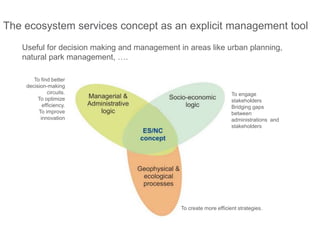
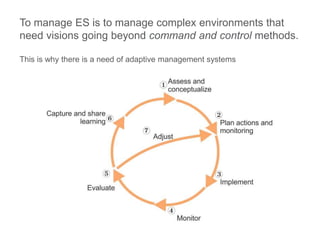
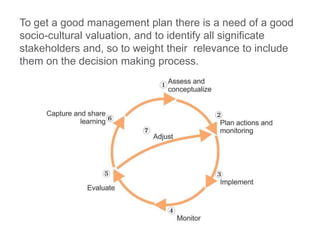
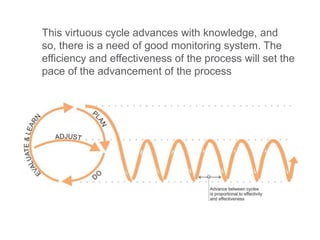
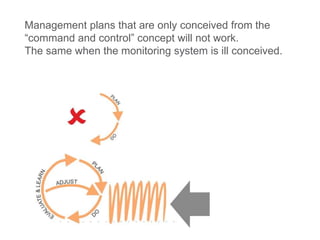
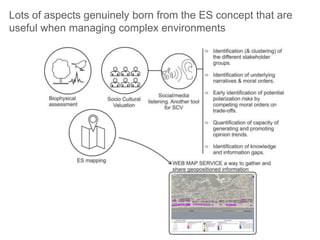
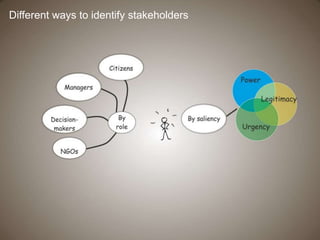
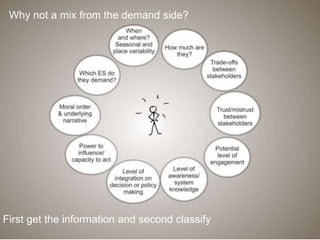
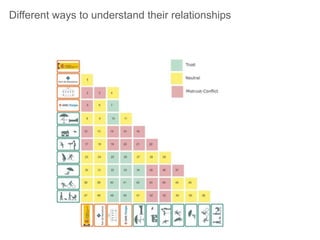
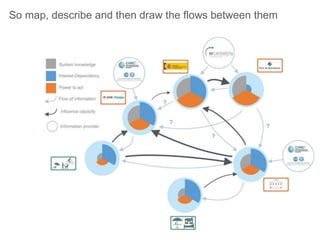
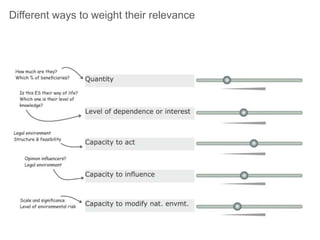
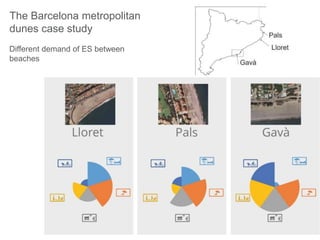
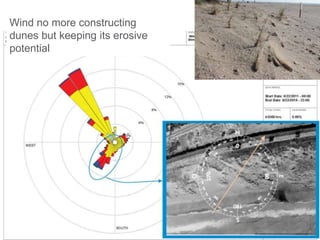
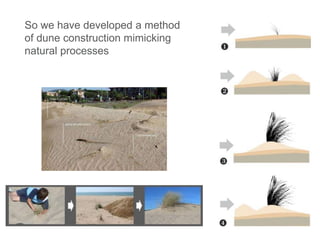
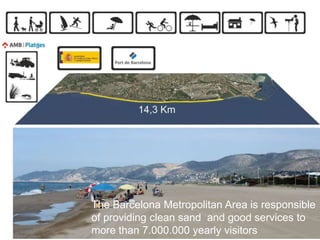
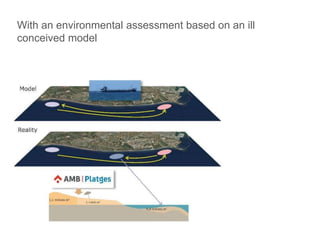
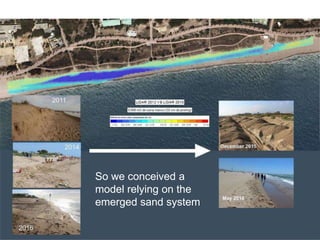
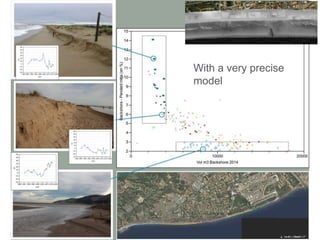
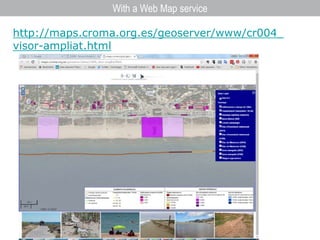
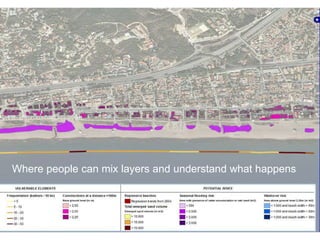
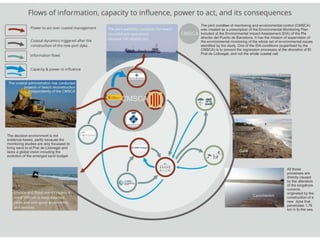
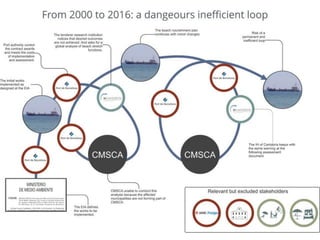
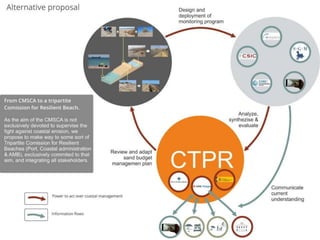
This document discusses governance of ecosystem services and transforming the ecosystem services concept into an explicit management tool. It outlines that management of complex environments requires adaptive management beyond traditional command and control methods. This requires good socio-cultural valuation and inclusion of all significant stakeholders in decision making. Effective management plans also require robust monitoring systems. The document argues that mix of demand-side identification of stakeholders is needed, and different ways to understand their relationships and weight their relevance. It provides an example of managing dunes in the Barcelona metropolitan area.