Embed presentation
Download to read offline



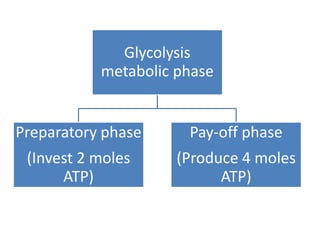
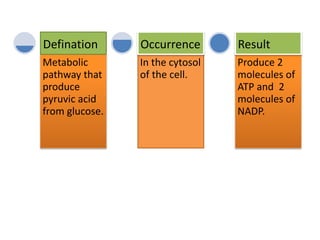
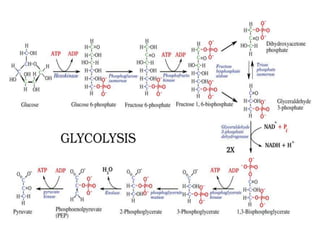
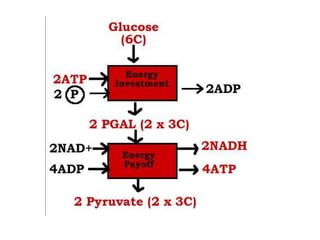





Glycolysis is a metabolic pathway that breaks down glucose in the cytosol of cells to produce pyruvic acid, generating energy in the form of ATP. It occurs in two phases: the preparatory phase requires energy to break down glucose but produces no ATP, while the pay-off phase yields a net production of 4 ATP molecules from each glucose molecule. Glycolysis is significant as the first step in glucose breakdown, providing products that enter subsequent energy-generating metabolic pathways to produce much needed ATP as the main energy currency of cells.












