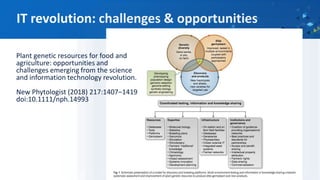
Genebank managers should be knowledgeable about the history of genebank management including past courses, current courses, and existing training resources. International instruments emphasize the importance of building human capacity in areas like genetic resources policy, taxonomy, seed physiology, incentives for crop diversity, and linking crop diversity to climate change. Effective genebank management also requires knowledge of neglected areas like financial management, strategic partnerships, traditional knowledge, sample tracking, and disease testing. The future of genebank manager training should involve modular, flexible courses tailored for different audiences that focus on quality management and include mentorship opportunities.