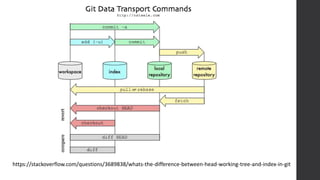
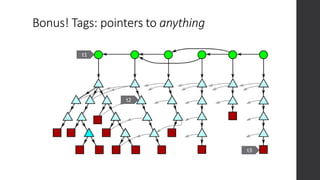
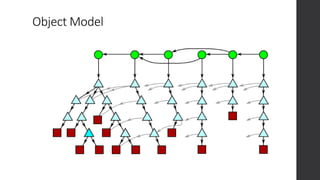
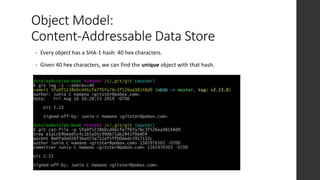
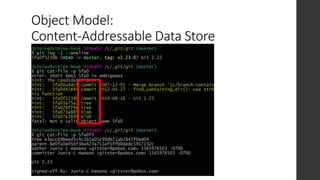
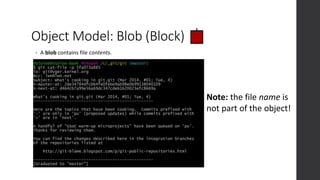
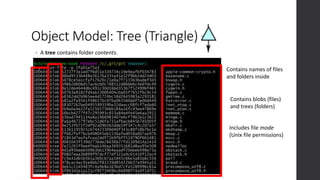
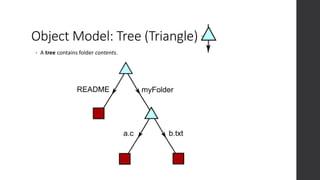
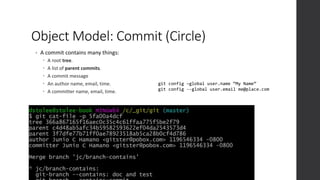
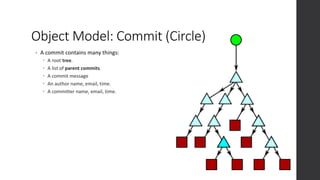
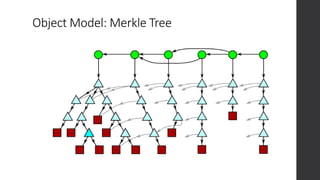
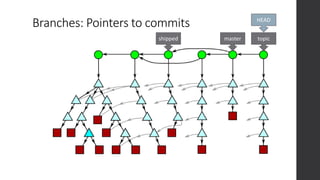
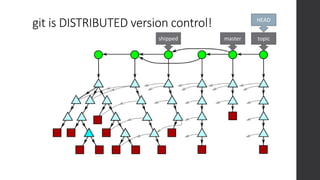
The document is a presentation on advanced Git concepts aimed at beginners, covering installation methods, the object model of Git, and key commands. It highlights the importance of understanding Git's distributed version control system and best practices for using Git effectively, such as avoiding the 'git pull' command to prevent unexpected results. Additional resources and links for further learning are provided at the end of the document.





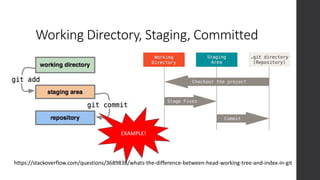
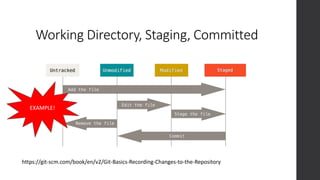

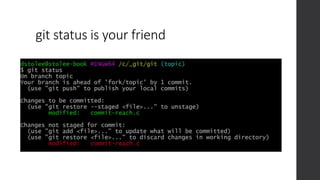
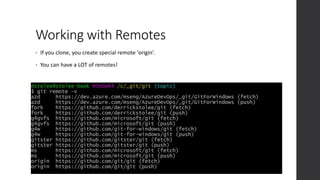
![Working with Remotes
Get new data: git fetch <remote> [branch]
Upload your data: git push <remote> <branch>
Hot Take: Don’t use git pull! This does the following:
1. git fetch
2. git merge
This can have unexpected results! Instead, do your merges yourself!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/git-230118234015-501fd55f/85/git-pptx-24-320.jpg)