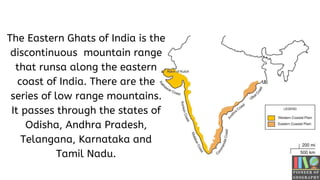
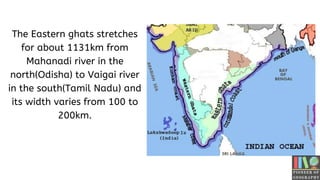
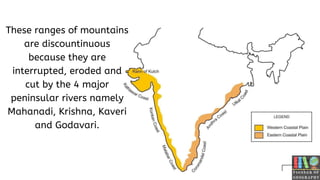
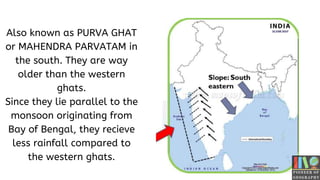
The Eastern Ghats of India is a discontinuous mountain range that runs along India's eastern coast through several states. It stretches over 1,131 km from northern Odisha to southern Tamil Nadu. Though interrupted by rivers, it contains hilly regions with peaks as high as 1,690 meters. Several major rivers like the Godavari and Mahanadi originate from the Eastern Ghats, irrigating the surrounding plains. The region also contains important wildlife, including elephants, tigers, deer and bears.