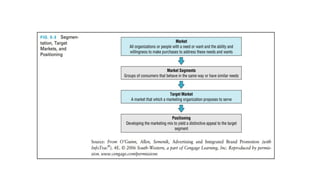
The document explores various aspects of green marketing, including types of green consumers, their motives, and buying strategies, as well as green business opportunities and innovations. It highlights the importance of eco-design, sustainability in product development, and various technologies aimed at environmental conservation. Additionally, it discusses policies and subsidies aimed at promoting green practices across different sectors.