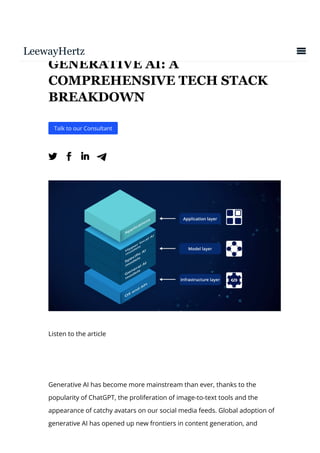
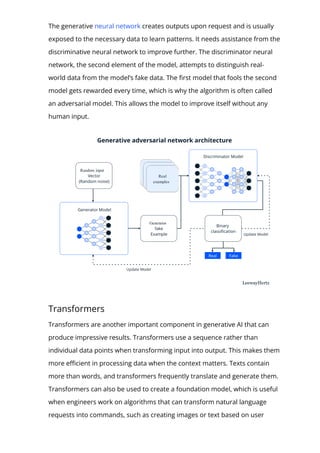
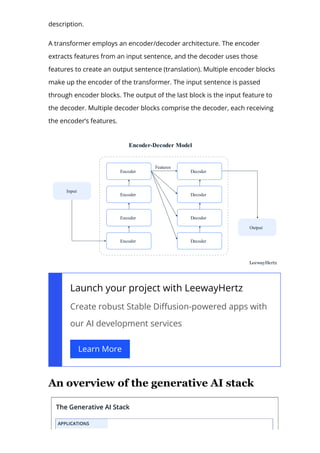
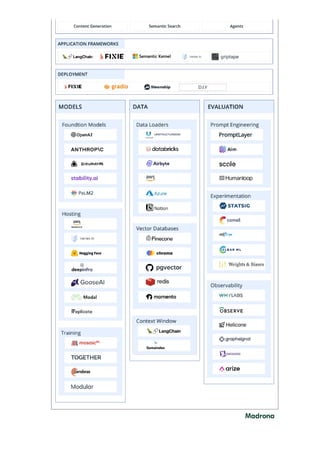
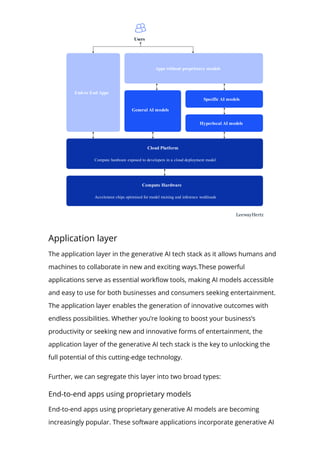
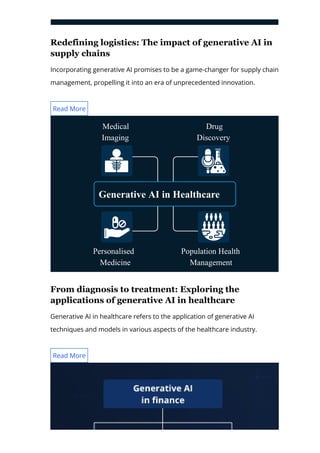
The document provides an in-depth overview of generative AI, highlighting its growing significance in content creation and business innovation. It outlines the essential components of the generative AI tech stack, including application frameworks, models, data handling, and deployment processes. The text emphasizes the evolving nature of generative AI technology and its diverse applications across various industries.