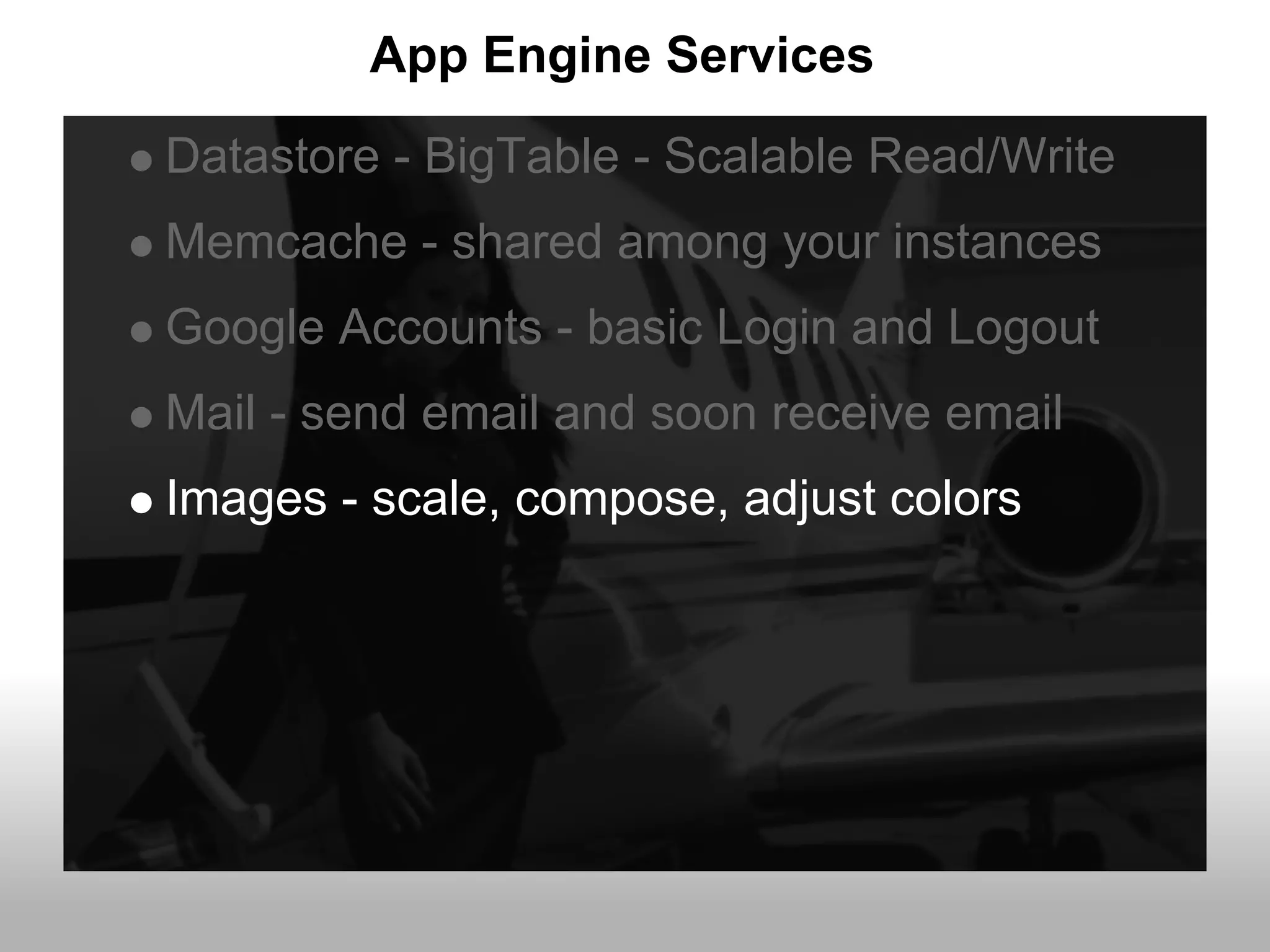
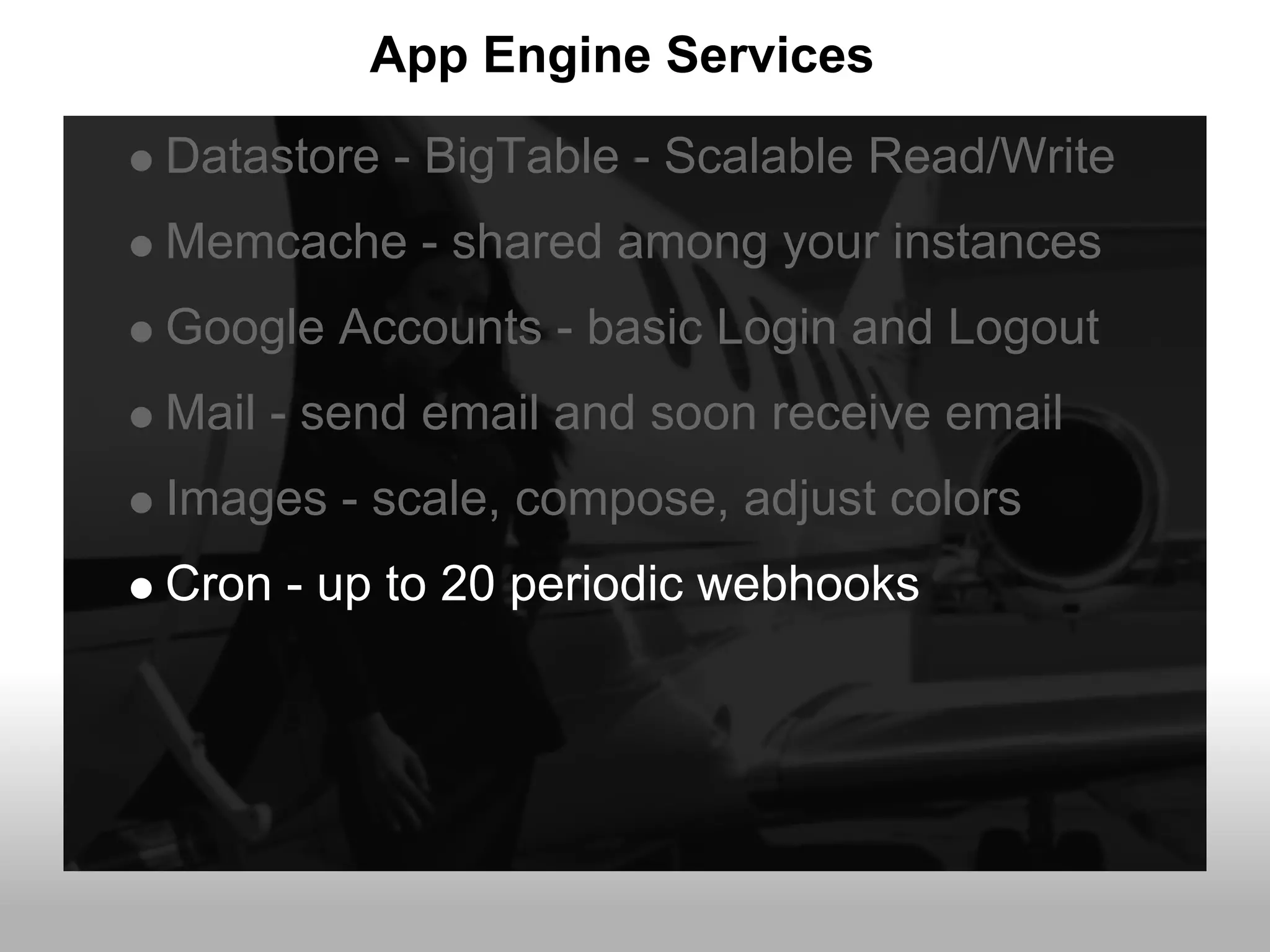
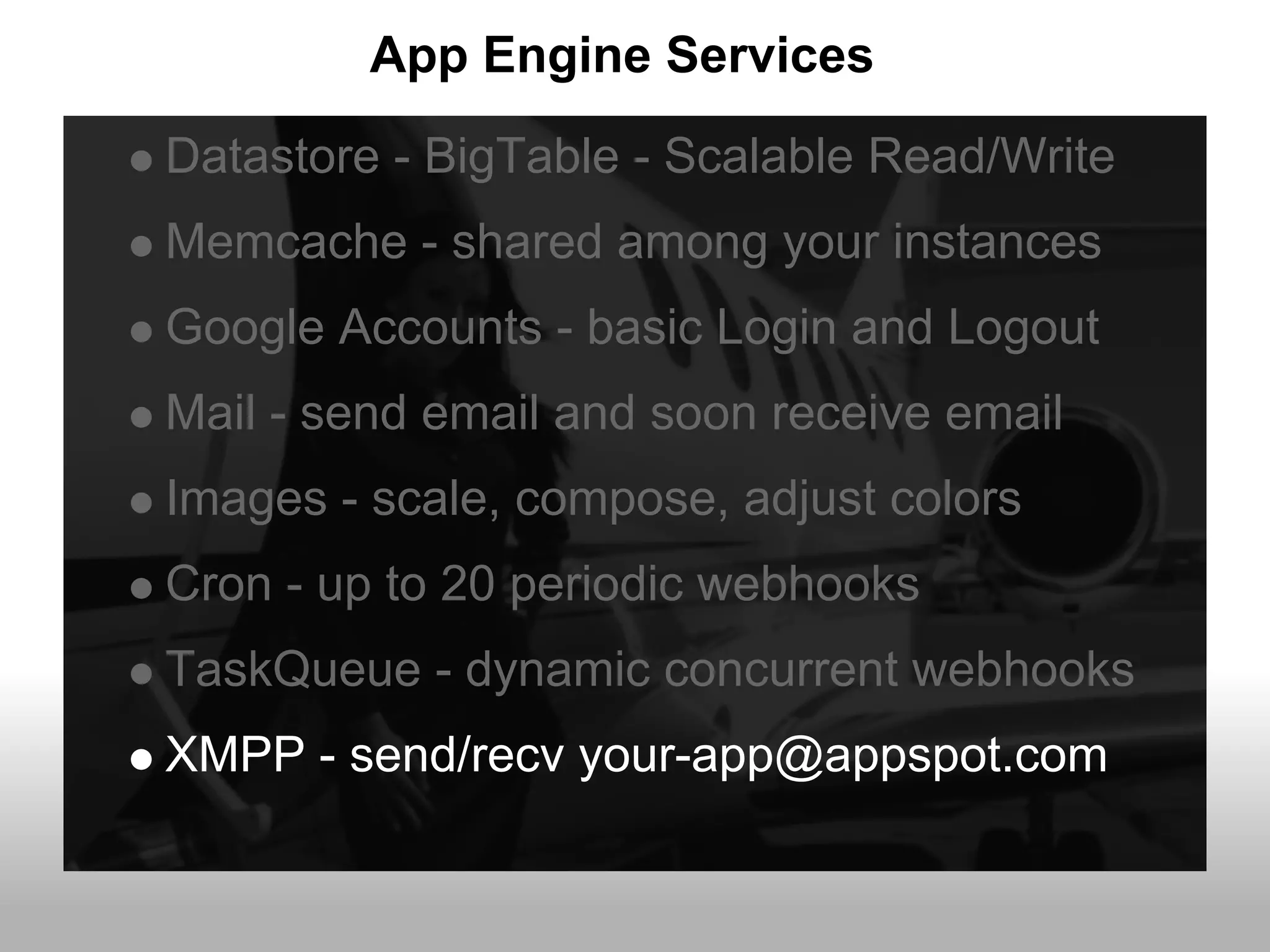
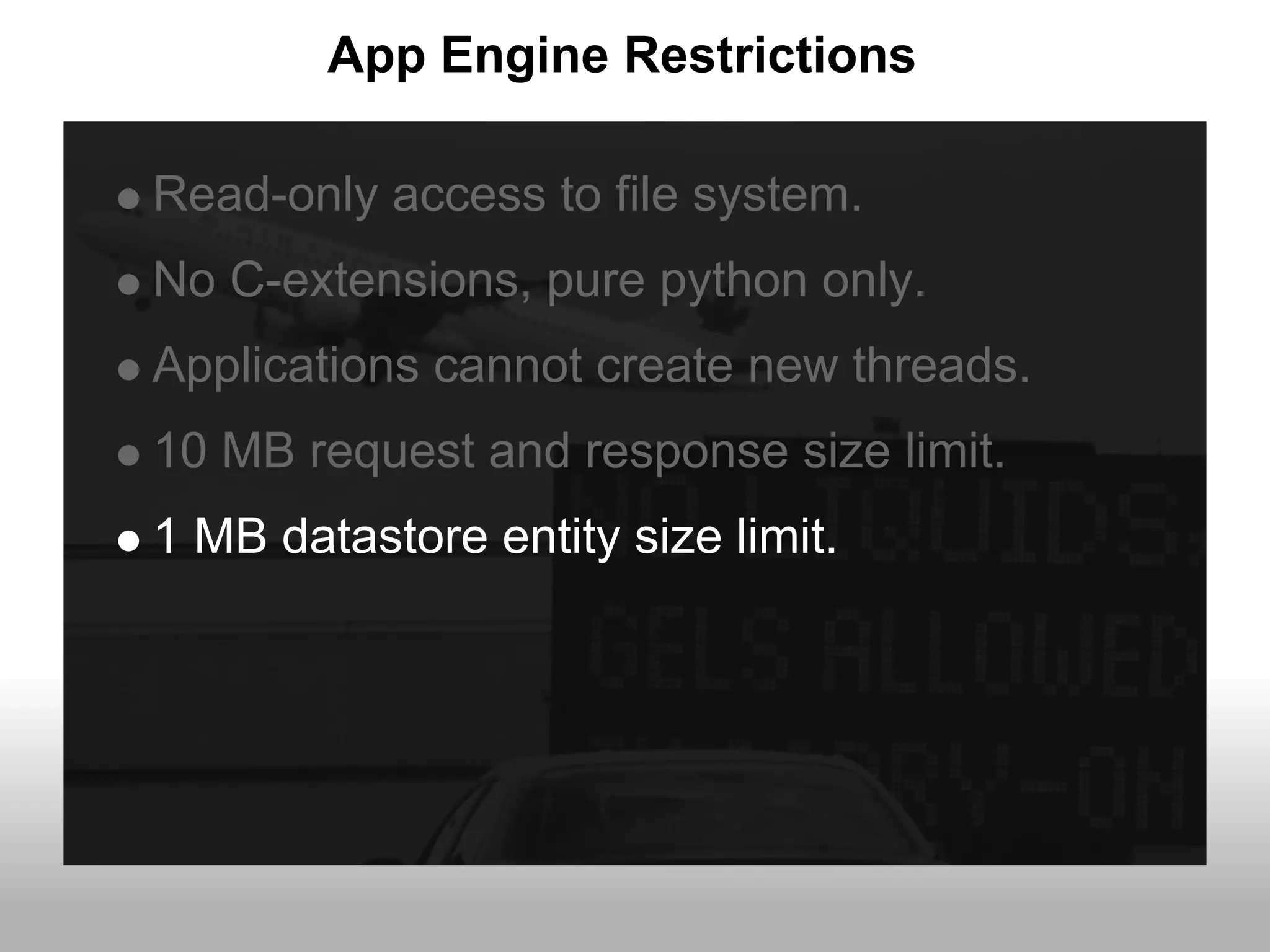
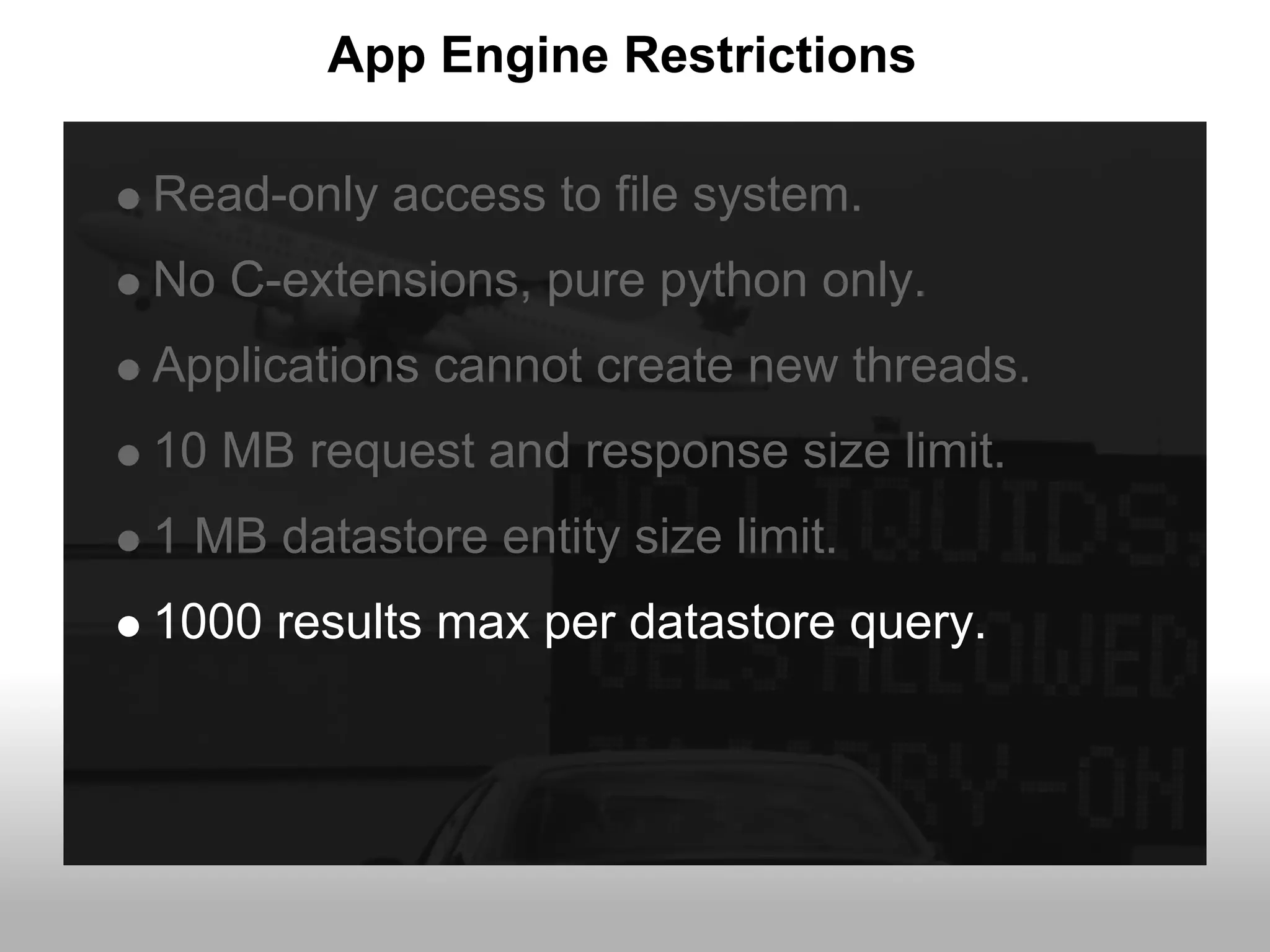
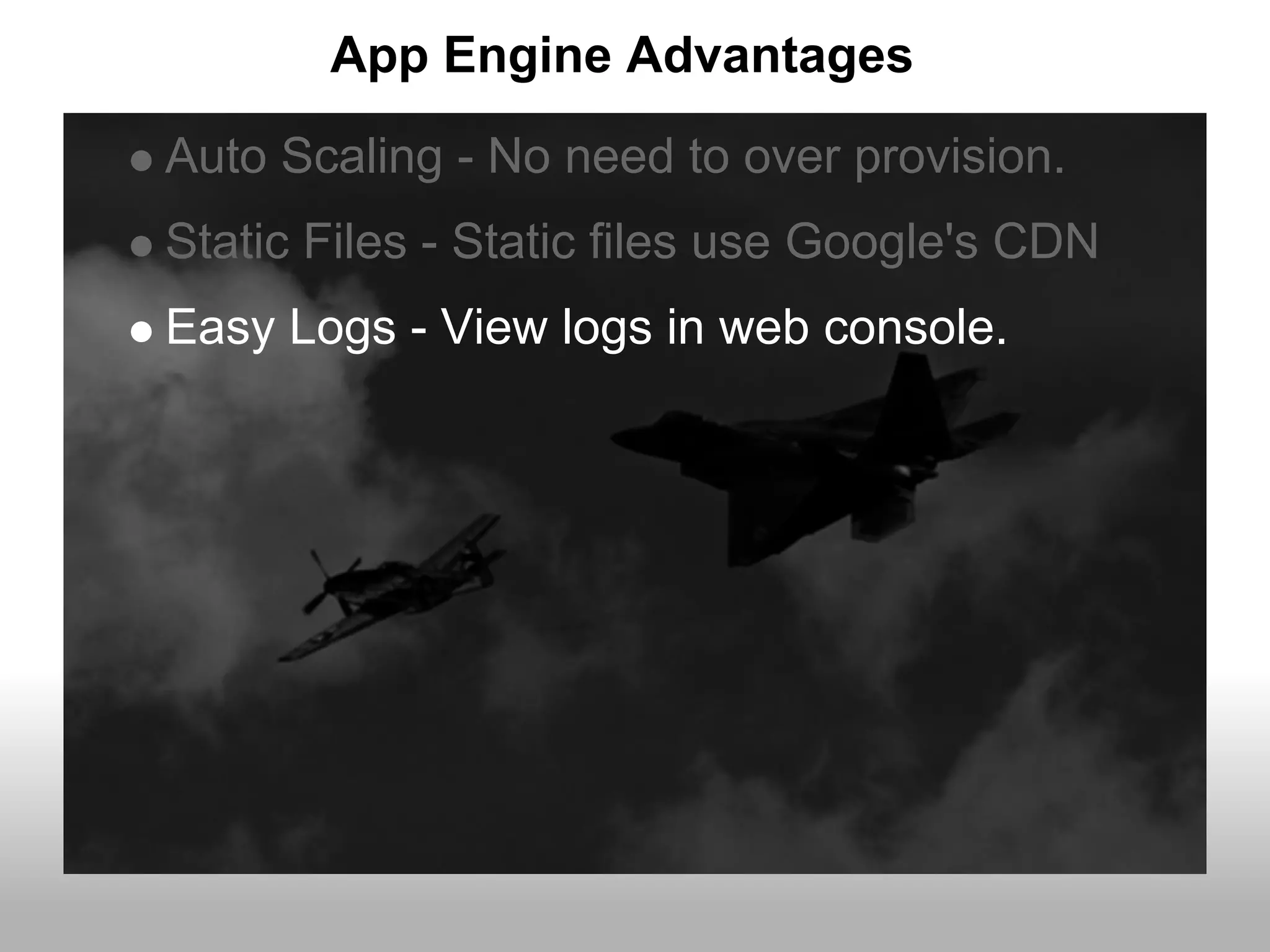
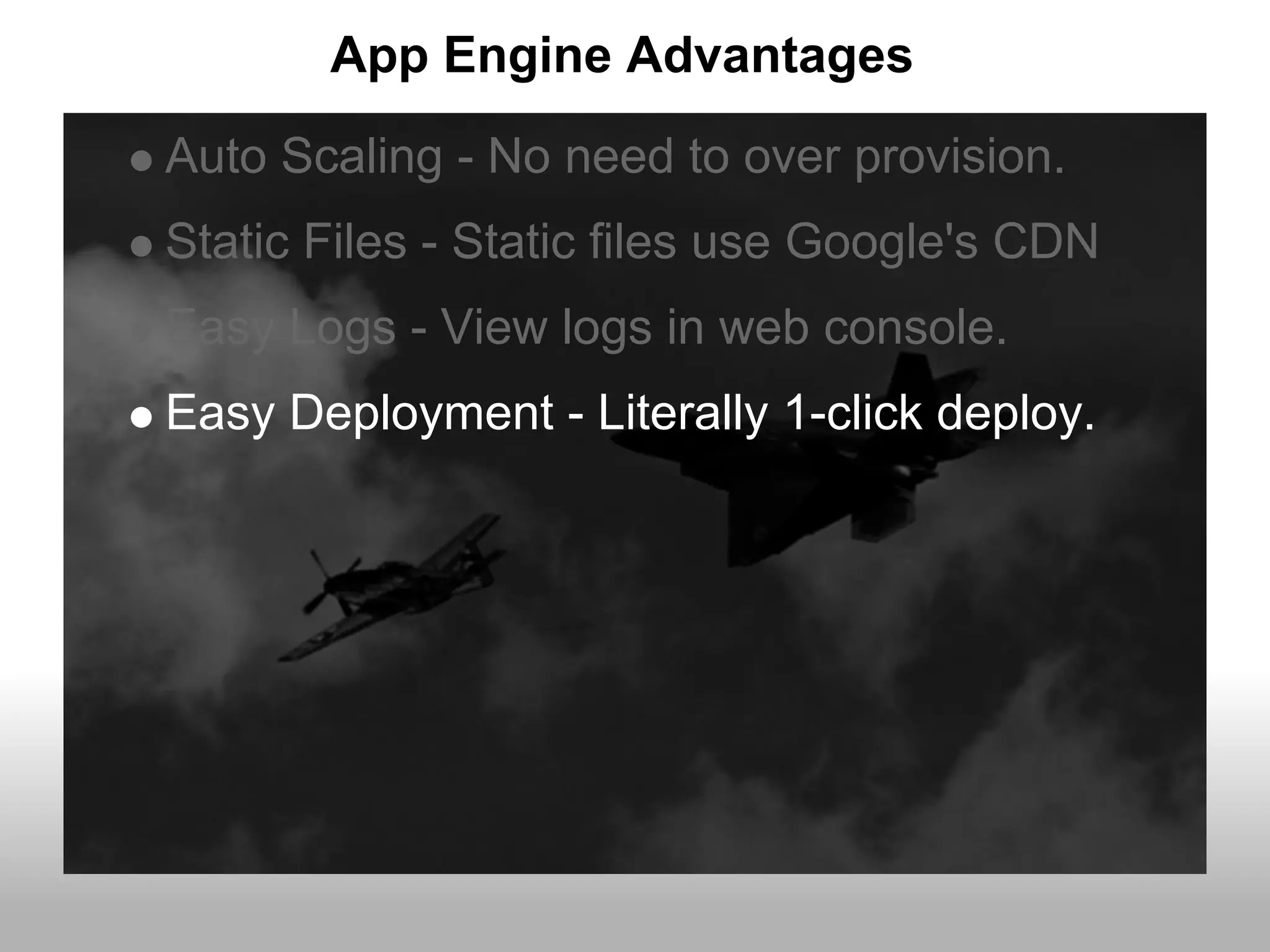
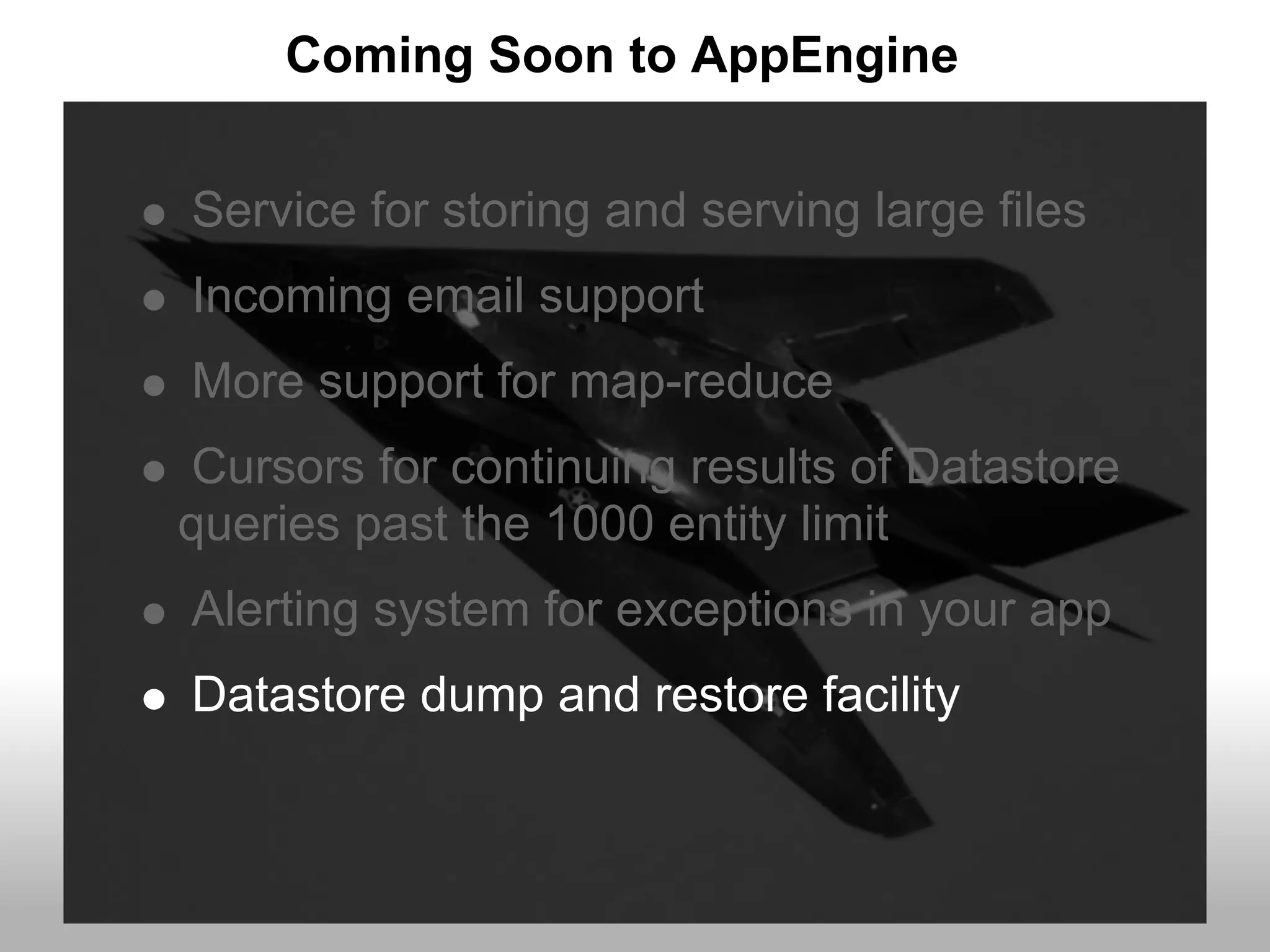
Google App Engine allows users to host web applications on Google's infrastructure without having to maintain servers or databases. It provides automatic scaling, free quotas for storage and bandwidth usage, and a simple deployment process. The document provides an overview of App Engine, including how to get started, the services it offers like Datastore and Memcache, and best practices for building scalable applications on the platform.

















![How to Run with Python on App Engine
from wsgiref.handlers import CGIHandler
def helloworld( environ, start_response):
status = '200 OK'
headers = [('Content-Type', 'text/plain')]
start_response(status, headers)
return ['Hello, World!']
def main():
CGIHandler().run(helloworld)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gentleappengineintro-091009001520-phpapp01/75/Gentle-App-Engine-Intro-24-2048.jpg)
![How to Run with Python on App Engine
from wsgiref.handlers import CGIHandler
def helloworld( environ, start_response):
status = '200 OK'
headers = [('Content-Type', 'text/plain')]
start_response(status, headers)
return ['Hello, World!']
def main():
CGIHandler().run(helloworld)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gentleappengineintro-091009001520-phpapp01/75/Gentle-App-Engine-Intro-25-2048.jpg)
![How to Run with Python on App Engine
from wsgiref.handlers import CGIHandler
def helloworld( environ, start_response):
status = '200 OK'
headers = [('Content-Type', 'text/plain')]
start_response(status, headers)
return ['Hello, World!']
def main():
CGIHandler().run(helloworld)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gentleappengineintro-091009001520-phpapp01/75/Gentle-App-Engine-Intro-26-2048.jpg)
![How to Run with Python on App Engine
from wsgiref.handlers import CGIHandler
def helloworld( environ, start_response):
status = '200 OK'
headers = [('Content-Type', 'text/plain')]
start_response(status, headers)
return ['Hello, World!']
def main():
CGIHandler().run(helloworld)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gentleappengineintro-091009001520-phpapp01/75/Gentle-App-Engine-Intro-27-2048.jpg)
![How to Run with Python on App Engine
from wsgiref.handlers import CGIHandler
def helloworld( environ, start_response):
status = '200 OK'
headers = [('Content-Type', 'text/plain')]
start_response(status, headers)
return ['Hello, World!']
def main():
CGIHandler().run(helloworld)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gentleappengineintro-091009001520-phpapp01/75/Gentle-App-Engine-Intro-28-2048.jpg)