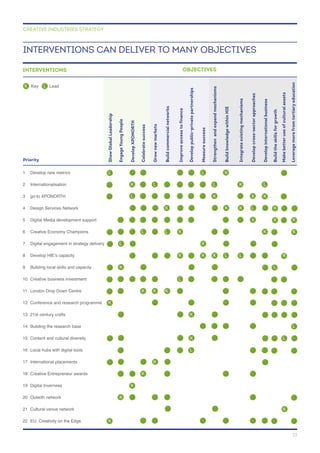
The document outlines a creative industries strategy for 2014-2019 in Scotland's Highlands and Islands region. The strategy's vision is to establish a vibrant, sustainable creative economy by building on the region's remote communities and global connections. It proposes several objectives and interventions to achieve this vision, including developing talent, providing business support, and increasing international engagement.