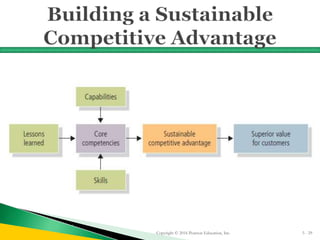
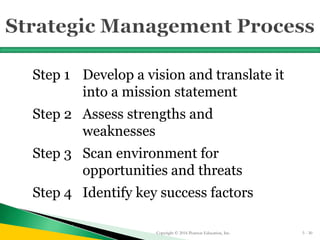
The document provides guidance on creating an effective business plan and strategic plan for a small business. It discusses the key elements of a business plan, including an executive summary, description of products/services, marketing strategy, and financial projections. It also explains the importance of strategic planning and developing a competitive advantage. A strategic plan should follow nine steps: develop a vision/mission, assess strengths/weaknesses, scan for opportunities/threats, identify success factors, analyze competition, create goals/objectives, formulate strategies, take action, and establish controls.