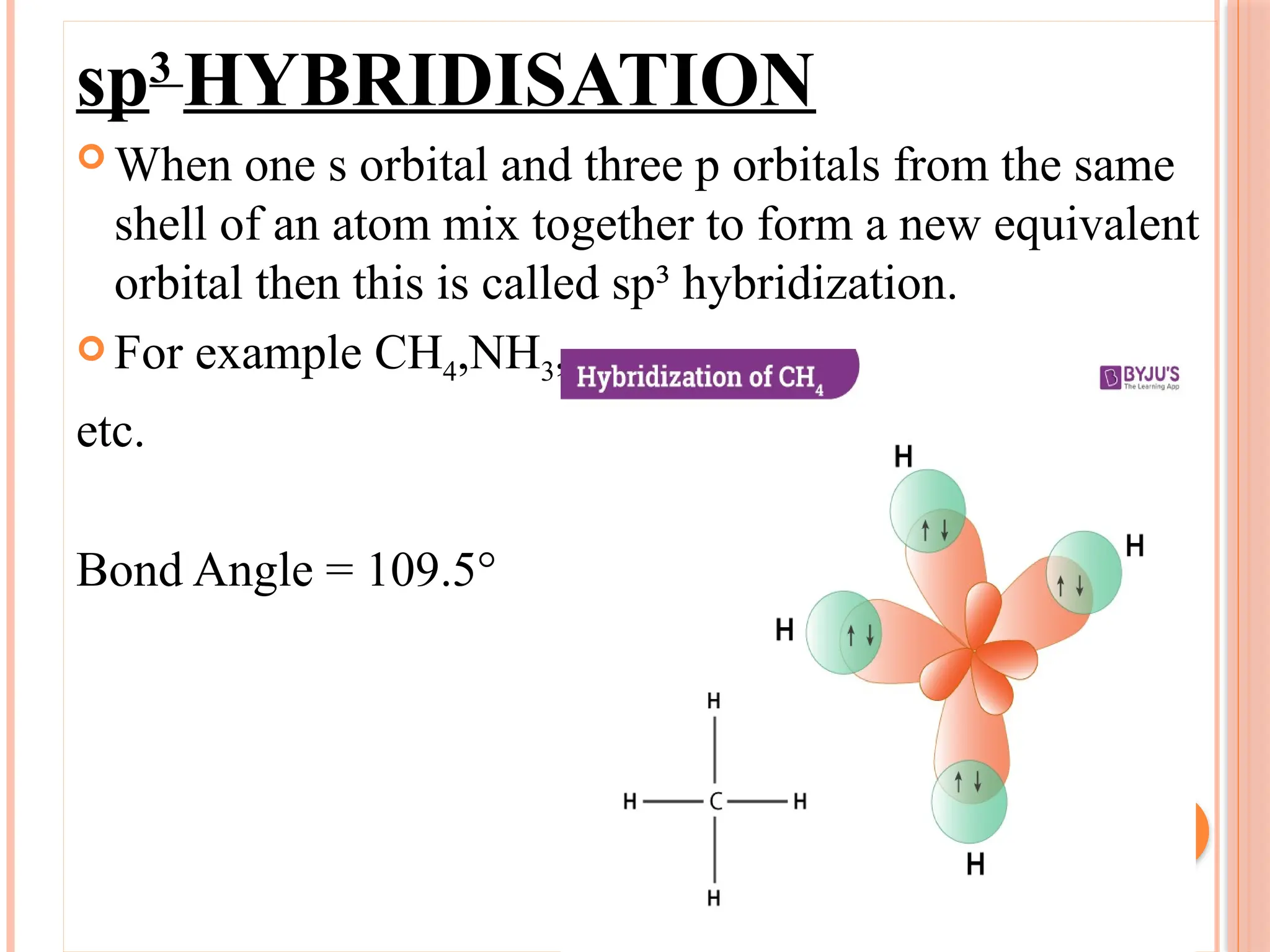
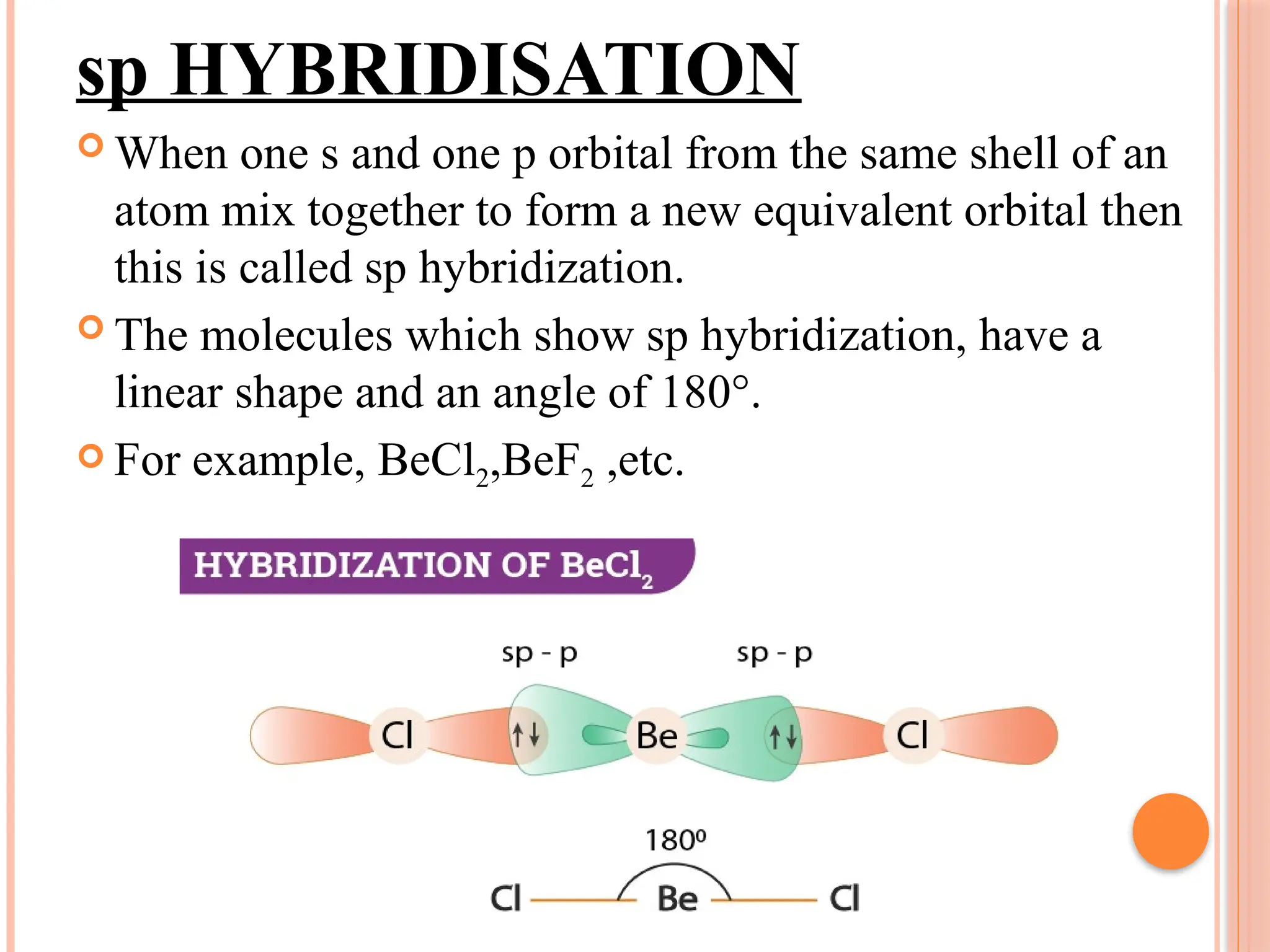
The document discusses hybridization in chemistry, detailing how atomic orbitals combine to form new hybrid orbitals, specifically outlining sp, sp2, and sp3 hybridization with examples. It also describes the molecular geometry of simple inorganic molecules and ions, categorizing them into five main shapes and providing bond angles and examples for each type. References include an NCERT textbook and Byju’s for further reading.