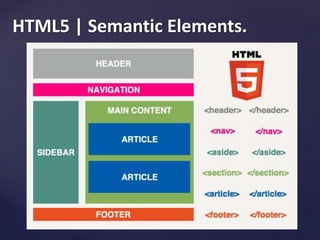
This document provides an overview of HTML5 and CSS3 topics. It begins with an agenda for HTML5 that covers basics like tags, attributes and elements. It then discusses HTML5 semantic elements and features like video, audio, and forms. For CSS3, it outlines modules including borders, backgrounds, gradients, text effects, web fonts, transforms, transitions, animations, columns and user interface. The document aims to introduce key concepts and properties for front-end development.