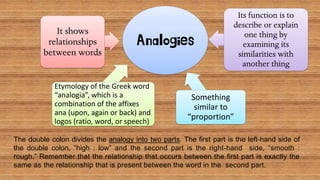
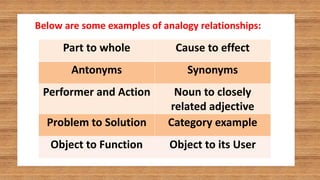
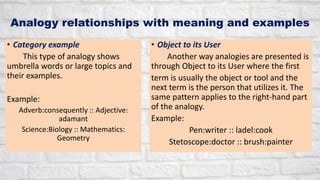
This document contains an English class discussion on analogies. It defines analogy and provides examples of different types of analogy relationships including part to whole, antonyms, action, problem to solution, object to function, cause to effect, synonyms, noun to adjective, category example, and object to user. Students are assigned activities in their modules to practice identifying and explaining different analogy relationships.