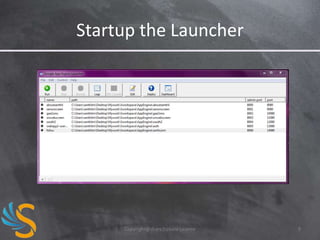
Google App Engine is a development platform that allows users to build and host web applications on the same infrastructure as Google. It provides four runtime environments - PHP, Python, Java, and Go. Code runs in a secure sandbox that distributes requests across servers and scales automatically. Data storage options include the App Engine datastore, Cloud SQL, and Cloud Storage. The platform charges users based on usage rather than a fixed cost, allowing applications to scale as needed.








![Main.py
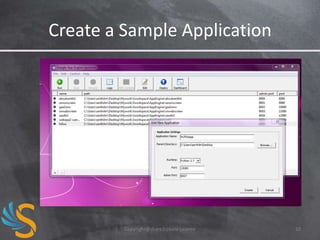
#!/usr/bin/env python
import webapp2
class MainHandler(webapp2.RequestHandler):
def get(self):
self.response.write('Hello world!')
app = webapp2.WSGIApplication([
('/', MainHandler)], debug=True)
Copyright@share2create License
12](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/googleappengine-140206035847-phpapp01/85/Google-app-engine-12-320.jpg)


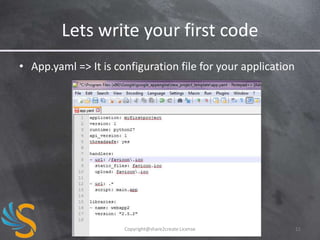
![Querying the Data store
from google.appengine.ext import ndb
def StoresByCity(city, limit):
query = Store.query(Store.city == city).order(Store.name)
return query.fetch(limit, projection=[Store.name, Store.address])
•
•
•
•
The Data store API is Object Oriented.
Queries are objects
Filters and projections are specified by calling methods
Make sure you know the limits!
Copyright@share2create License
15](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/googleappengine-140206035847-phpapp01/85/Google-app-engine-15-320.jpg)






