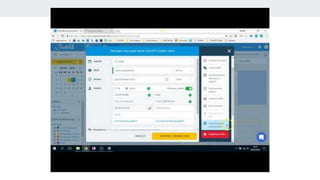
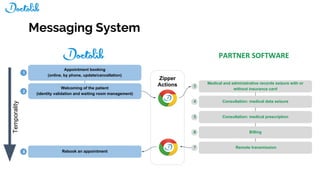
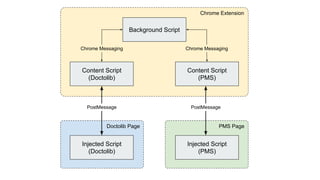
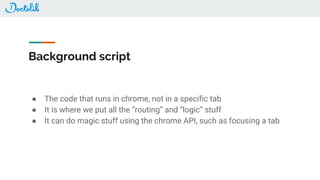
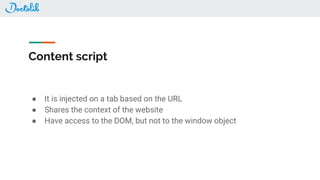
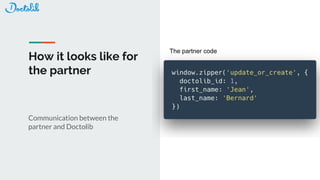
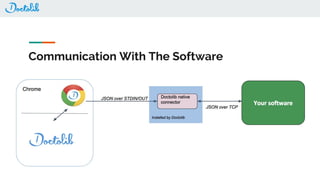
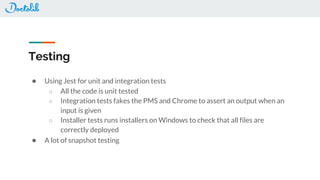
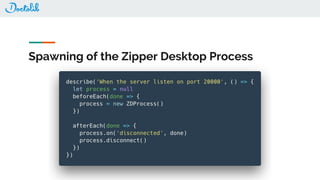
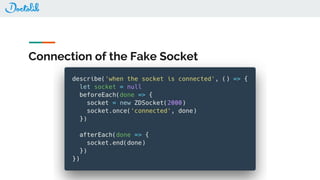
The document outlines the development of a Chrome extension for integrating Doctolib with a practice management system (PMS) to create a seamless user experience. It discusses technical aspects such as communication methodologies between components, including Chrome messaging and native messaging, code testing strategies, and integration guidelines. Additionally, it emphasizes the need for simple API communication with older desktop software used by half of their customers.