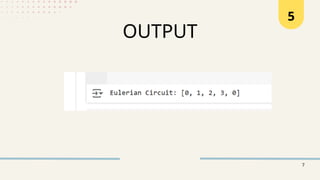
Hierholzer's algorithm is designed to find an Eulerian circuit in a graph by following specific steps to traverse edges and merge cycles. The algorithm is efficient and simple to implement, making it suitable for both directed and undirected graphs. The document includes an overview of the algorithm, steps for coding it in Python, and the benefits of using Hierholzer's for solving Eulerian circuit problems.