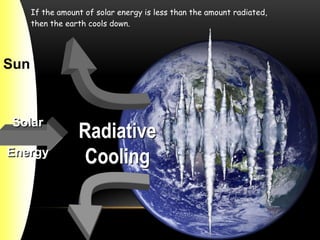
Global warming is caused by increased carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases trapping heat in the atmosphere. This is raising global temperatures and melting ice caps, which is causing sea levels to rise. If warming continues unchecked, it will have severe consequences for wildlife, ecosystems, and humans through more extreme weather, flooding, droughts, and potential food shortages. International agreements like the Kyoto Protocol aim to reduce greenhouse gas emissions but greater emissions cuts are needed to significantly impact global warming.