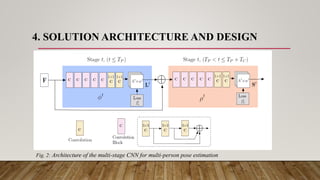
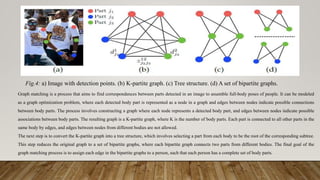
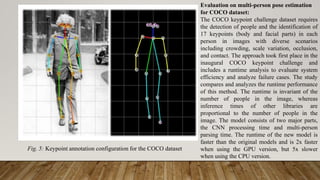
This dissertation report discusses a human pose skeleton-based estimation model designed for real-time multi-person 2D pose detection in images and videos. It presents an innovative approach using part affinity fields (PAFs) to efficiently detect and associate body parts while addressing limitations of traditional methods. Key experiments highlight the model's performance, computational efficiency, and challenges faced in crowded scenes or scenarios involving occlusions.