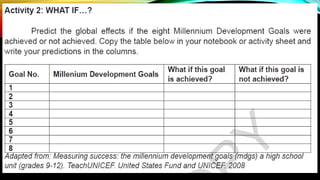
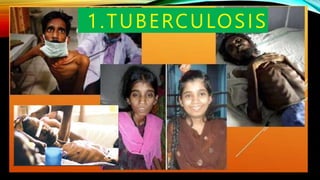
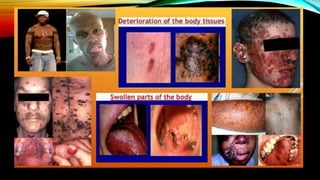
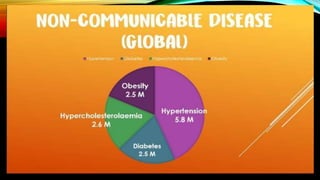
This document provides an overview of a lesson on global health trends, issues, and concerns. It defines key terms like global health and discusses major international health organizations. The eight Millennium Development Goals aimed to improve conditions in developing countries by 2015 and are summarized. Global health initiatives to address issues like tuberculosis, HIV/AIDS, and malaria are outlined. The document also lists ten global health trends and concerns discussed in the lesson, including non-communicable diseases, climate change, and immunization.