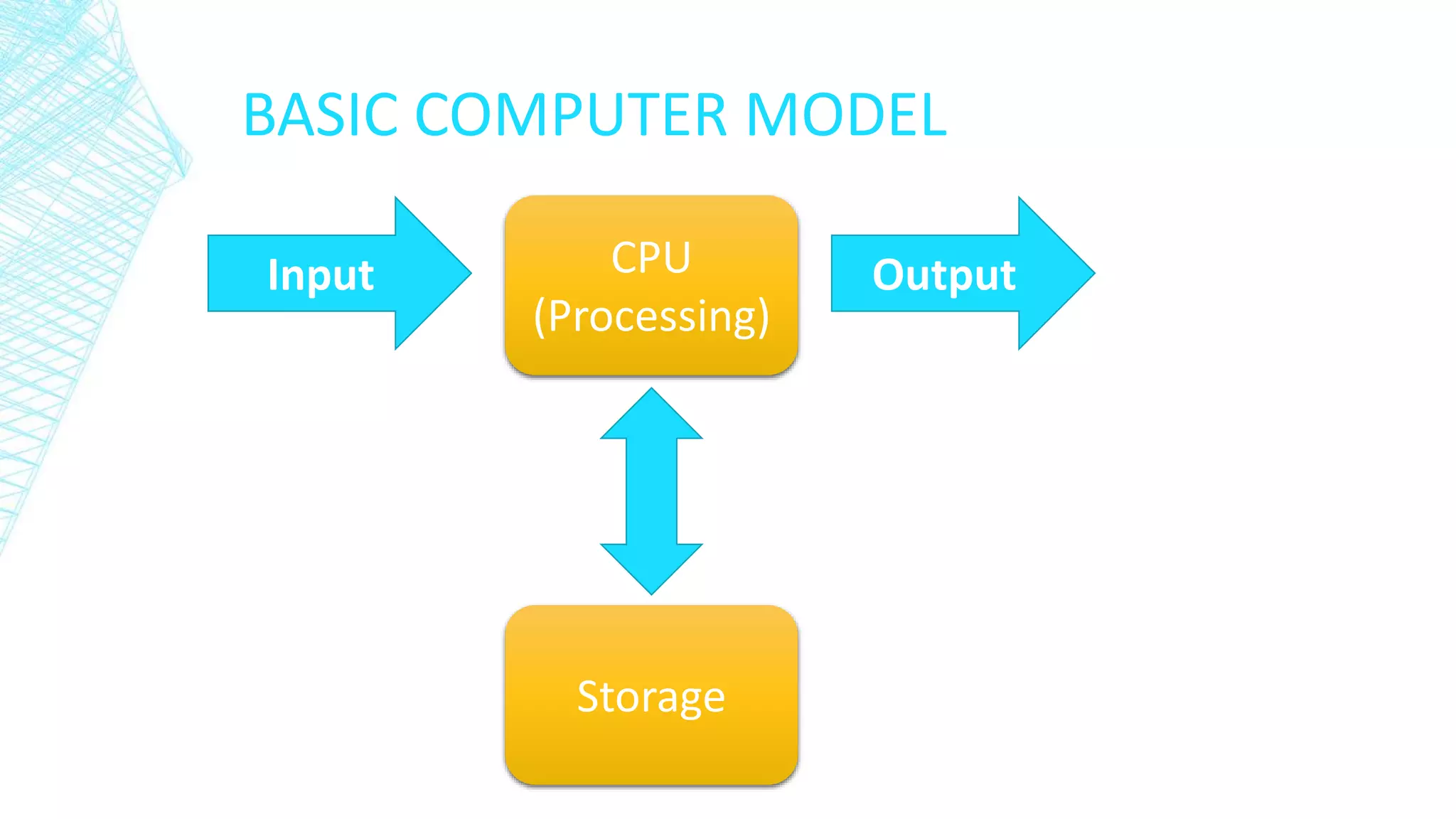
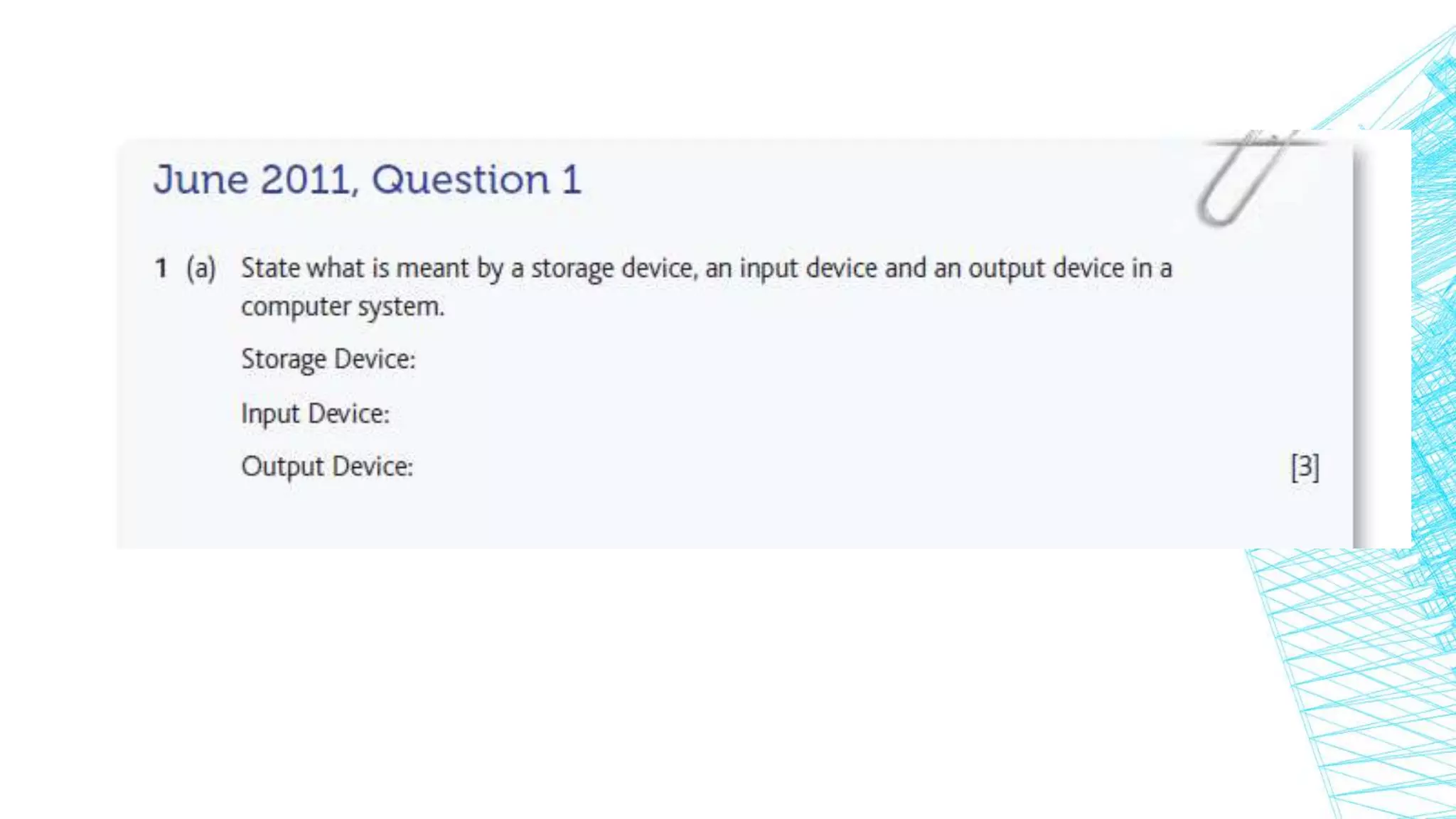
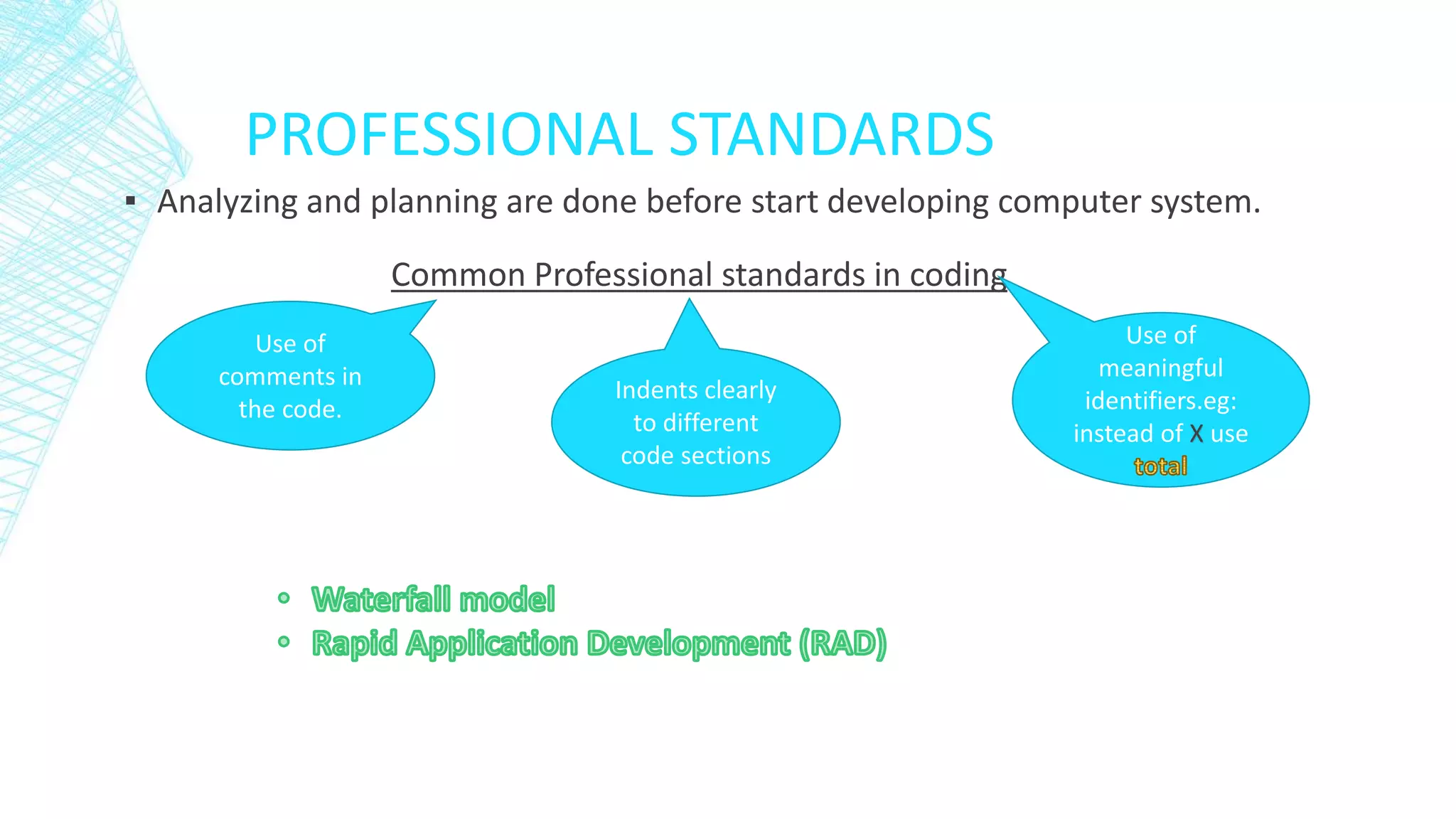
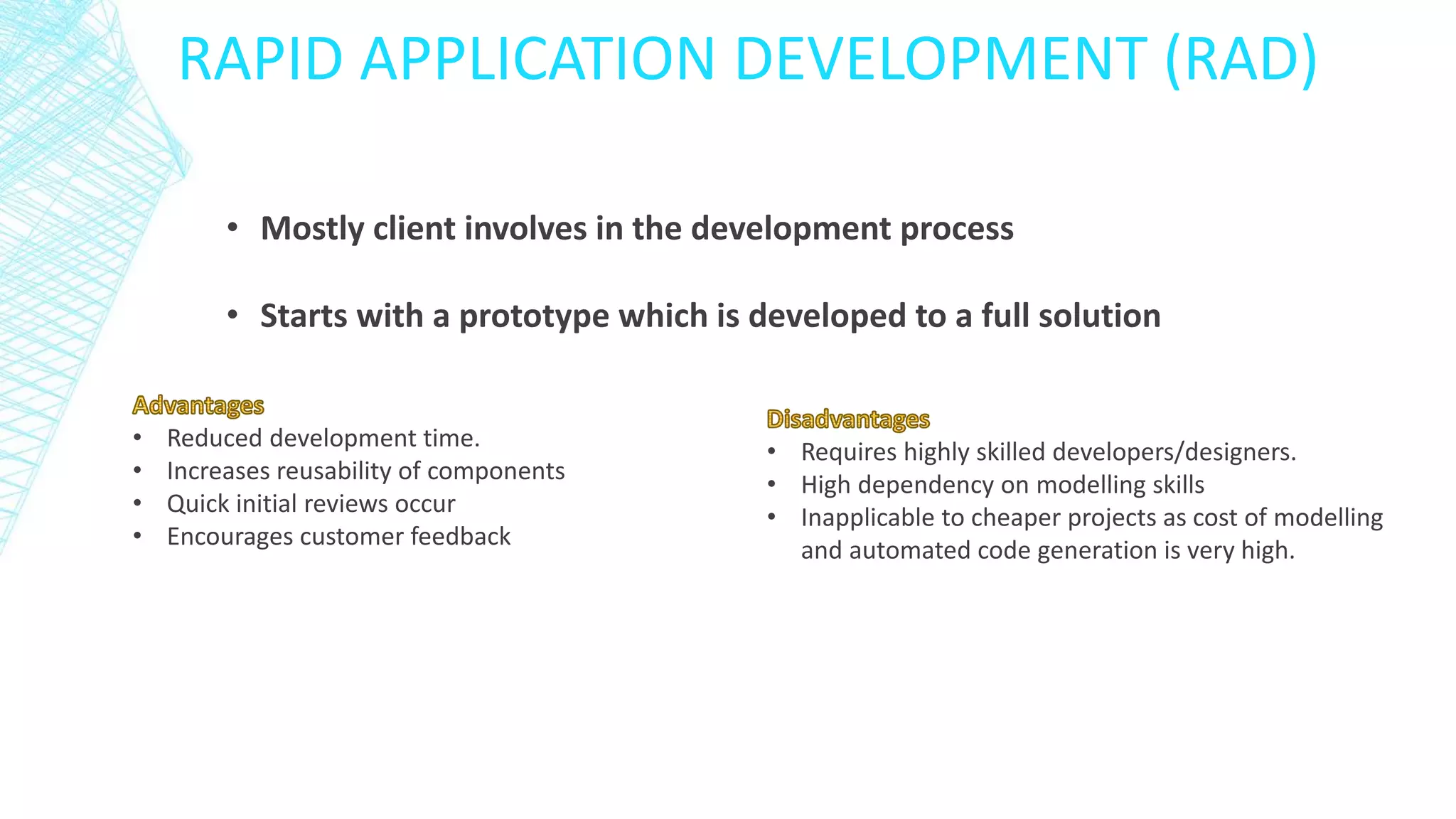
A computer system consists of hardware, software, and people working together to perform tasks. The basic computer model includes input, output, a central processing unit (CPU) for processing, and storage. Computers are found everywhere and their reliability is measured by factors like uptime and mean time between failures. Systems are protected against failure through hardware redundancy, disaster recovery methods like RAID systems, and following professional coding standards for comments, indentation, and meaningful identifiers. Development methods like waterfall and rapid application development (RAD) were discussed. Standards are needed for legal, environmental, and other considerations.