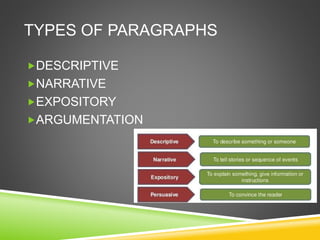
The document provides instructions on how to build an effective paragraph. It states that a paragraph should have a clear main idea, support that idea with examples or details, and be part of a longer composition. It also notes that paragraphs need unity with a topic sentence and coherence through logical organization and linking words. The document outlines different types of paragraphs including descriptive, narrative, expository, and argumentative paragraphs and provides examples of each type.