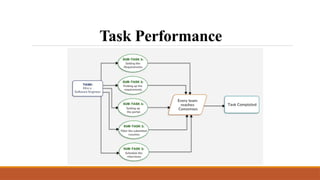
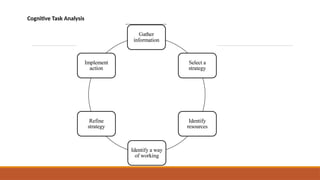
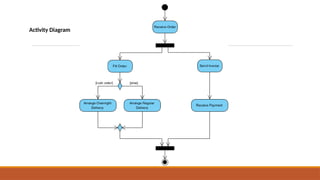
The document discusses data gathering and accessibility in Human-Computer Interaction (HCI), emphasizing universal design principles such as equitable use and flexibility. It details various methods of data collection, including task analysis, which involves observing users and mapping workflows to optimize their interaction with products or services. Additionally, techniques for analysis like hierarchical and cognitive task analysis, as well as user surveys and time-motion studies, are highlighted to enhance understanding of user tasks and improve overall user experience.