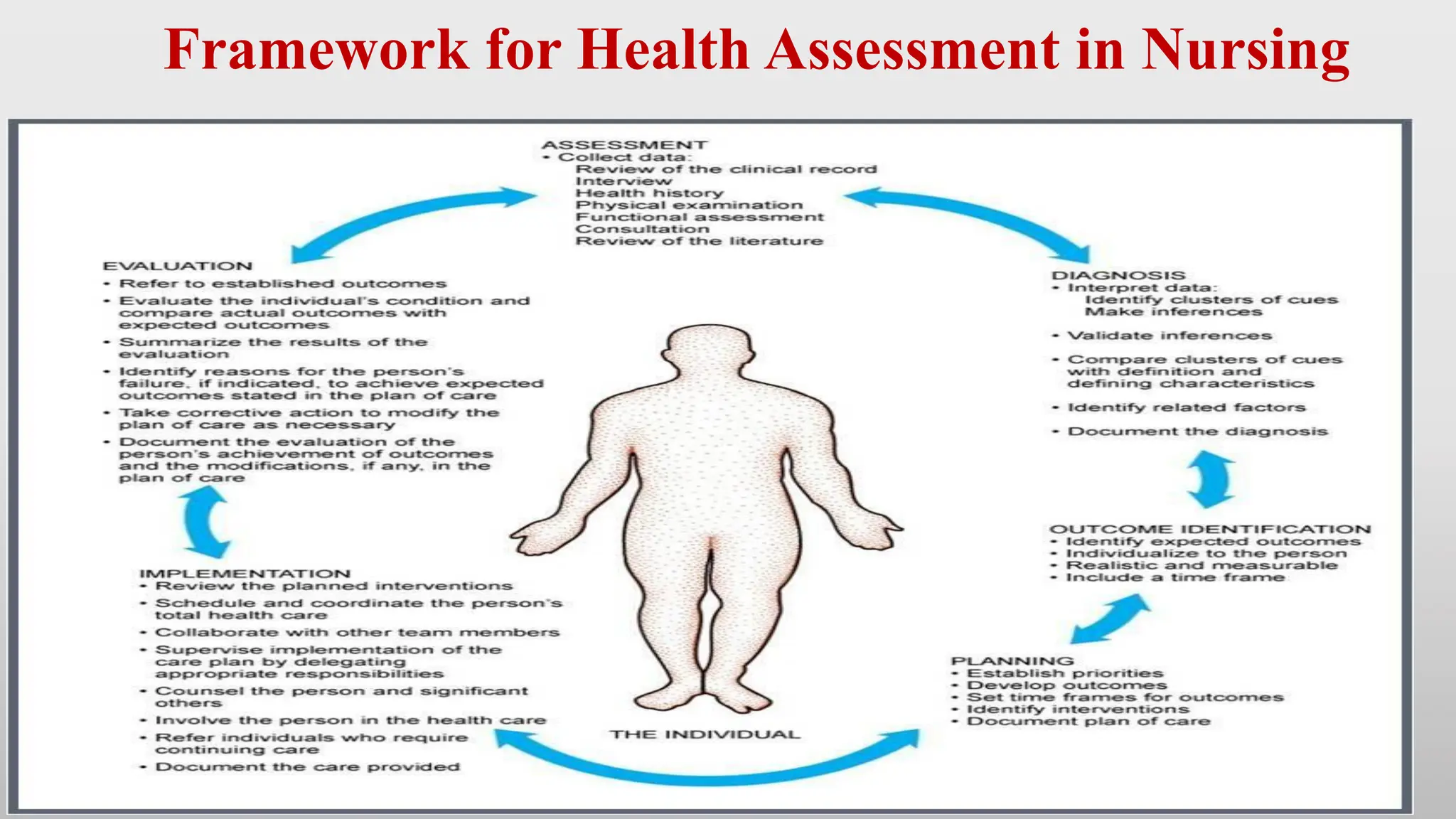
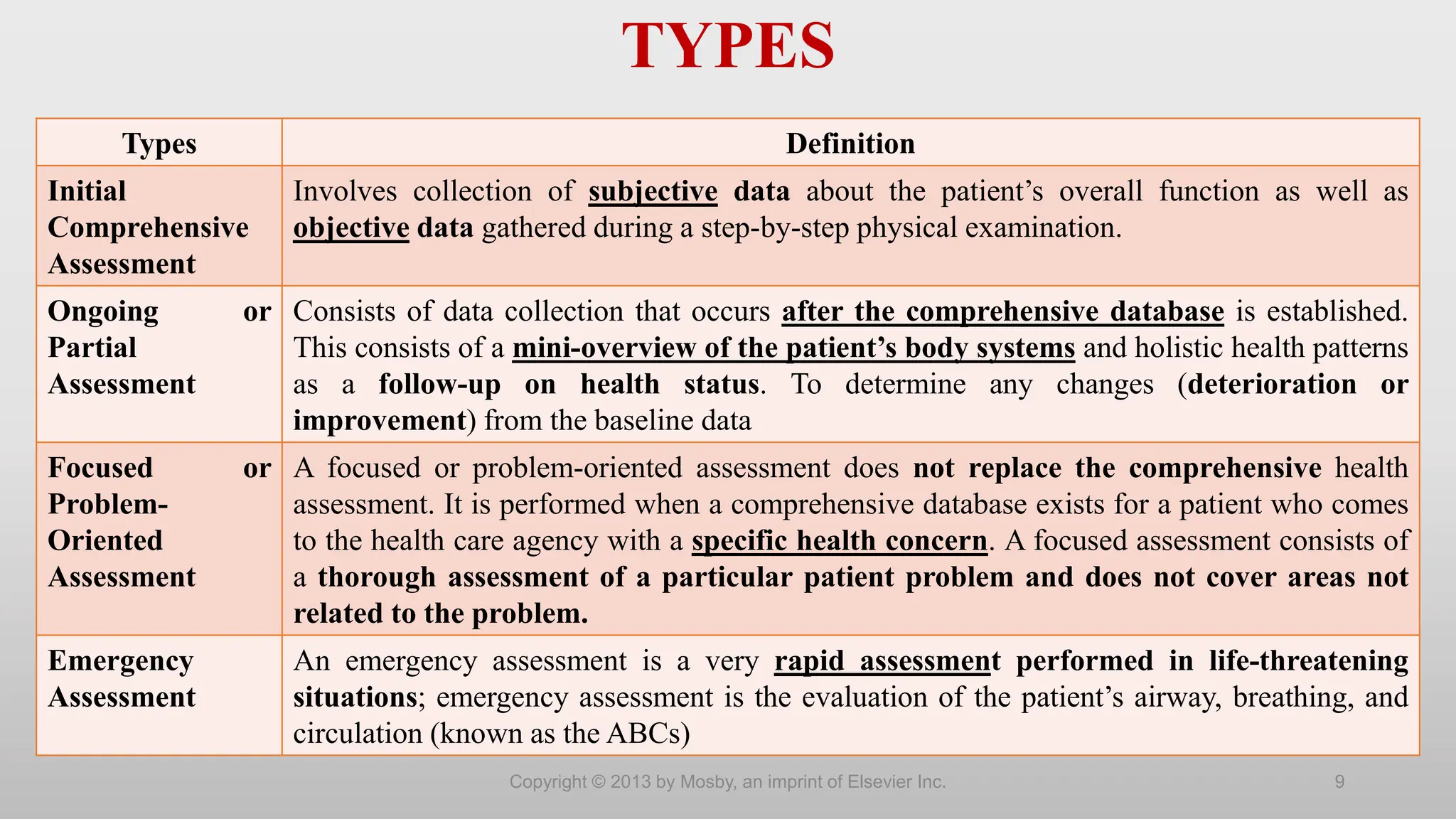
The document outlines the importance and frameworks of health assessment in nursing, emphasizing its role in establishing baseline data for patient care. Nursing assessments focus on the patient's response to health issues, gathering both subjective (health history) and objective (physical examination) data for comprehensive care planning. It highlights various assessment types, procedures, and necessary considerations for effective patient interactions and data collection.