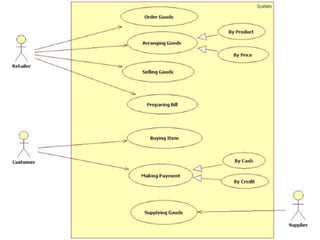
This document outlines the requirements for developing a software system to manage operations at a supermarket. The key goals of the system are to automate tasks like maintaining sales, stock, and accounting records; reduce calculation and paperwork; and store large amounts of data. It describes functions for administrators to manage product and employee data, customers to purchase items, and an automated billing process. The benefits of the system over a manual process are also summarized, such as reduced costs, errors, and improved reporting.