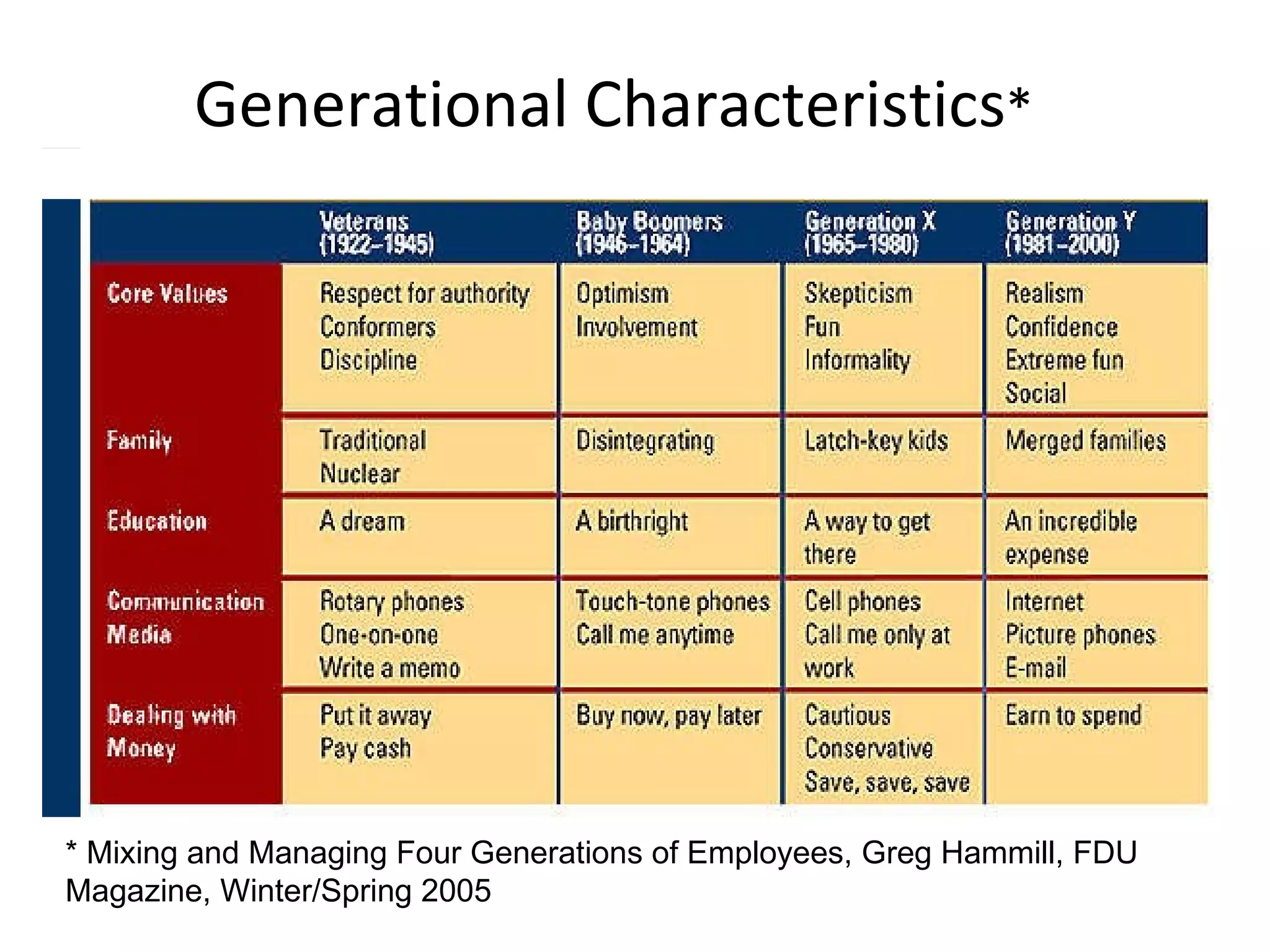
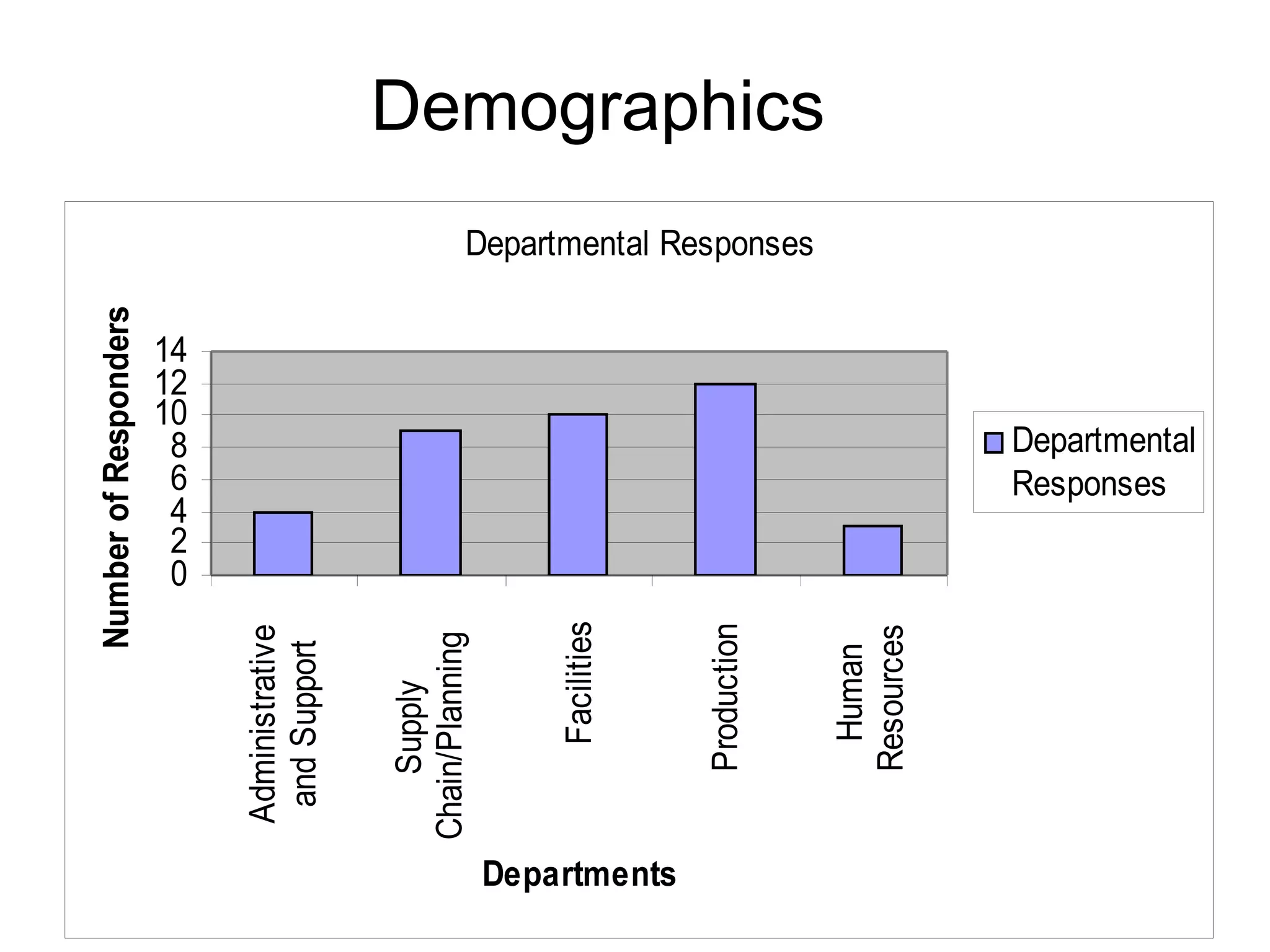
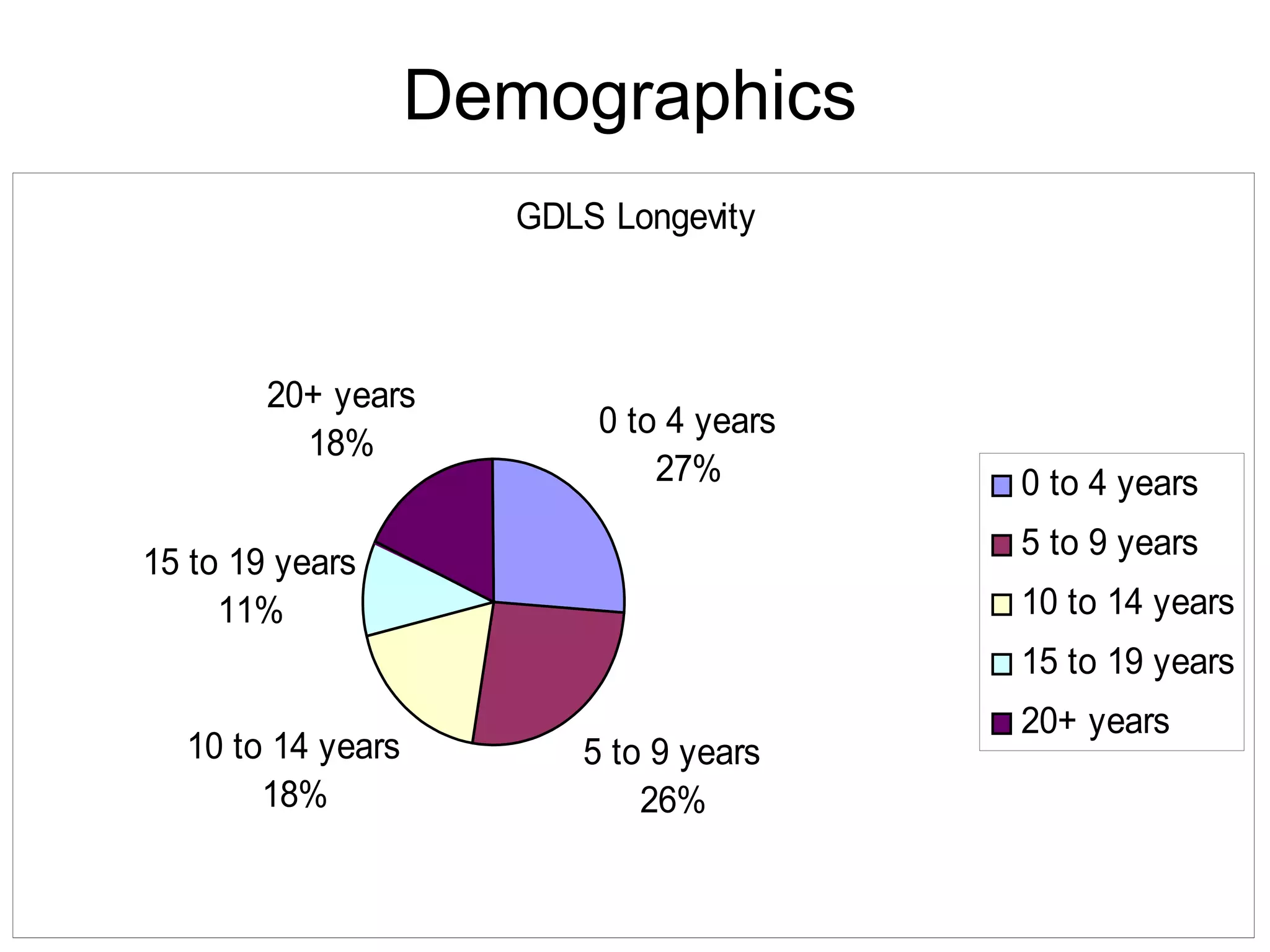
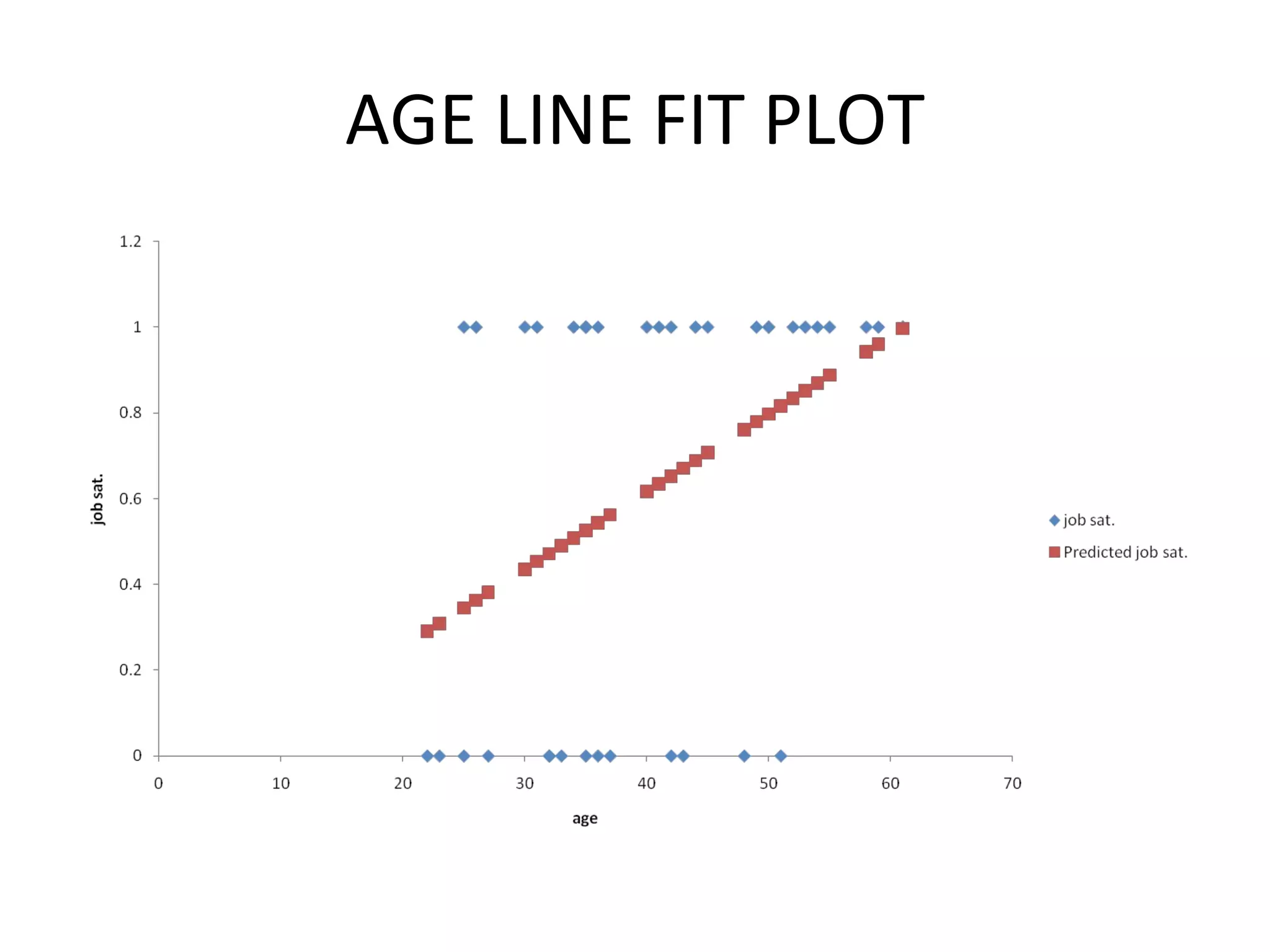
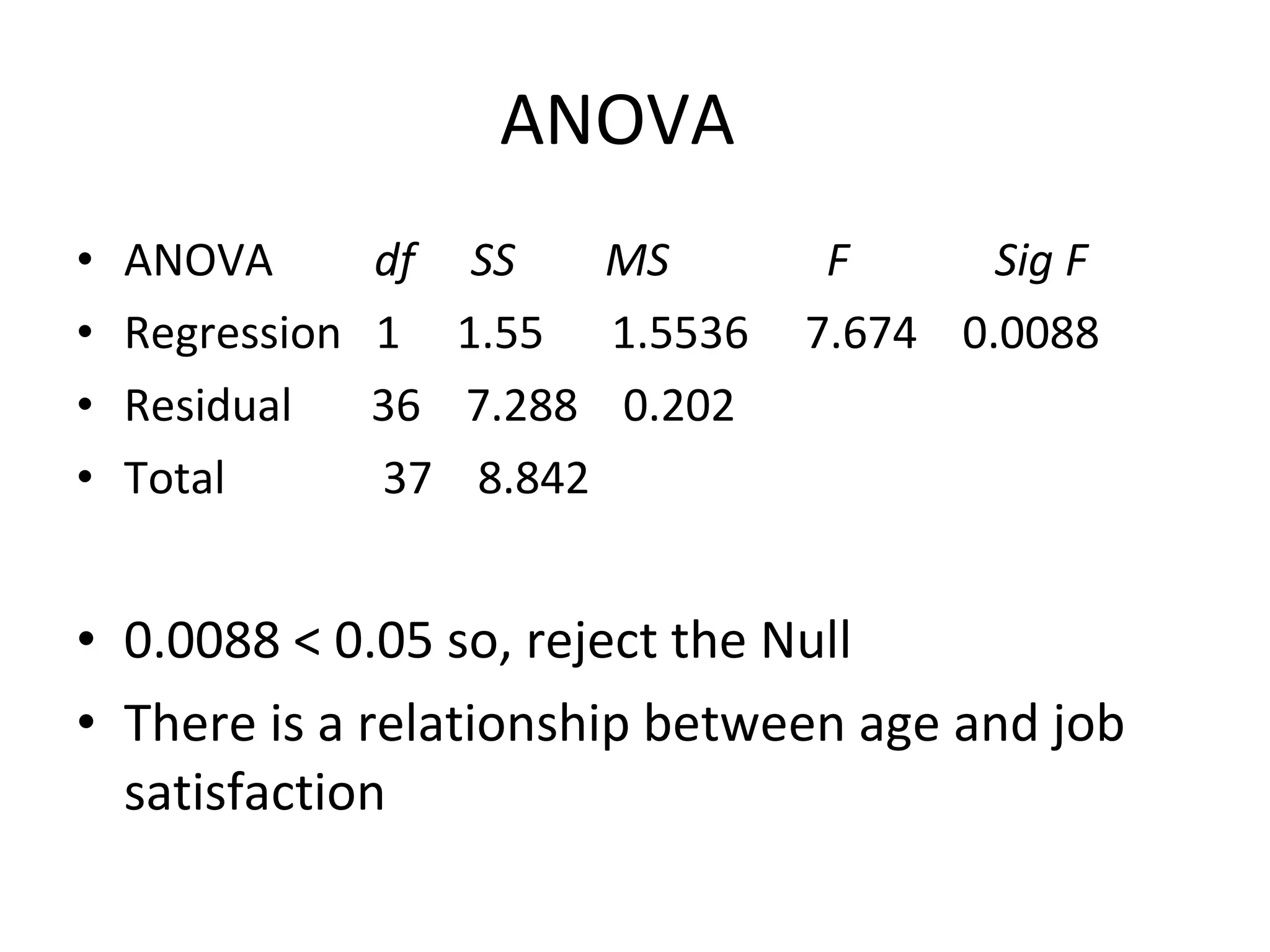
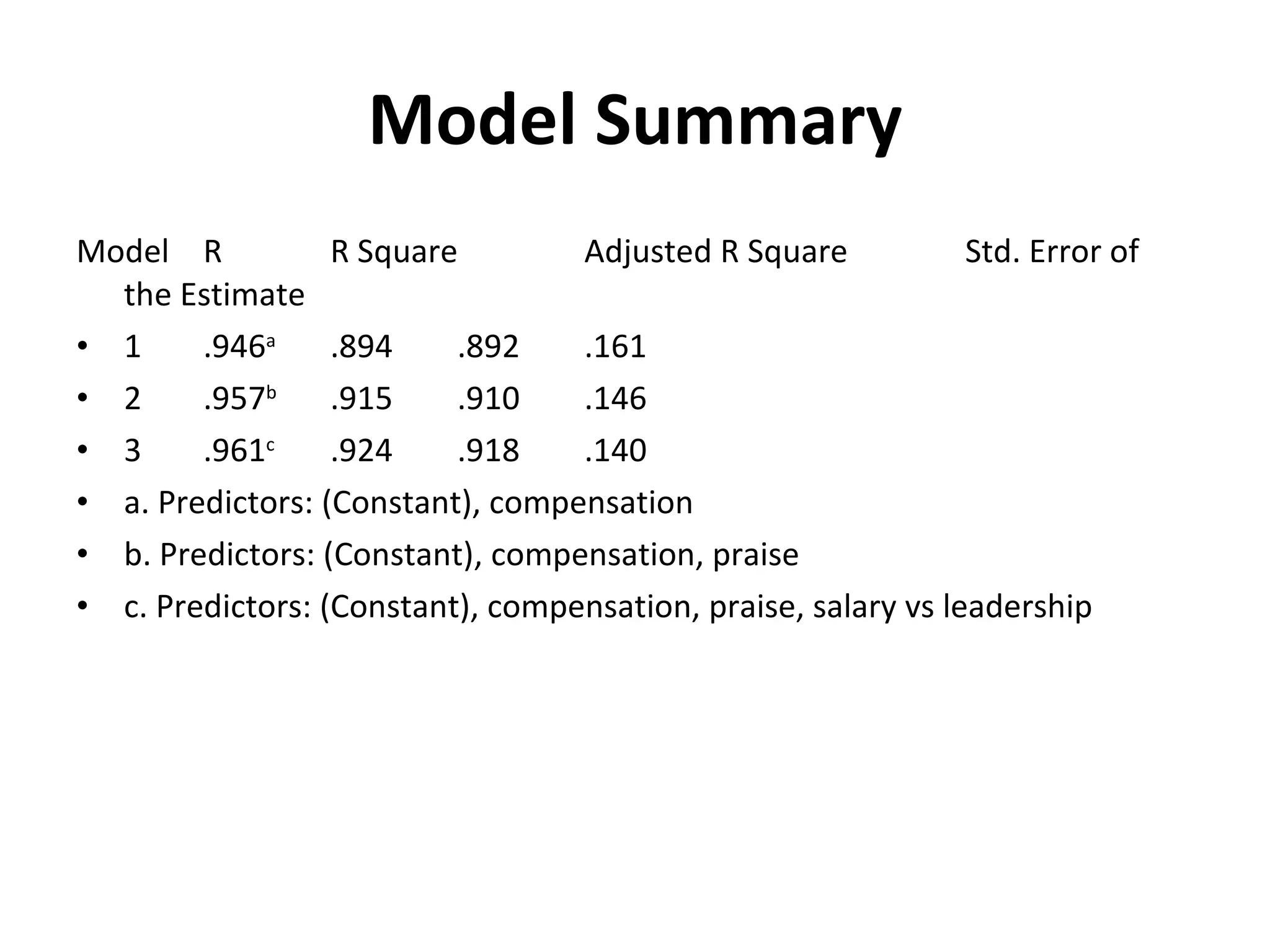
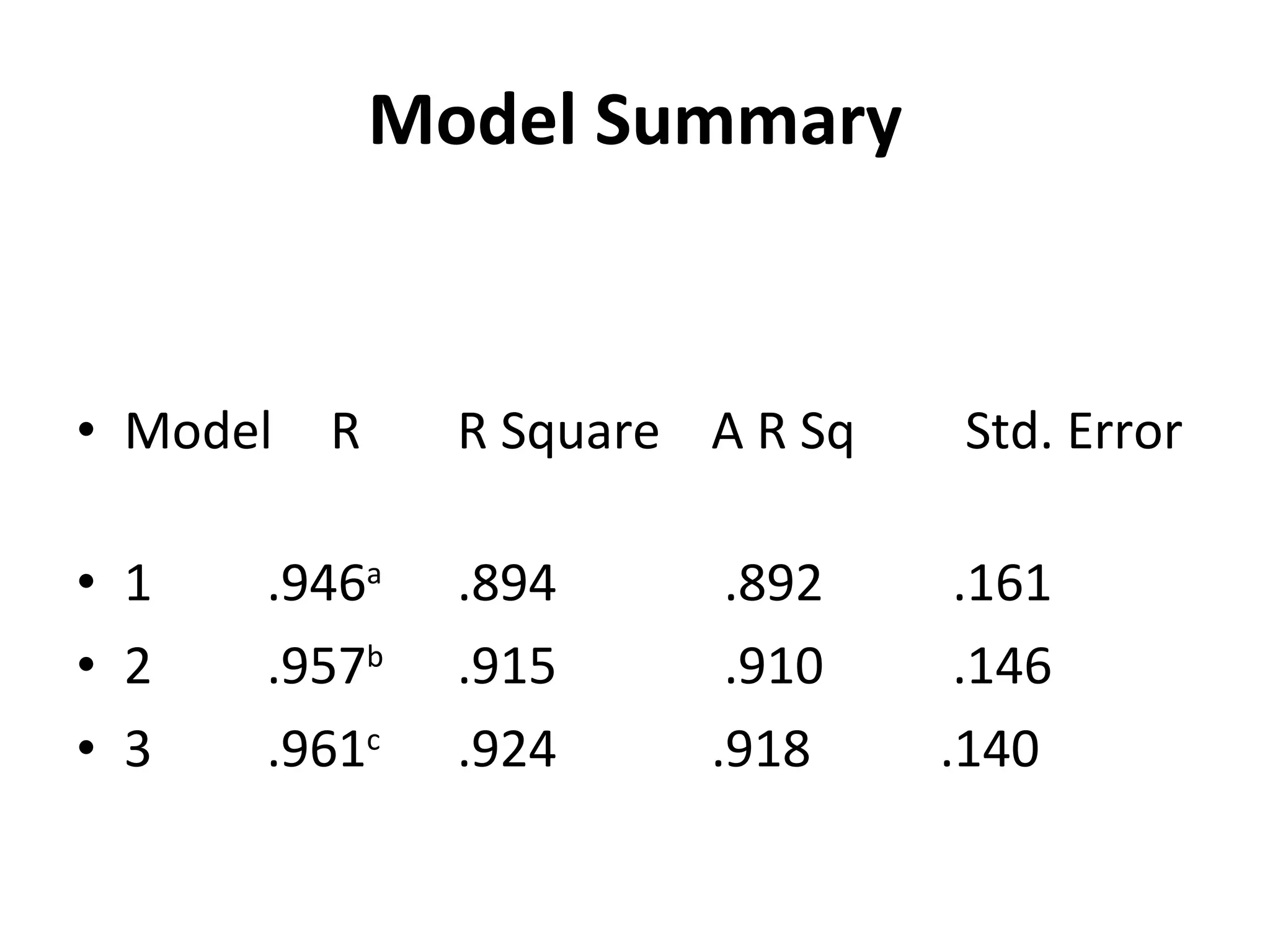
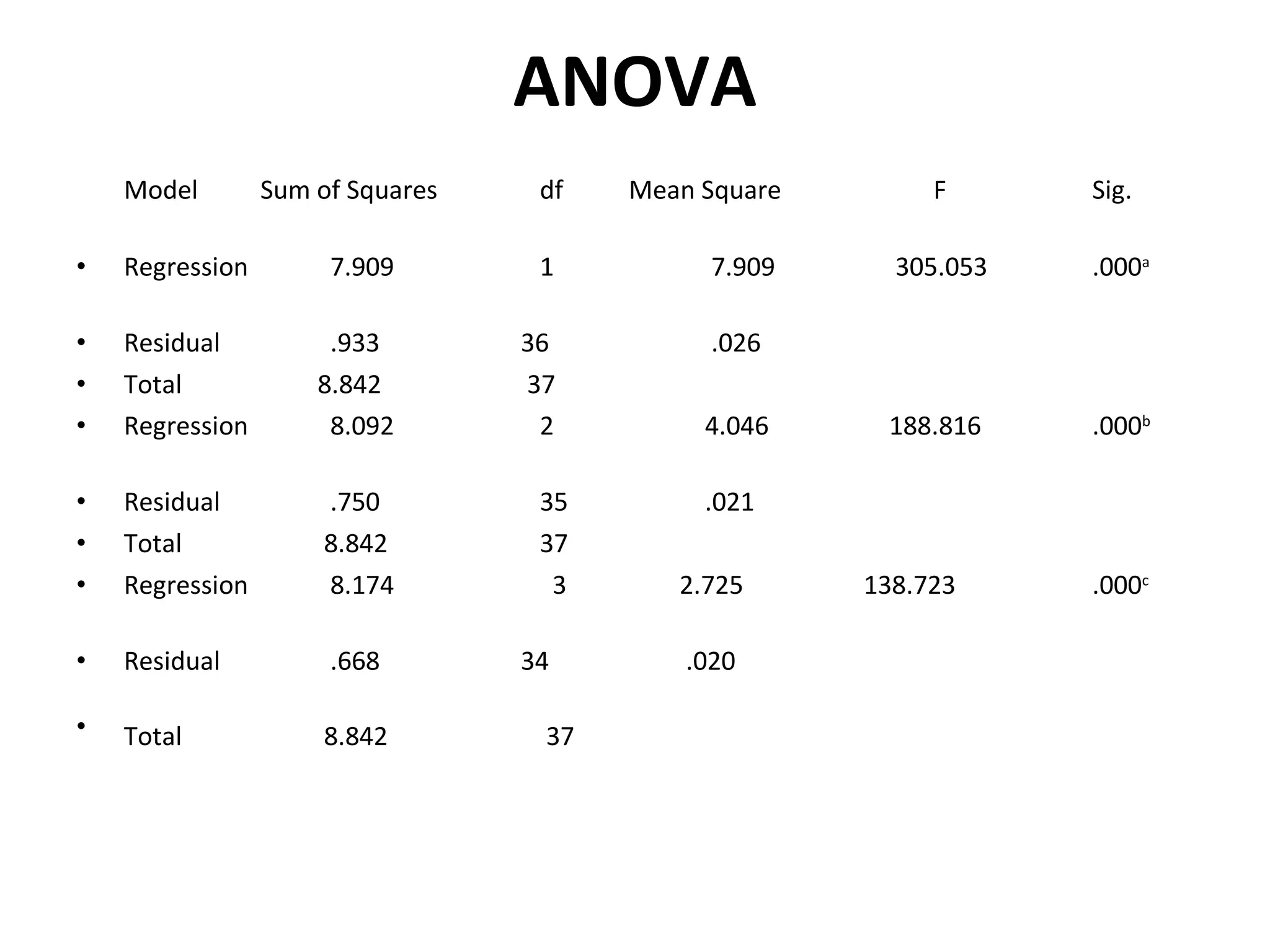
This document summarizes a study conducted on employee retention at a manufacturing facility with employees from multiple generations. A survey was distributed anonymously to 41 management employees to understand factors influencing job satisfaction. Simple linear regression found a relationship between age and job satisfaction. Multiple regression also found relationships between job satisfaction, compensation, praise, salary and managers' confidence. The conclusions recommend managers make greater efforts to earn younger employees' confidence, and further analysis is suggested to prioritize motivational factors.