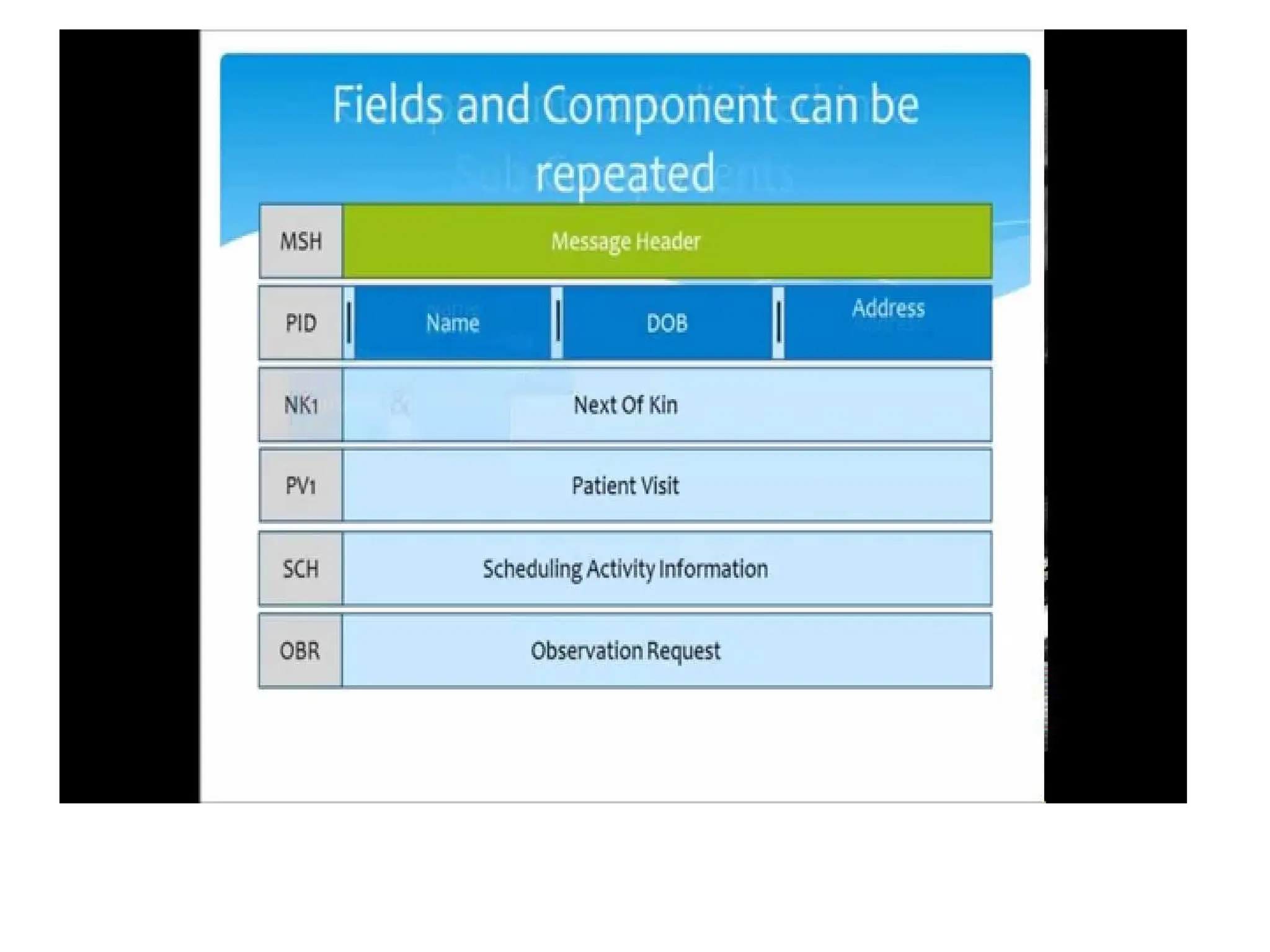
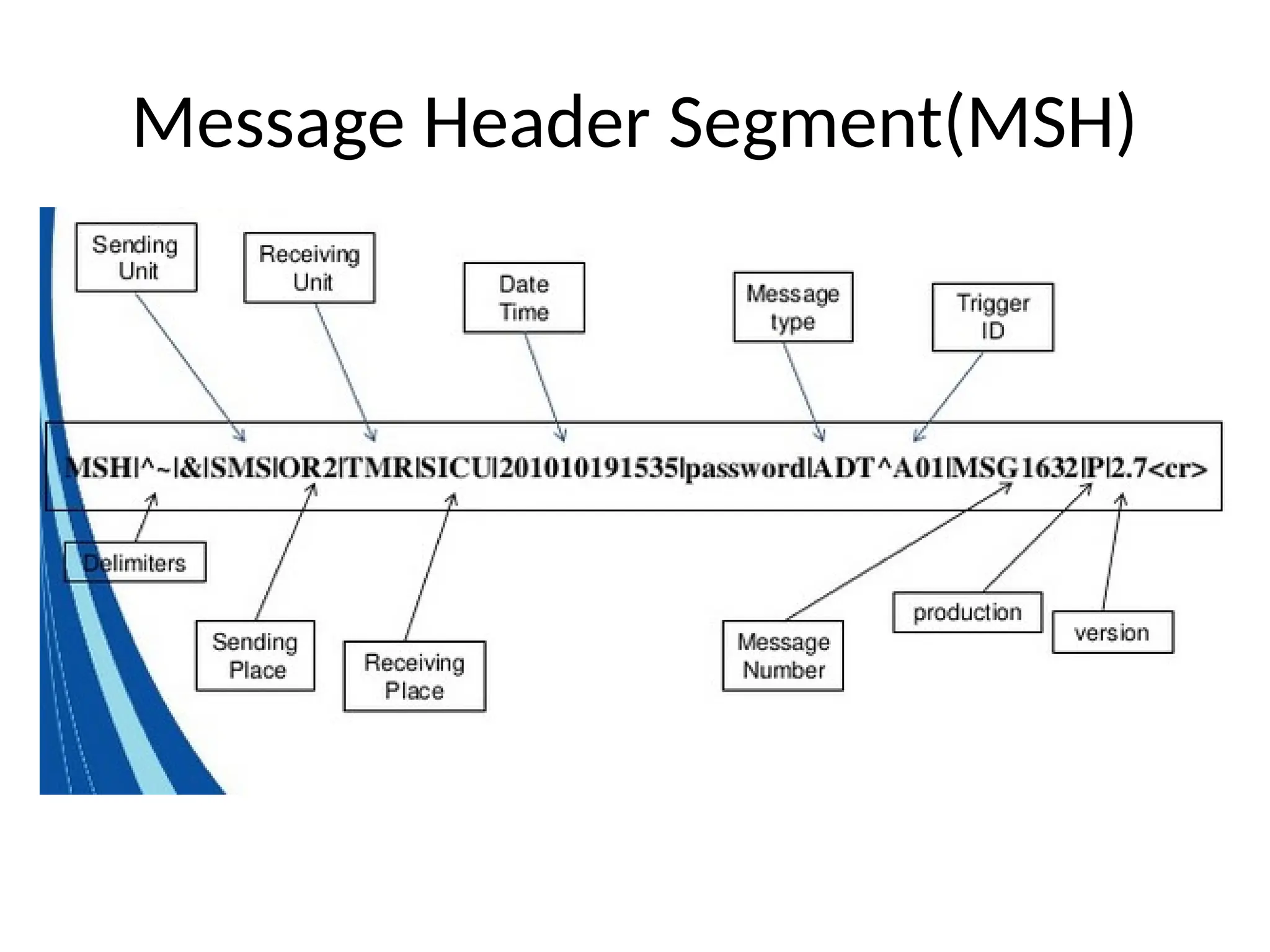
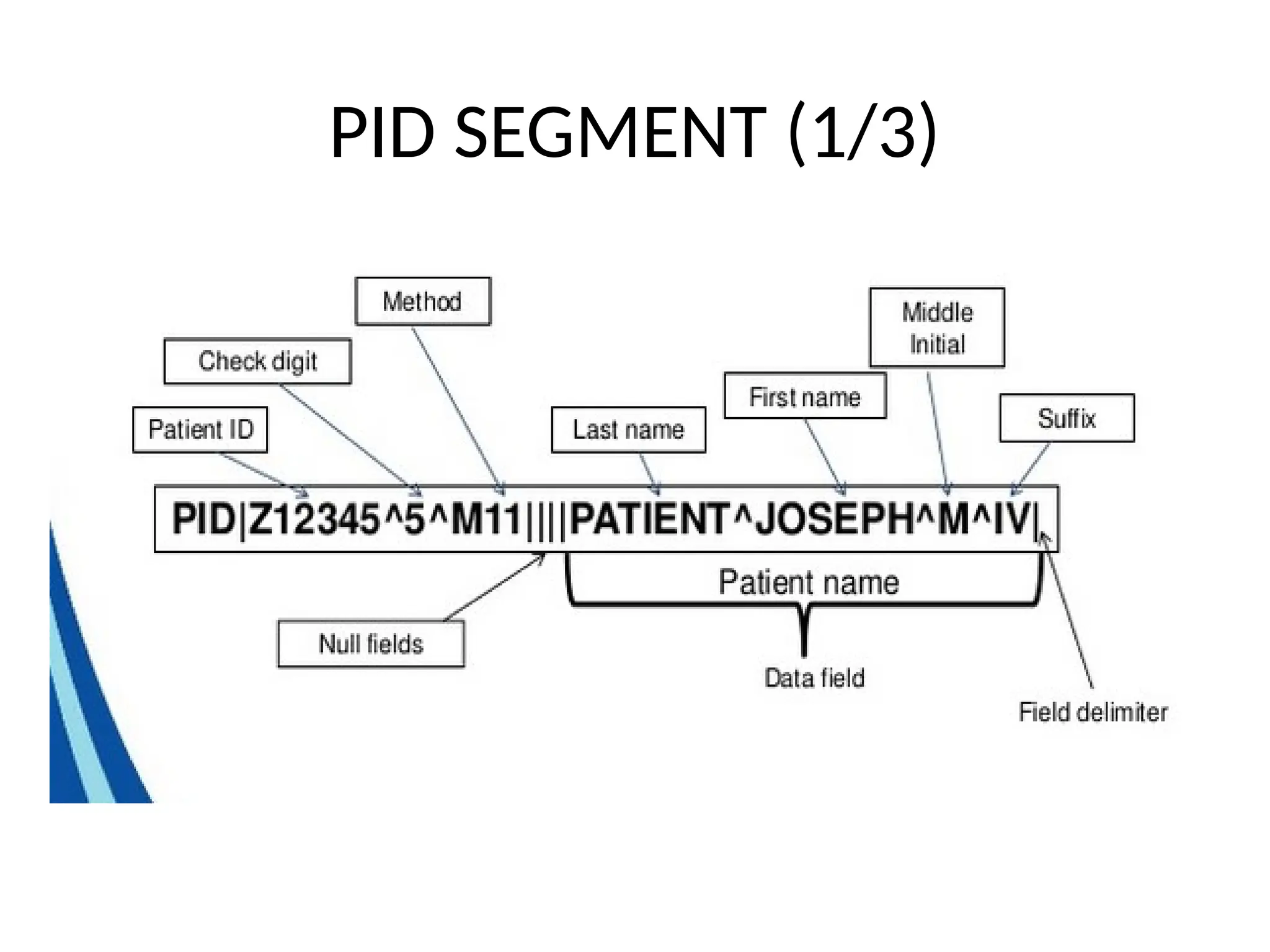
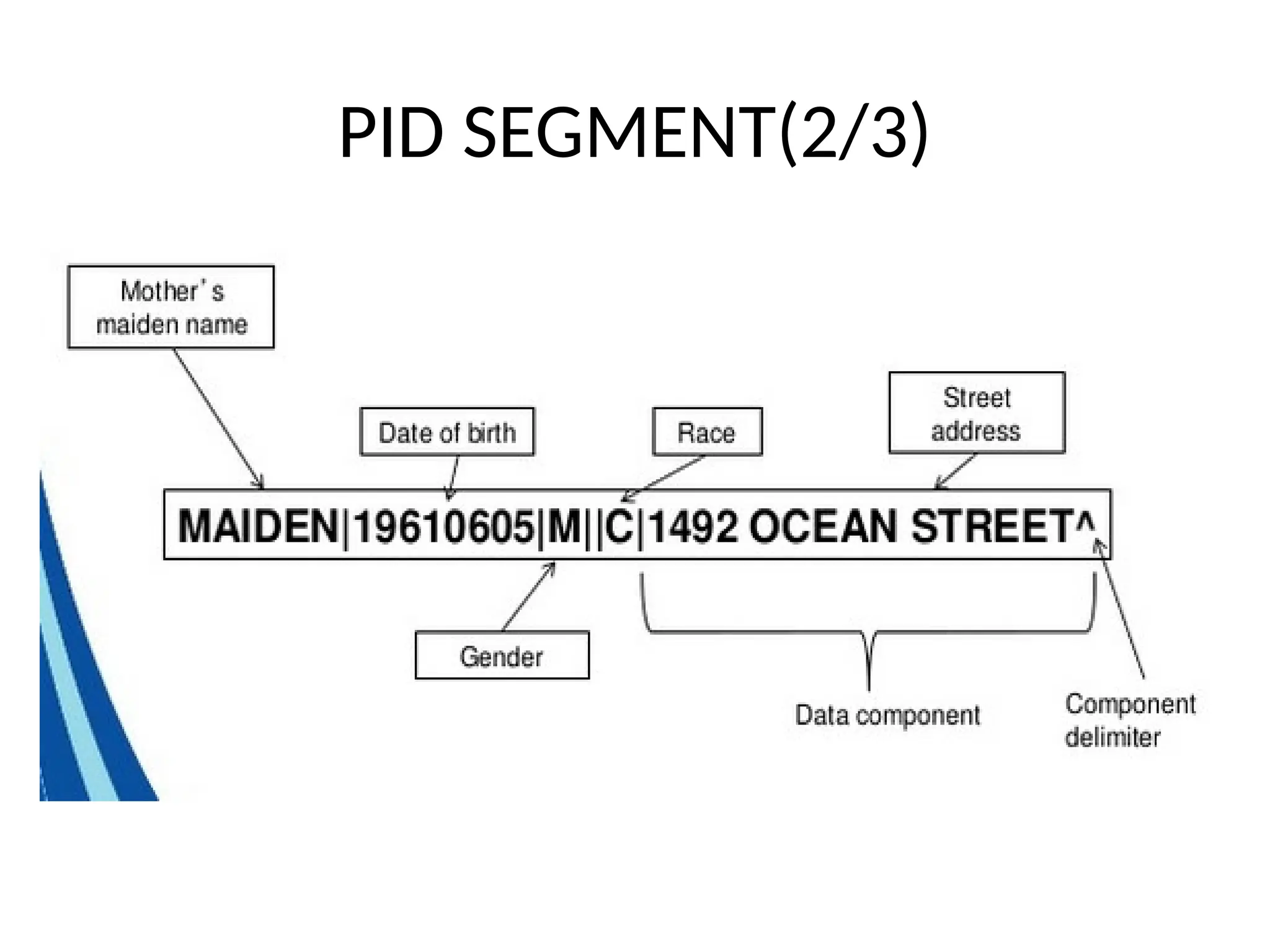
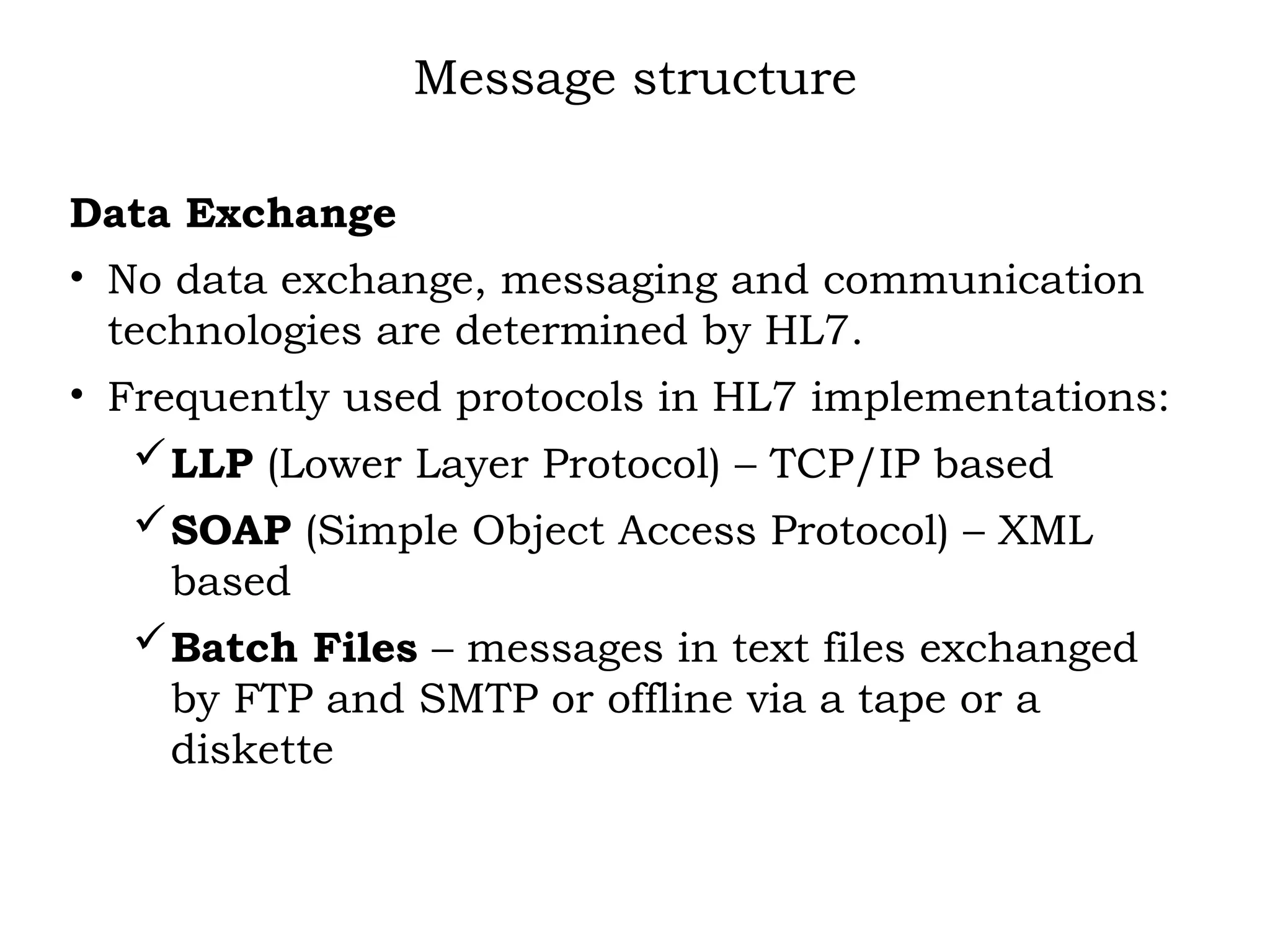
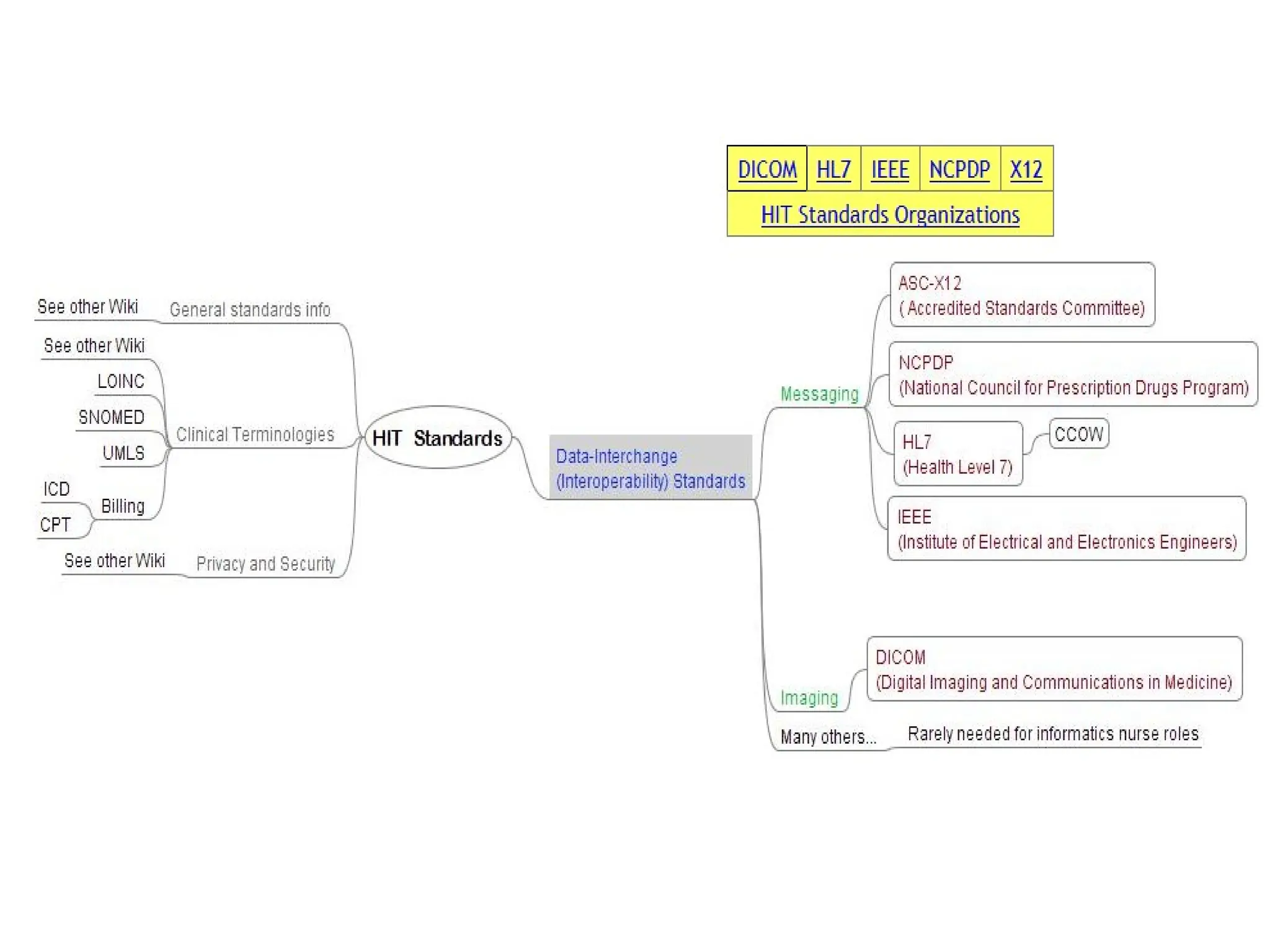
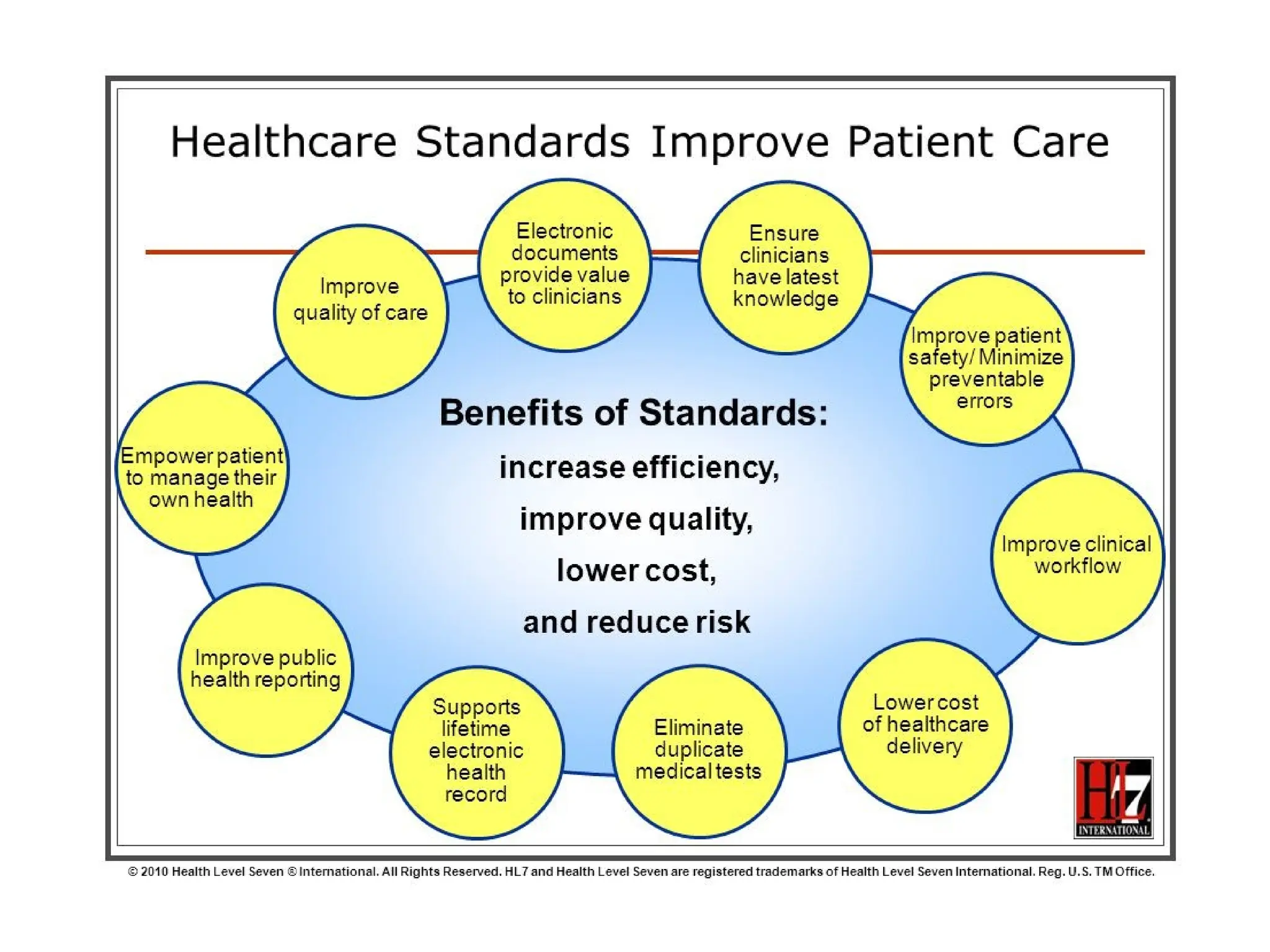
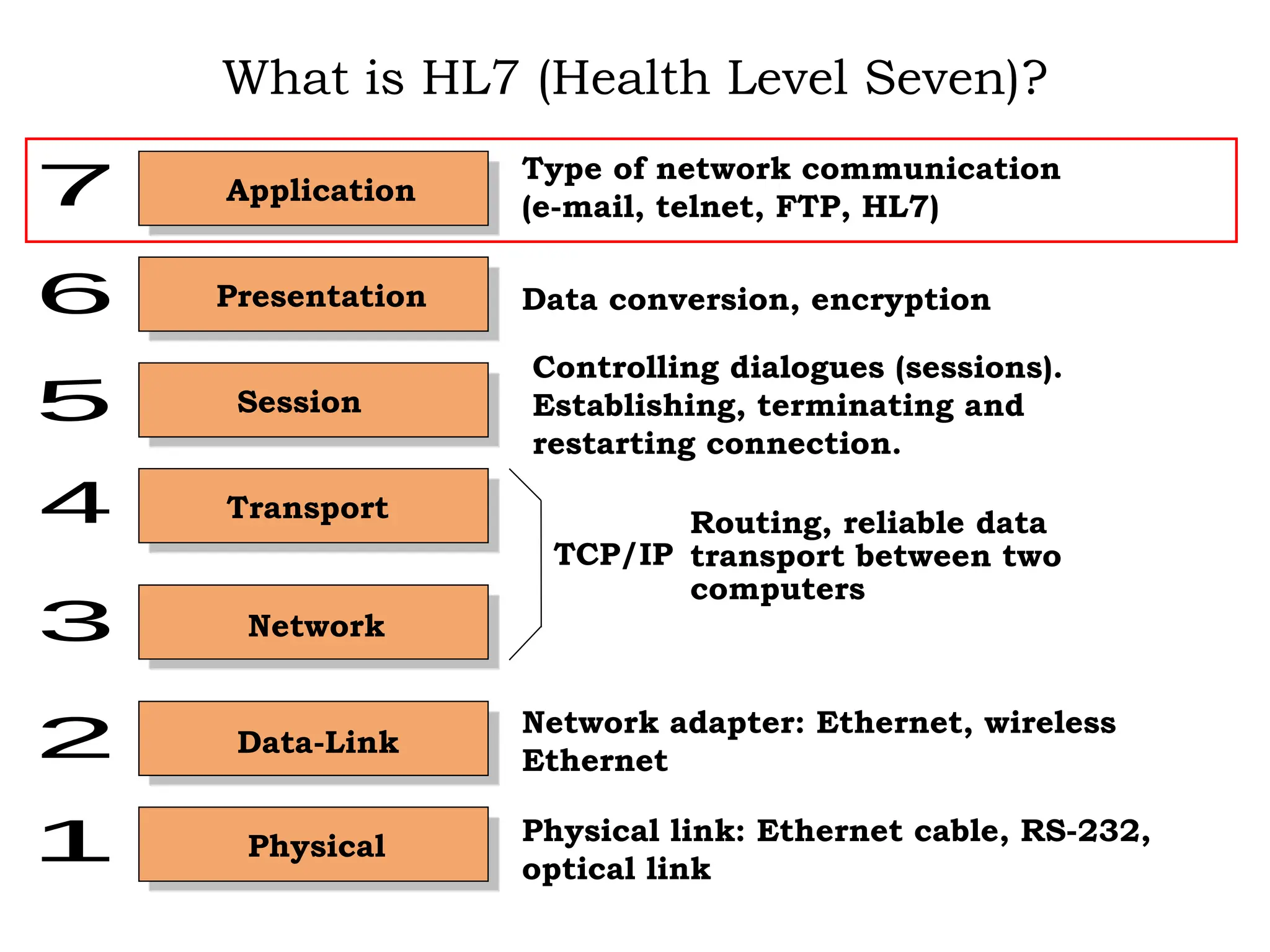
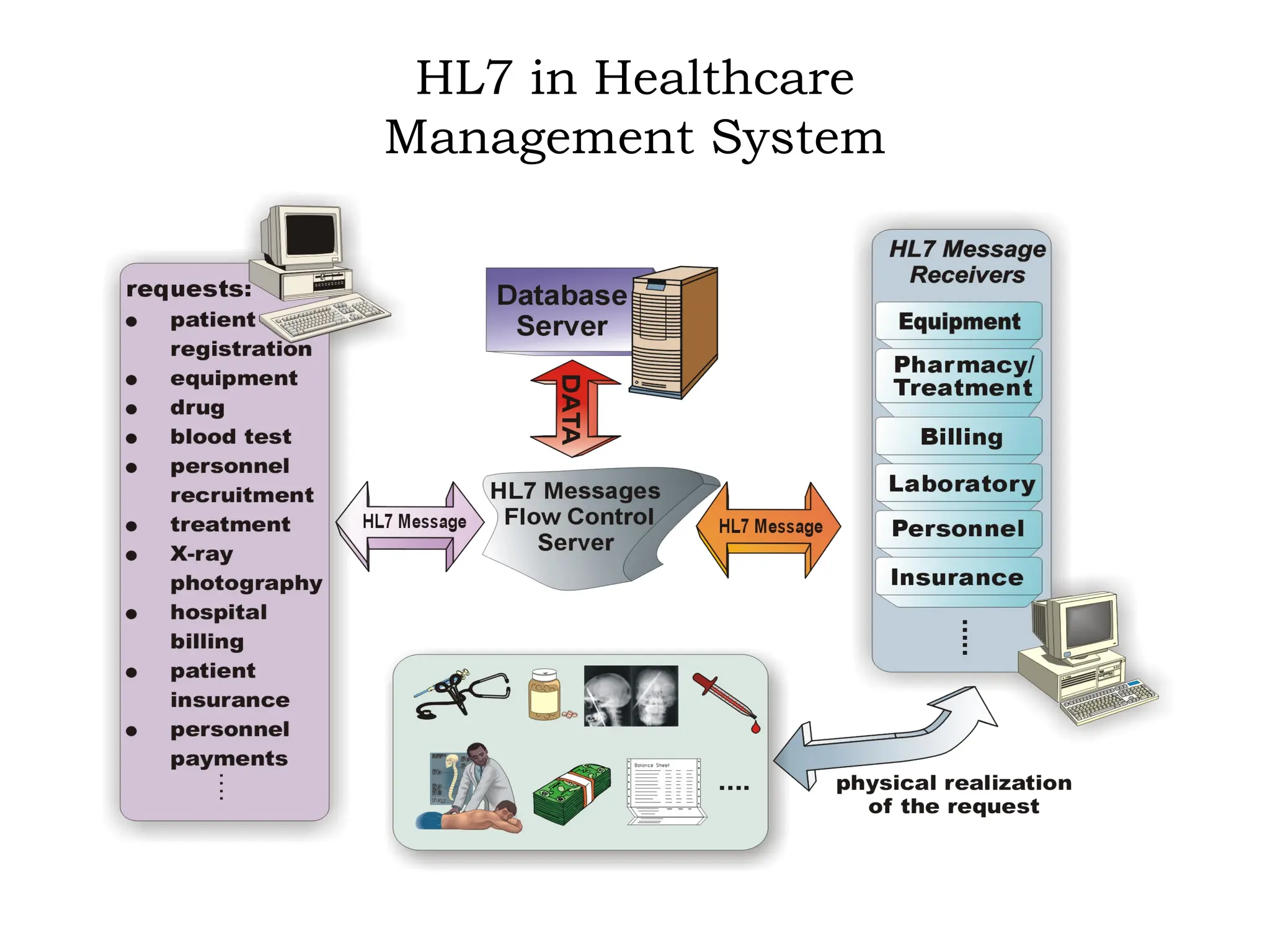
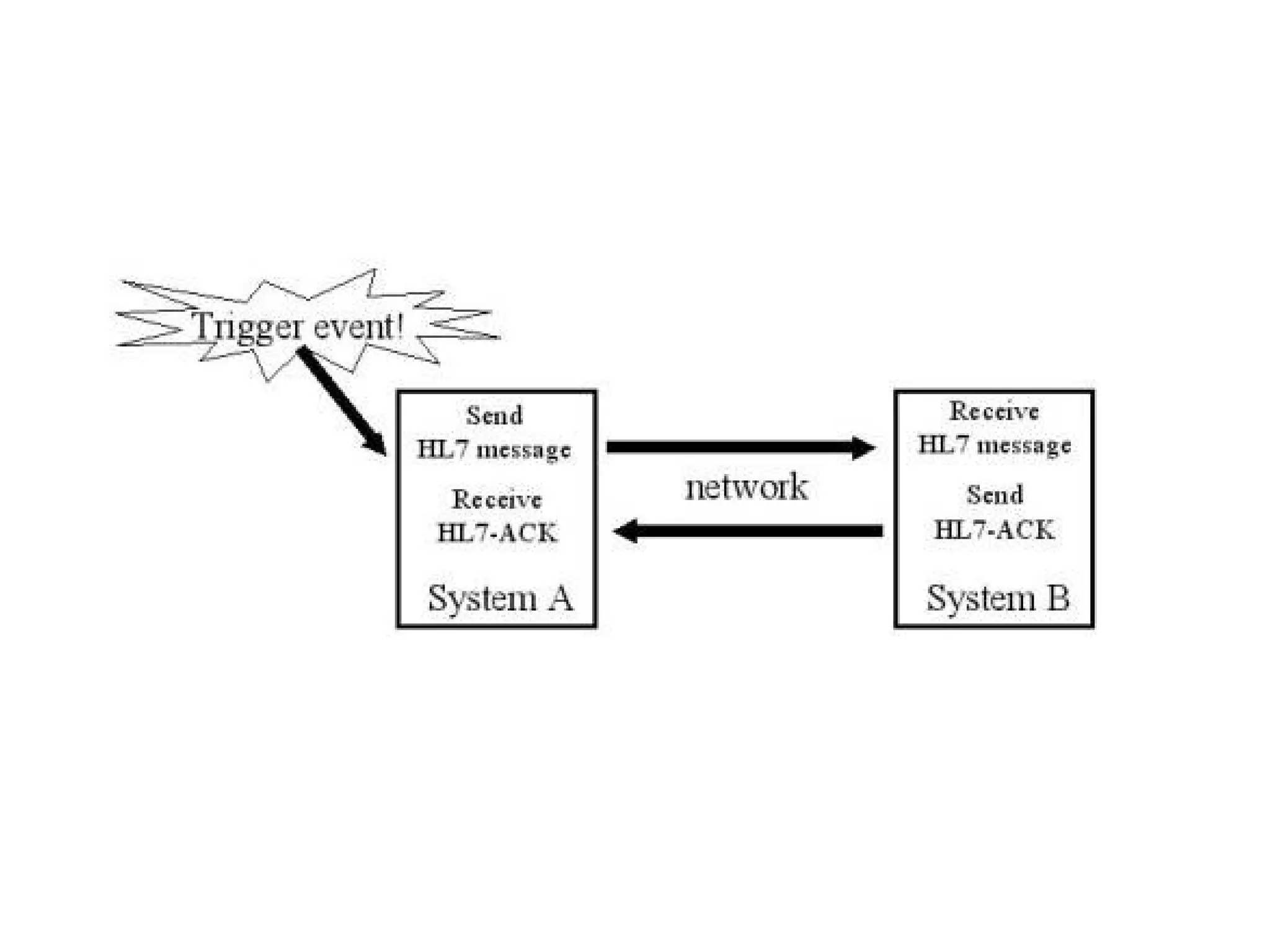
The document outlines the importance of medical informatics standards, focusing on HL7 (Health Level 7), which facilitates electronic data exchange in healthcare. It details HL7's origins, various versions, and message structures designed for interoperability within healthcare information systems. Additionally, it covers encoding schemes and common protocols used in HL7 implementations.













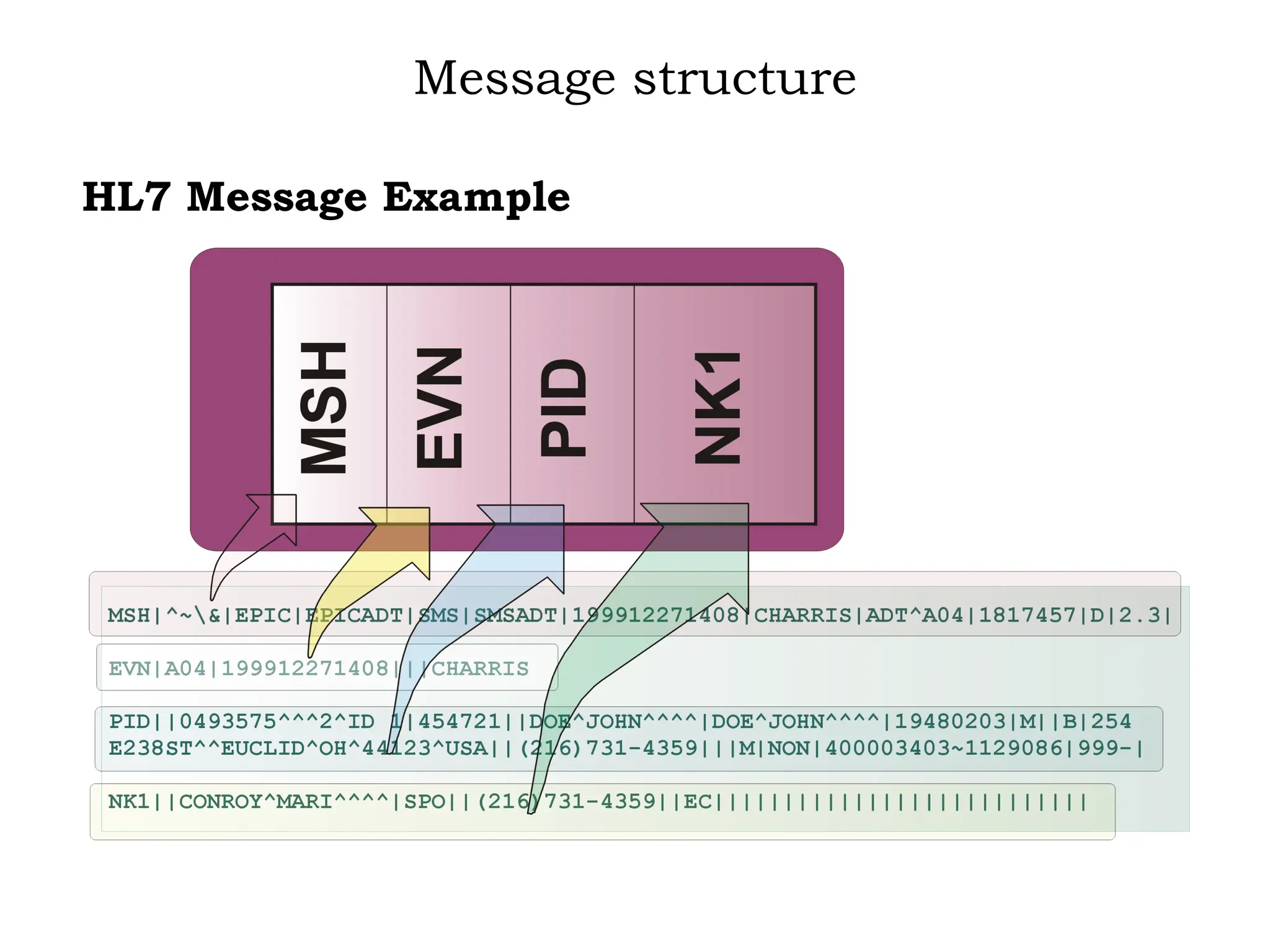
![[Square Brackets] indicate something is optional; and
{Curly Brackets} indicate something is repeatable.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hl7overview-240814054200-ea2933b3/75/HL7-STANDARDS-IN-DATA-CONTENT-STANDARDIZATION-20-2048.jpg)