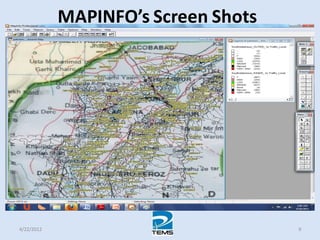
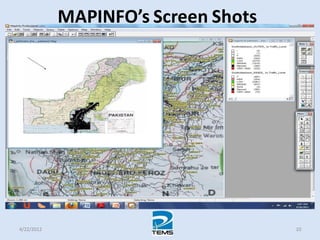
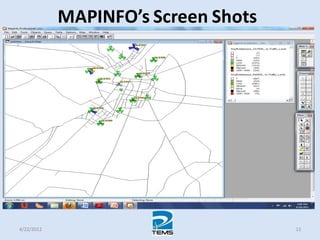
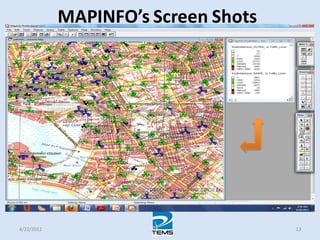
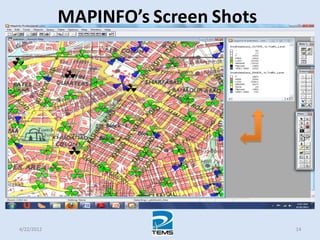
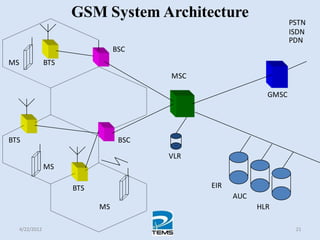
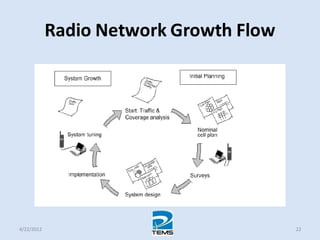
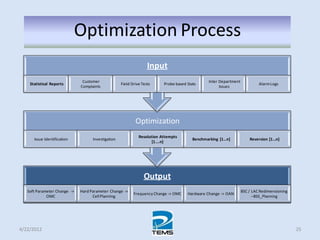
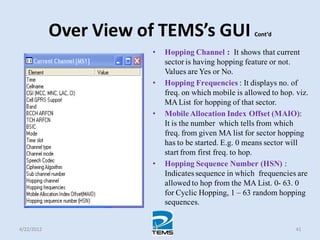
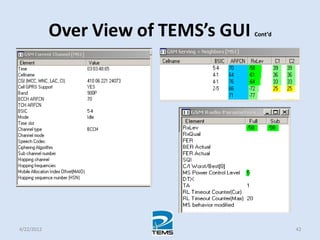
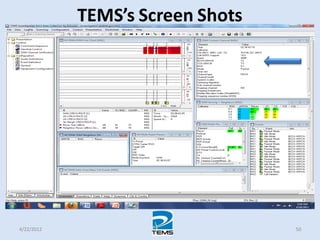
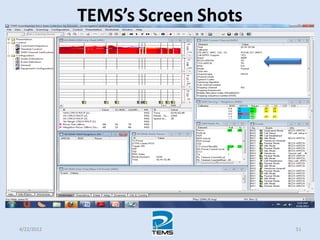
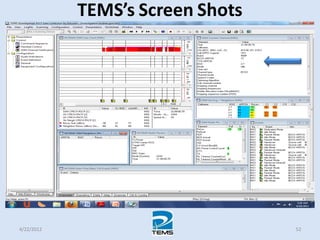
The document provides an overview of MAPINFO and TEMS Investigation software used for cellular network optimization. MAPINFO is a desktop GIS software that allows users to visualize and analyze spatial data. TEMS Investigation is a drive test tool used for troubleshooting, verification, optimization, and maintenance of wireless networks. The document discusses key concepts like optimization process, MAPINFO and TEMS interface, parameters, and how tools are used to observe network performance metrics and identify issues.