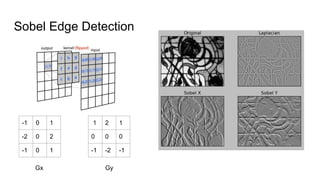
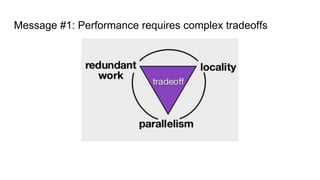
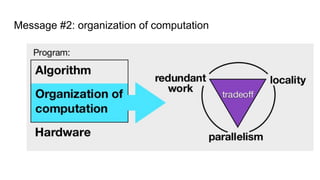
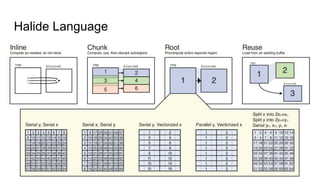
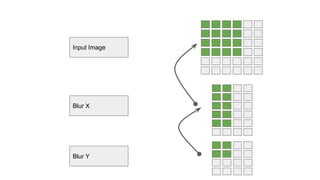
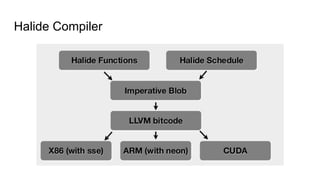
The document describes Halide, a domain specific language for image processing pipelines that decouples algorithms from schedules. This decoupling allows for easy optimization by specifying schedules that control parallelism, locality, and vectorization without changing the underlying algorithm. The Halide compiler then generates efficient code from the algorithm and schedule. Key features include expressing algorithms with Funcs and scheduling with operations like tile, split, fuse, and parallel. Halide is embedded in C++ and uses metaprogramming to represent programs as abstract syntax trees, enabling just-in-time or ahead-of-time compilation to optimized code.