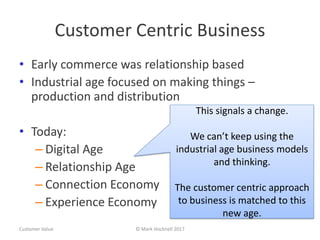
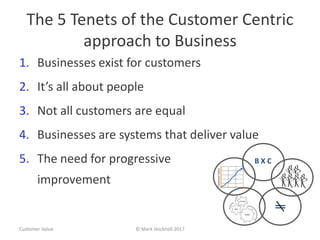
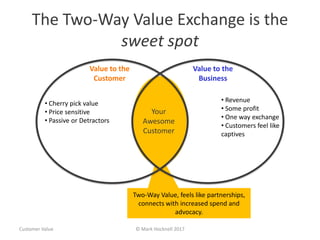
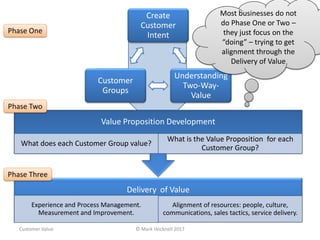
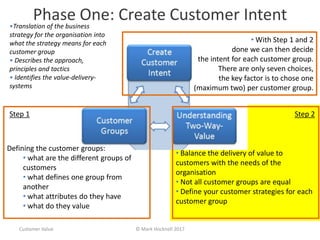
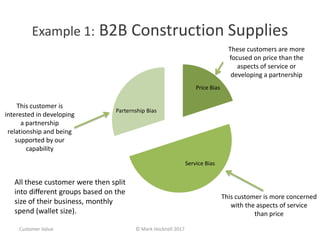
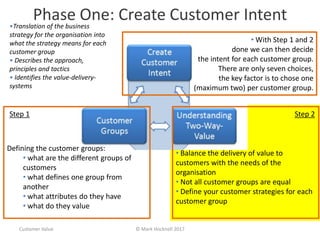
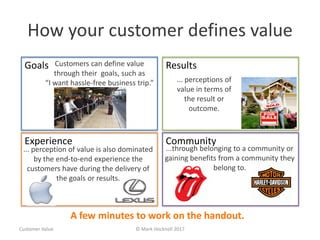
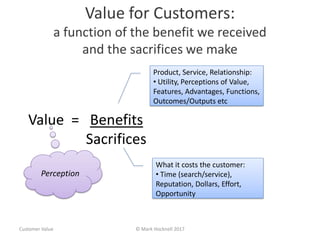
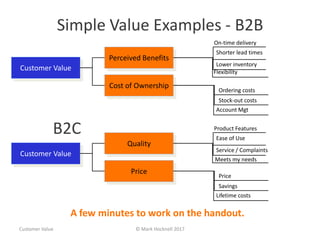
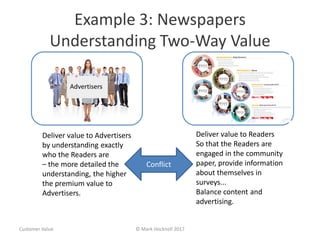
The document emphasizes a customer-centric approach to business that moves away from outdated industrial age models towards understanding and delivering value to customers. It discusses the importance of defining customer groups, the two-way value exchange, and how businesses must align their strategies with customer intent to enhance advocacy and profitability. Key concepts include recognizing that not all customers are equal and tailoring value propositions accordingly to cater to different customer needs and perceptions of value.