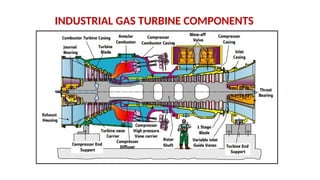
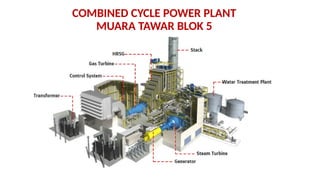
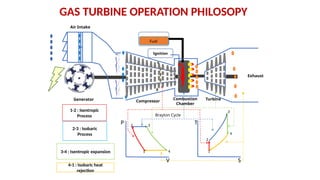
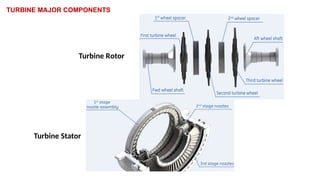
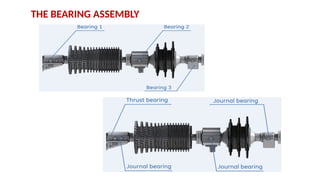
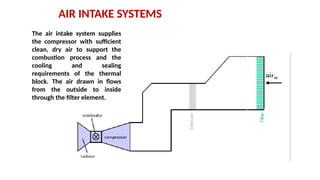
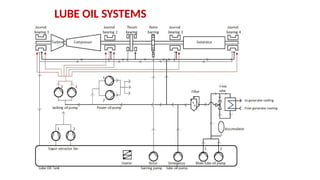
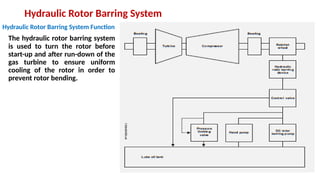
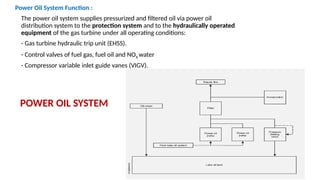
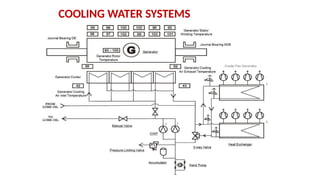
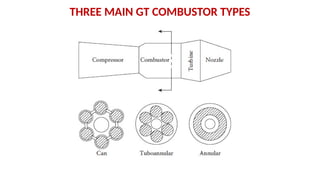
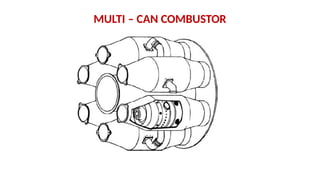
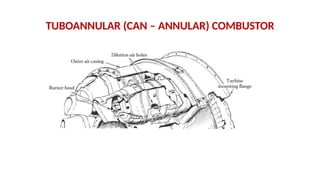
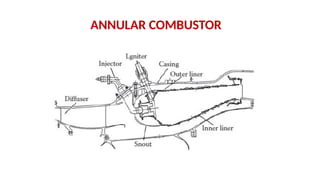
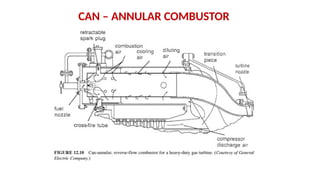
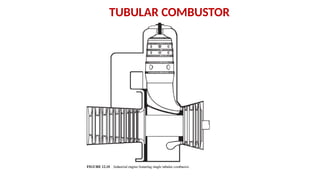
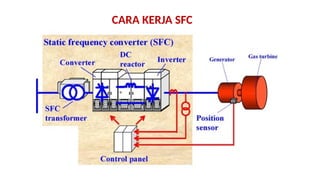
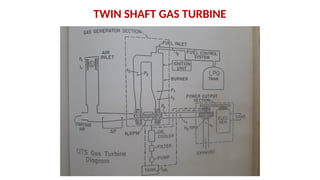
The document describes the components and operational philosophy of the MS9001E gas turbine used in a combined cycle power plant. It details the turbine's key parts such as the axial compressor, combustor, and turbine rotor, along with their functions in the Brayton cycle. Additionally, it outlines the ancillary systems supporting gas turbine operations, including air intake, lubrication, cooling, and the starting methods utilizing a static frequency converter.