Embed presentation
Download to read offline





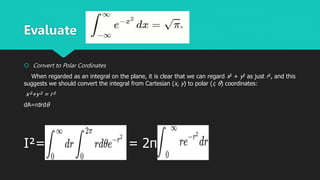

The document discusses calculating the Gaussian integral, which is the integral of the Gaussian function over the entire real number line. It shows converting the integral to double integral form and then to polar coordinates. This allows evaluating the integral in closed form, arriving at the result that the Gaussian integral equals the square root of pi.






