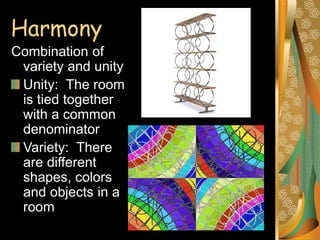
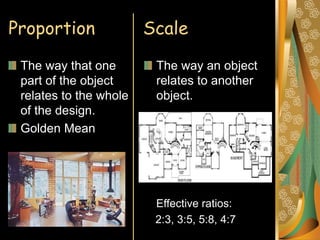
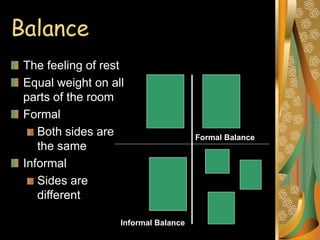
Interior design aims to create functional and beautiful living spaces. It considers elements of design like space, shape, line, texture and color as well as principles of design such as harmony, proportion, scale, balance, rhythm and emphasis. Harmony balances variety and unity in a room. Proportion and scale relate the size of objects and balance can be formal, with symmetrical sides, or informal. Rhythm creates movement through repetition, transition, radiation or gradation. Emphasis establishes a focal point.