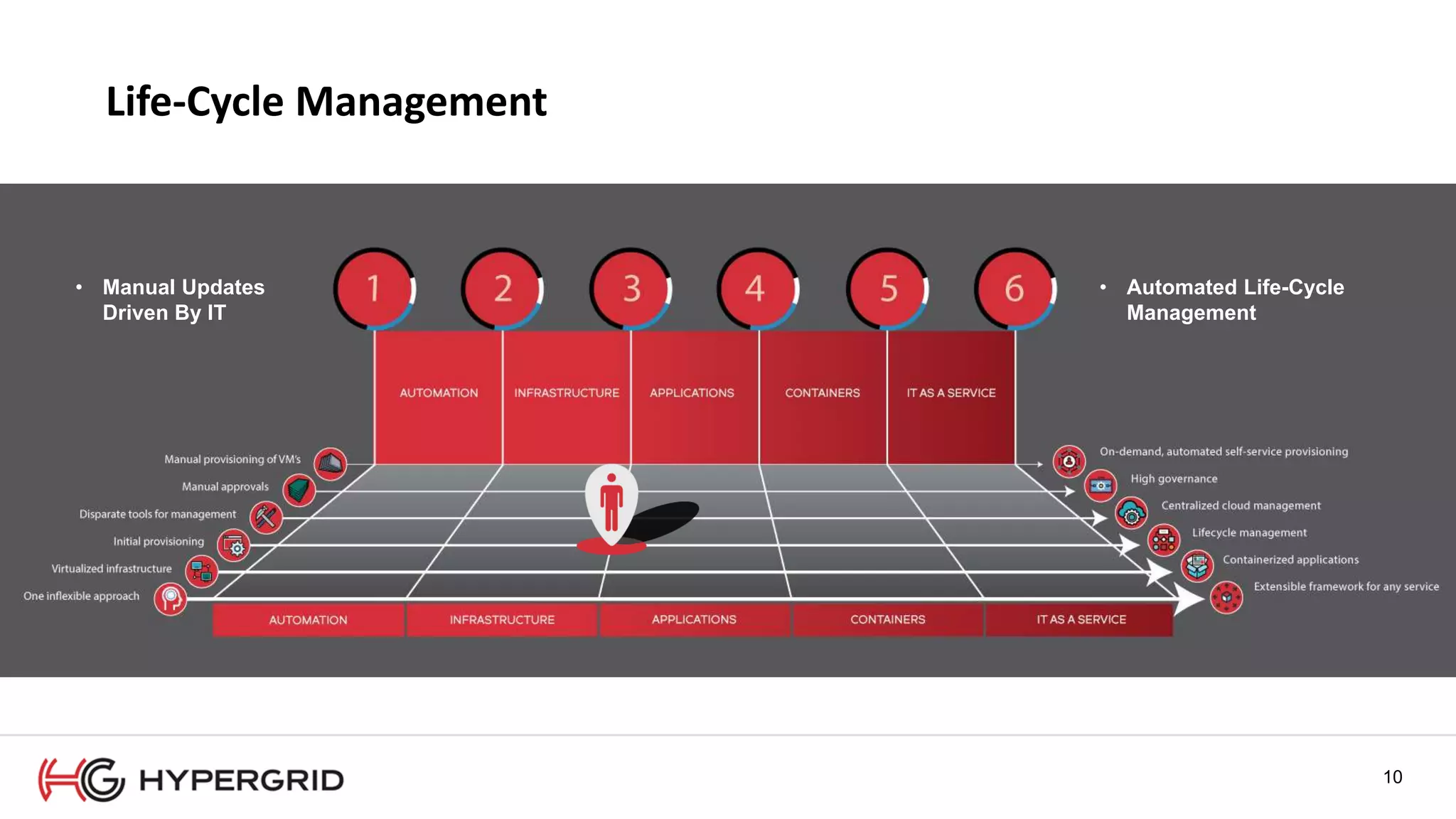
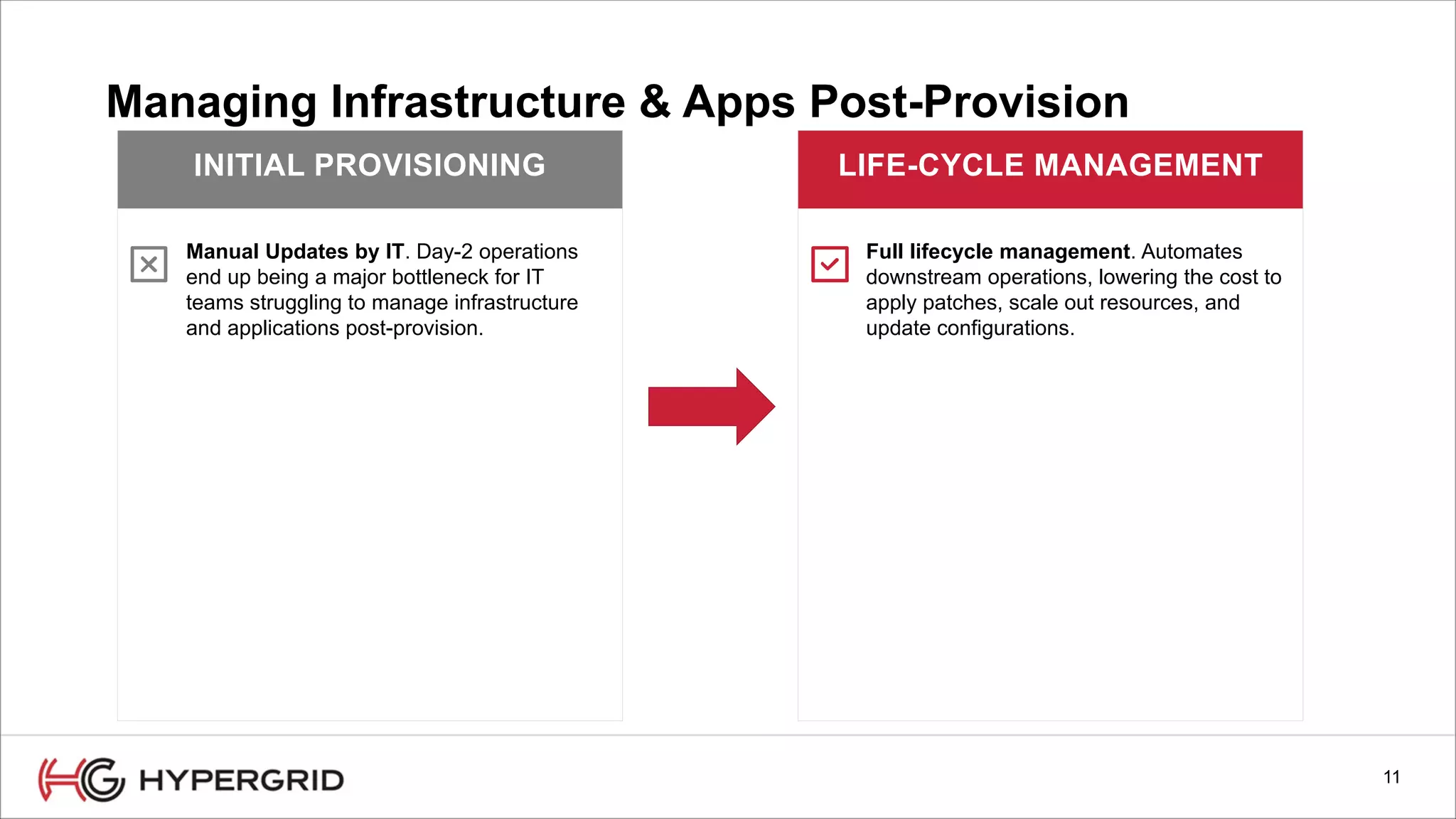
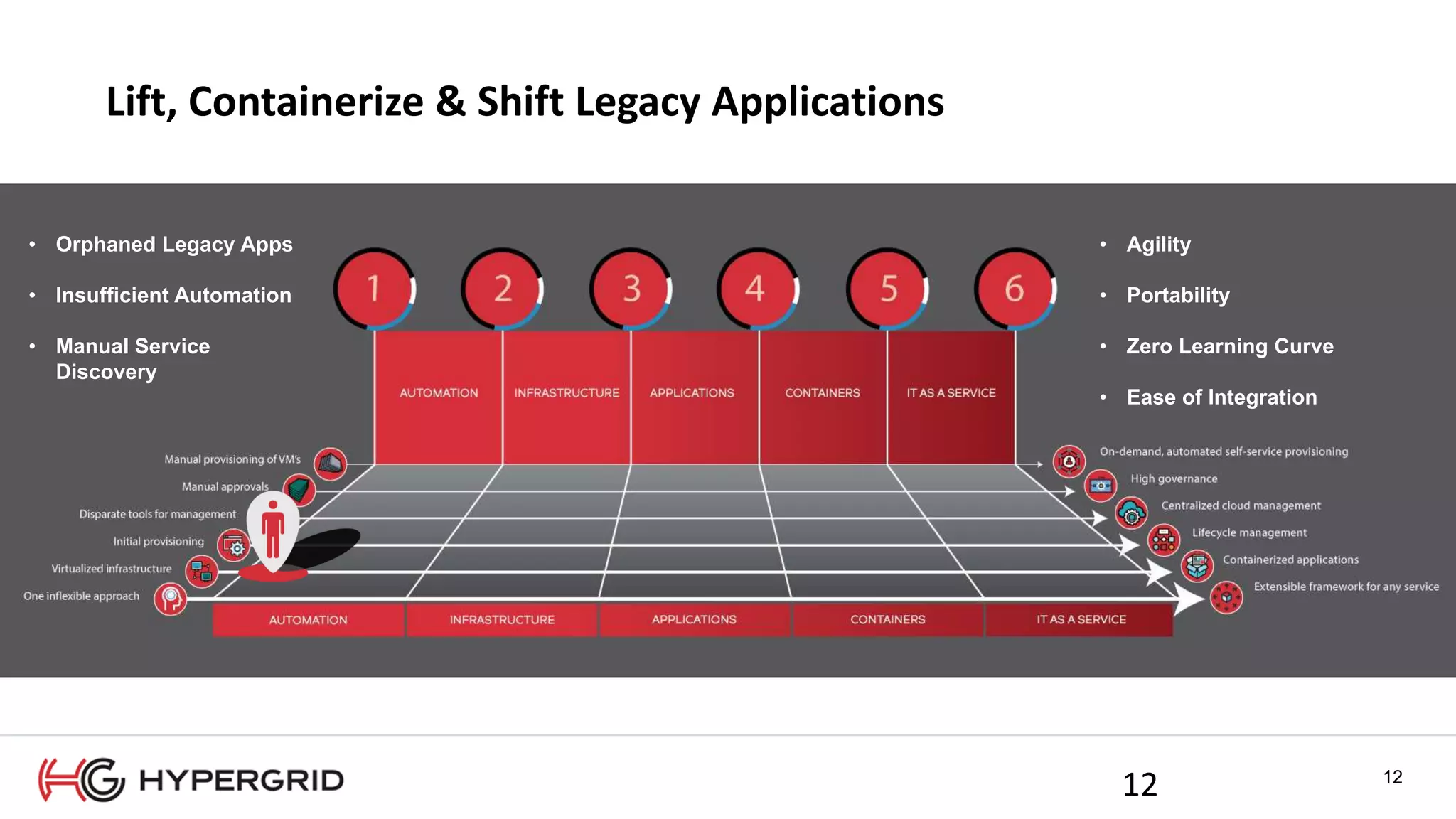
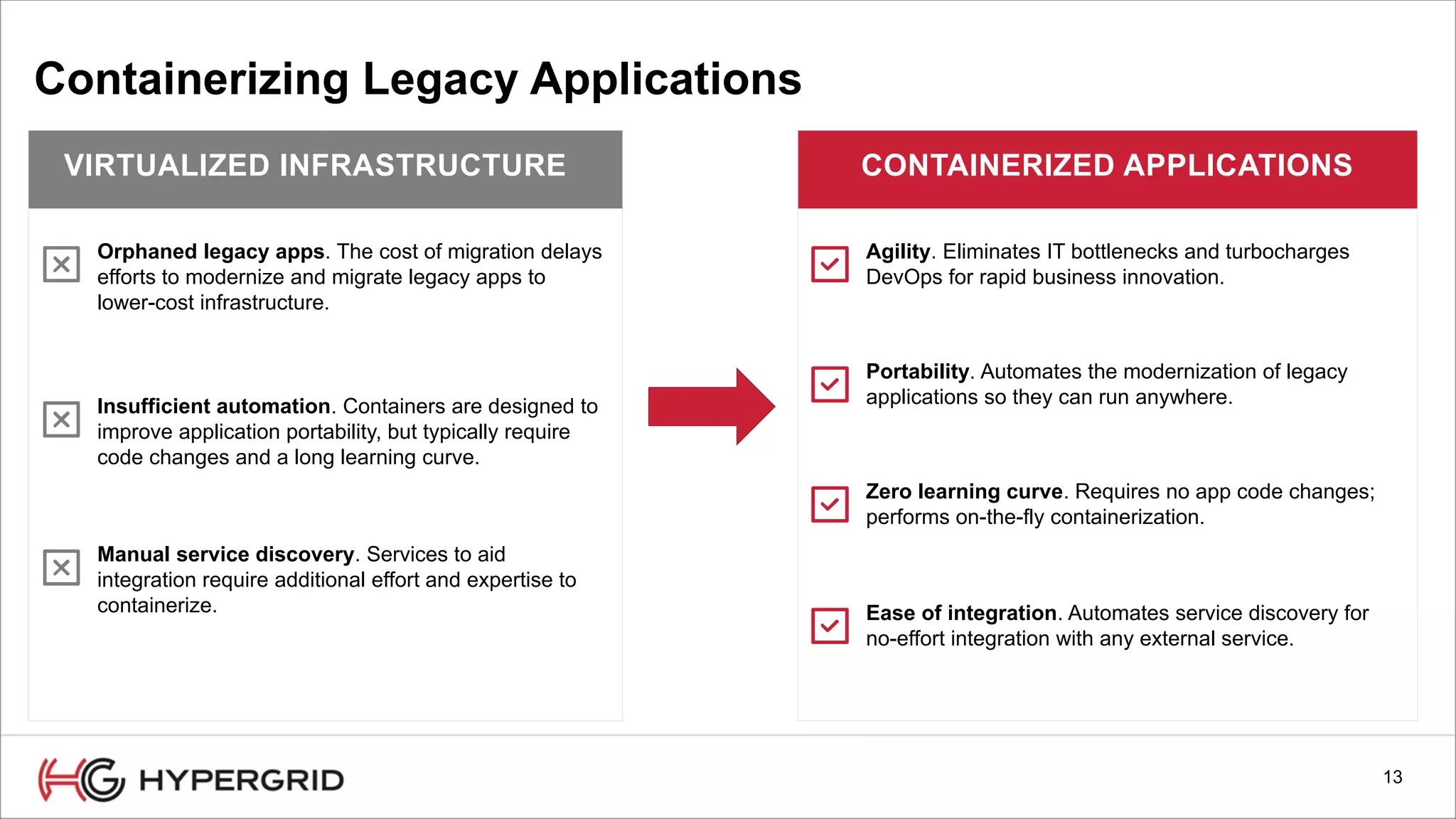
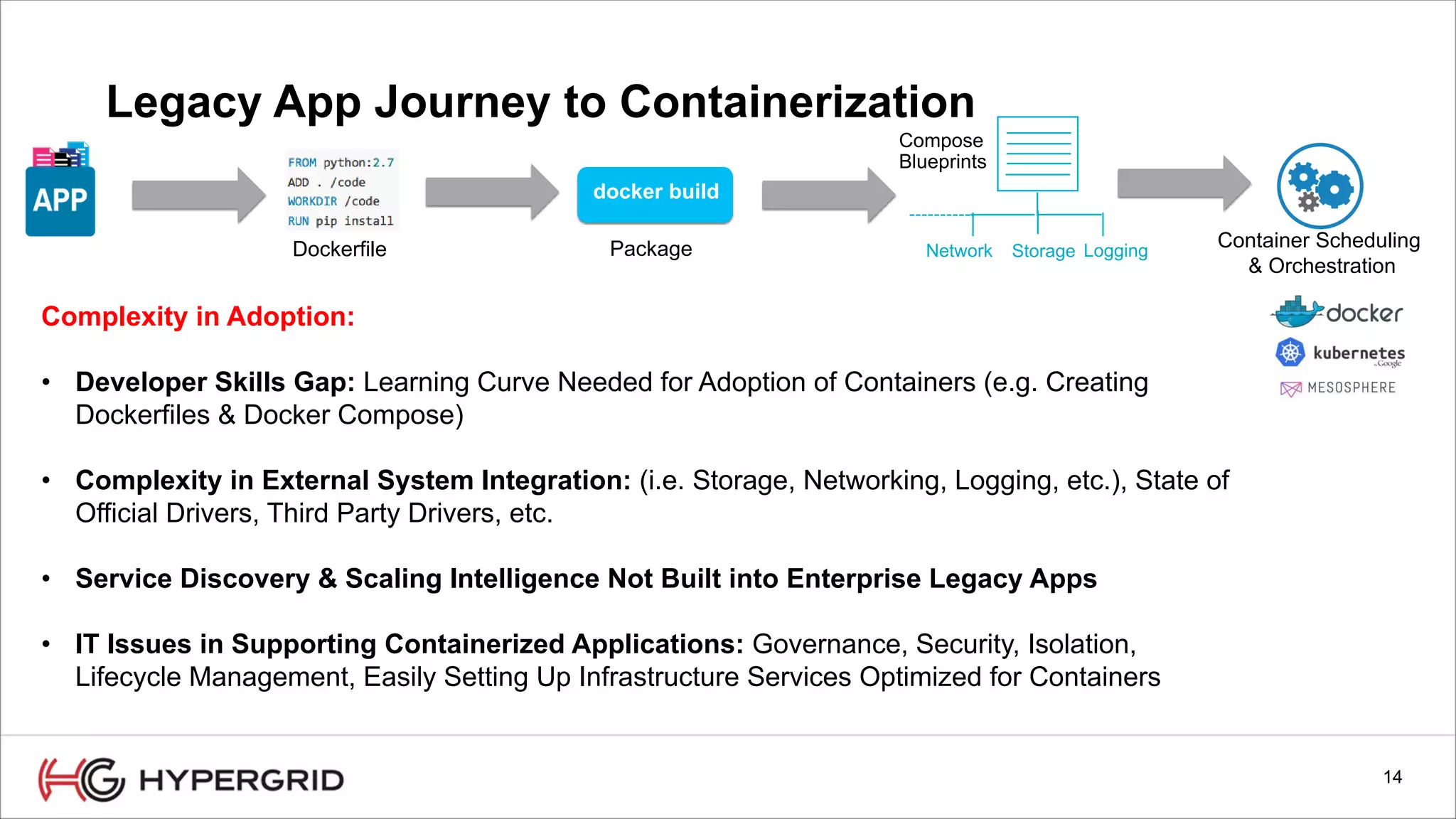
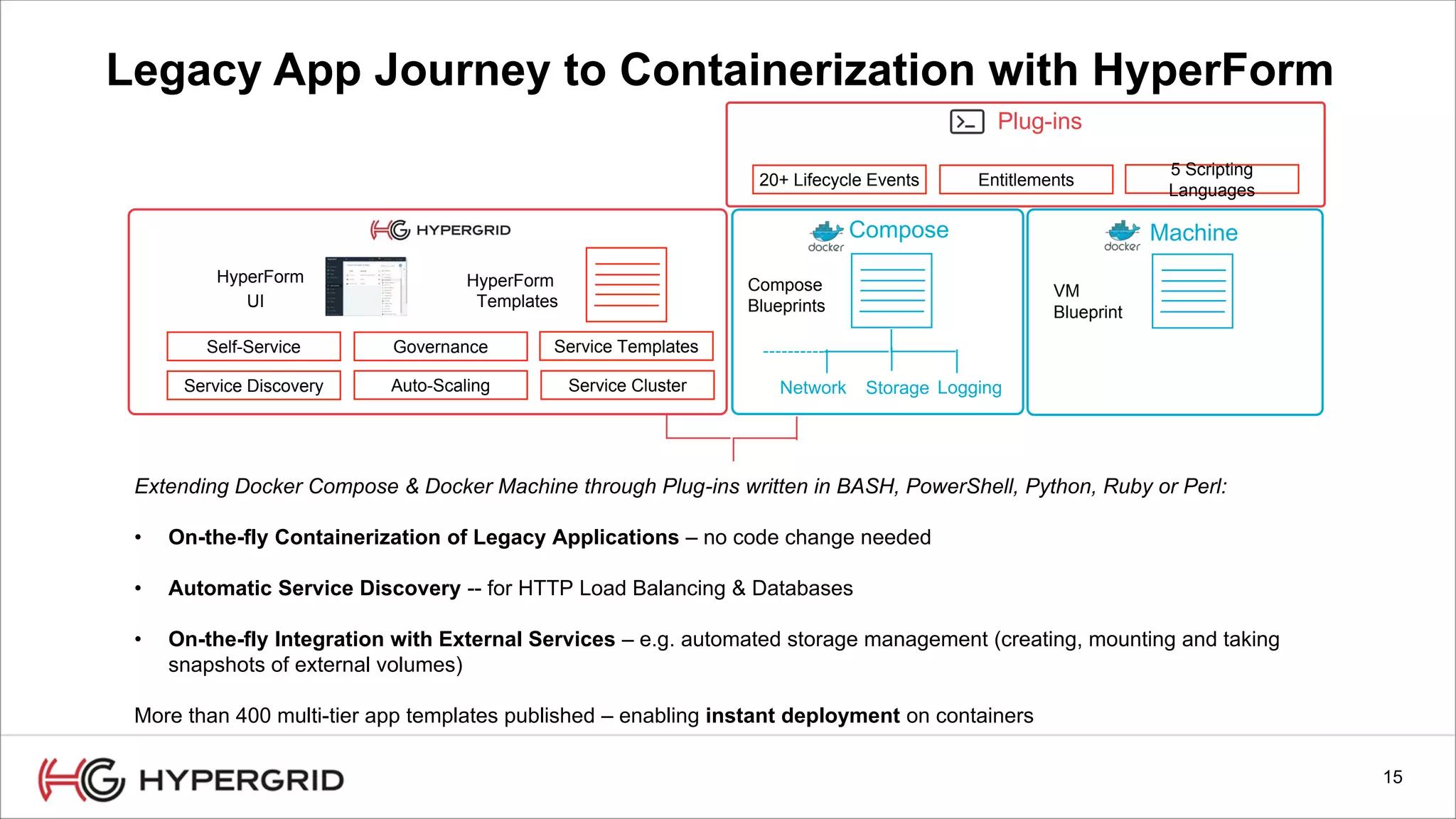
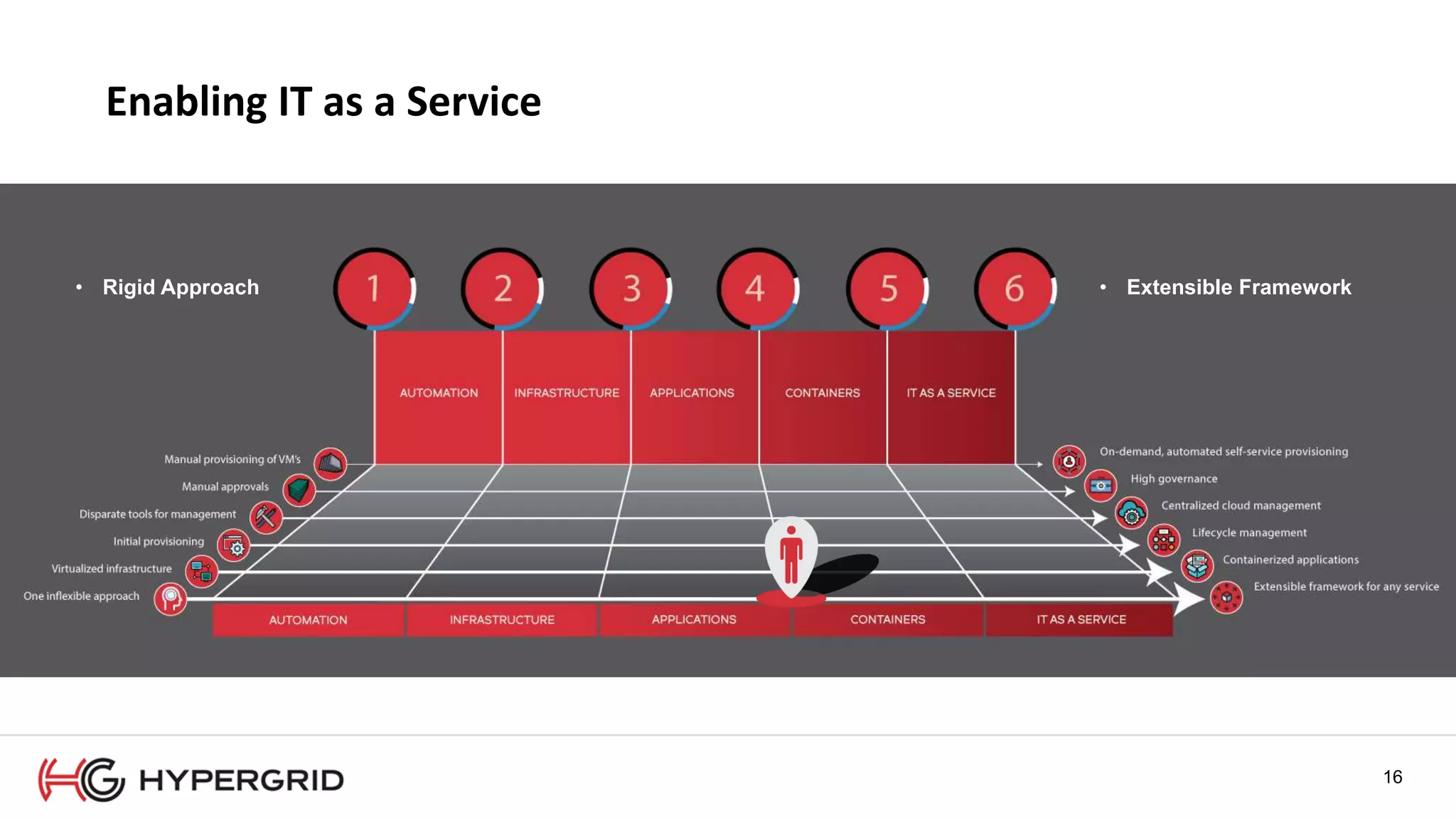
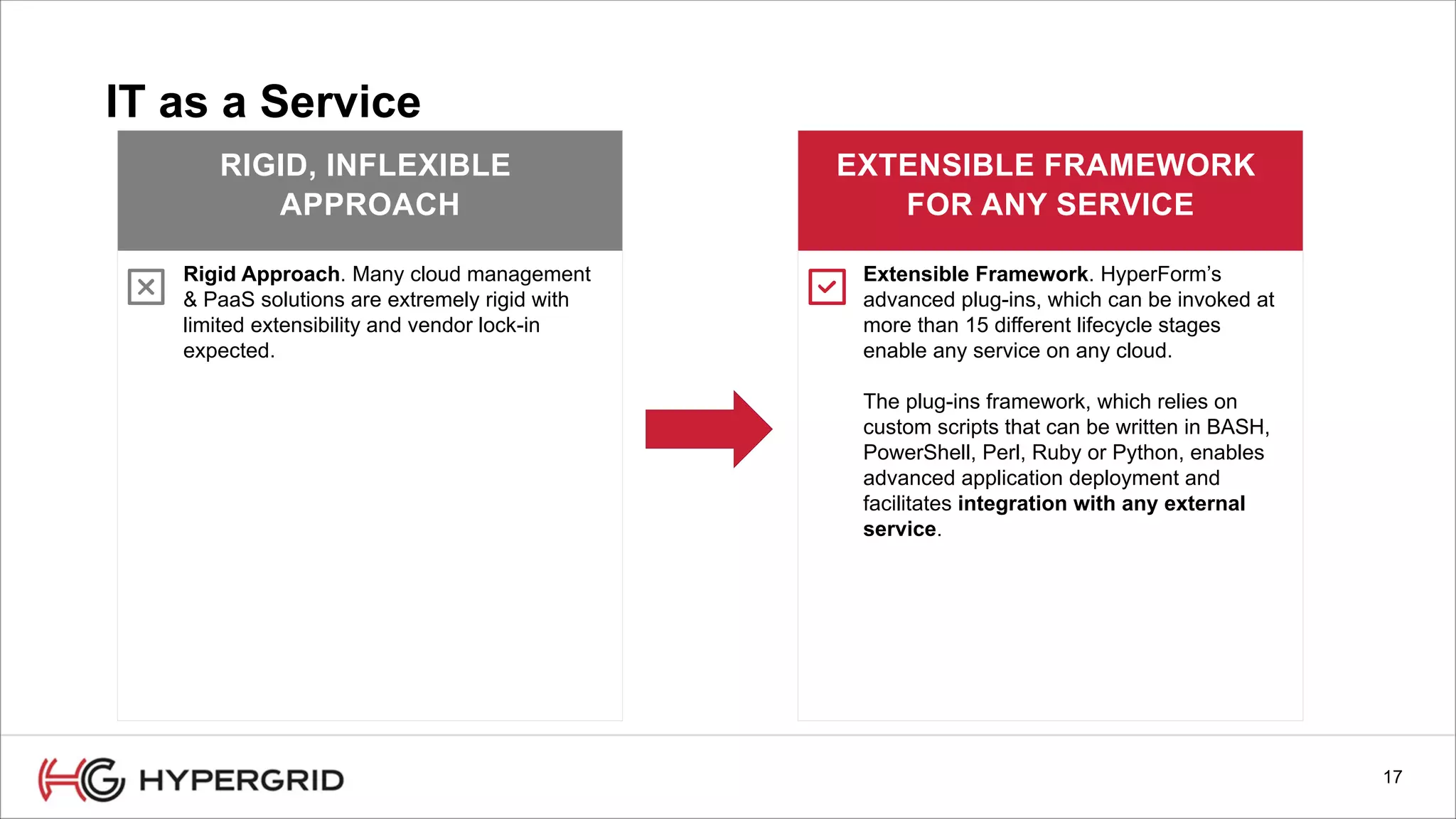
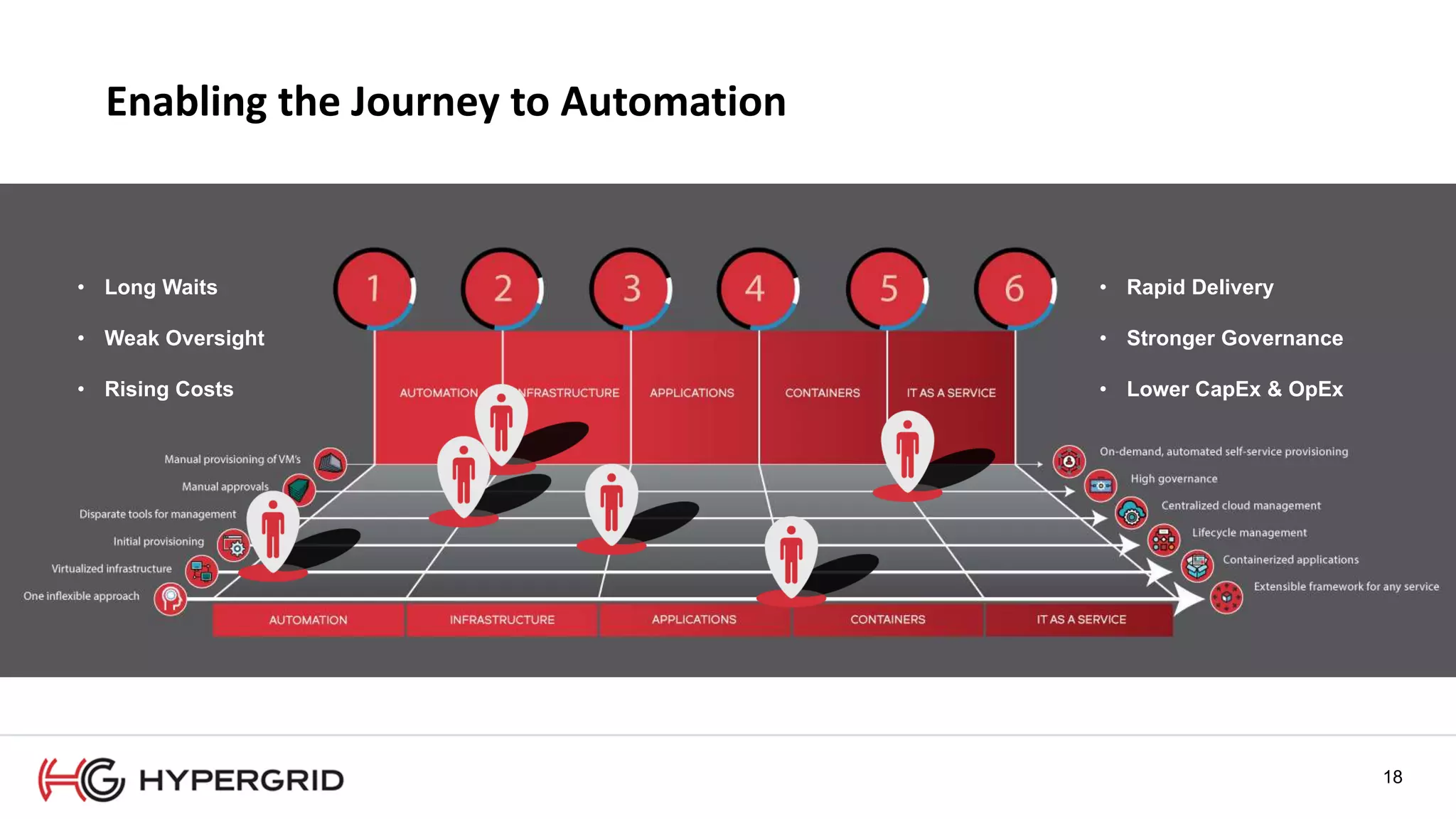
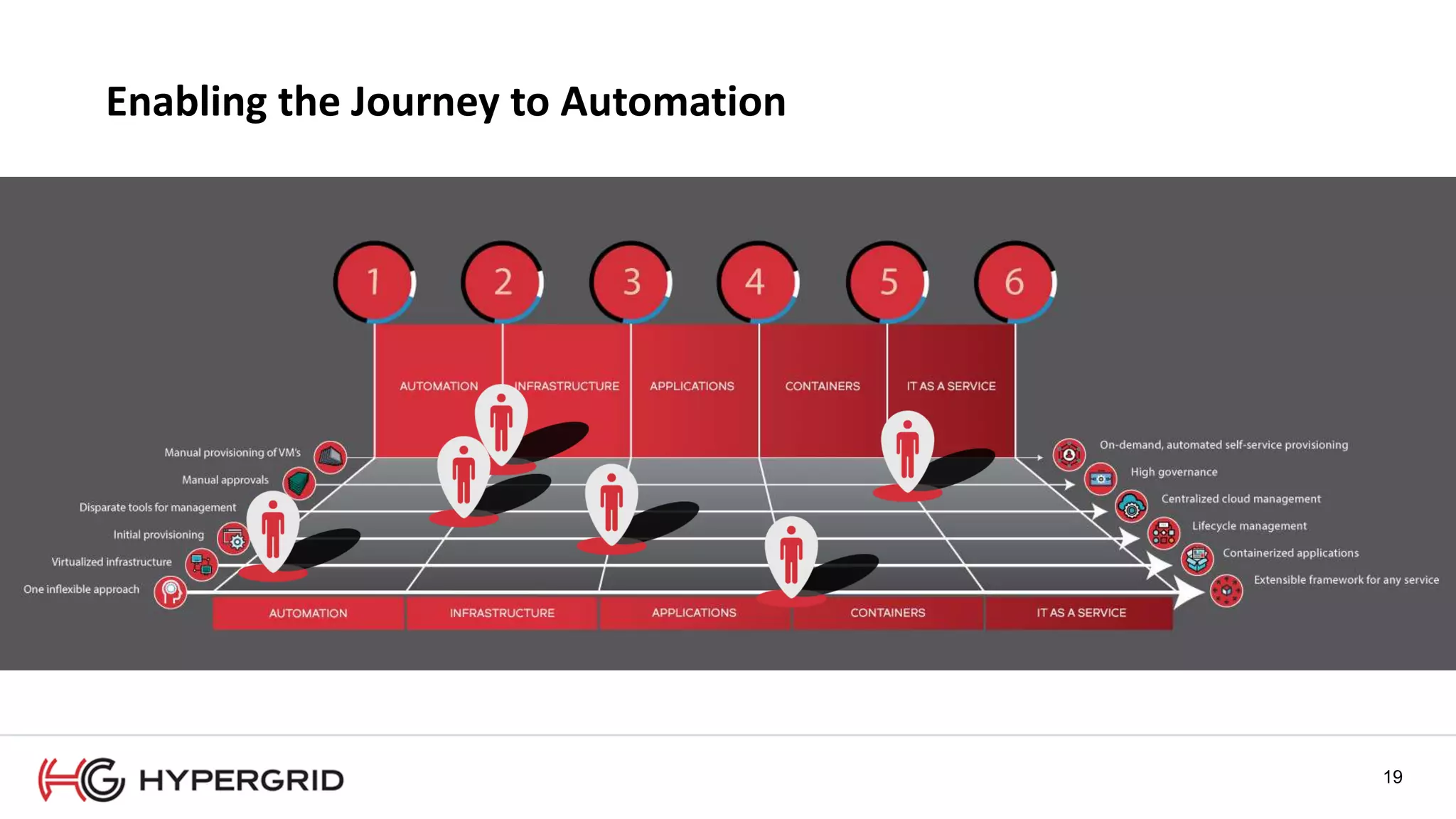
HyperForm enables organizations to automate their IT infrastructure and applications. This allows them to [1] deliver infrastructure and services faster, reducing wait times from weeks to minutes, [2] strengthen governance with consistent policy enforcement across clouds, and [3] lower costs through improved efficiency and utilization monitoring across hybrid cloud environments.