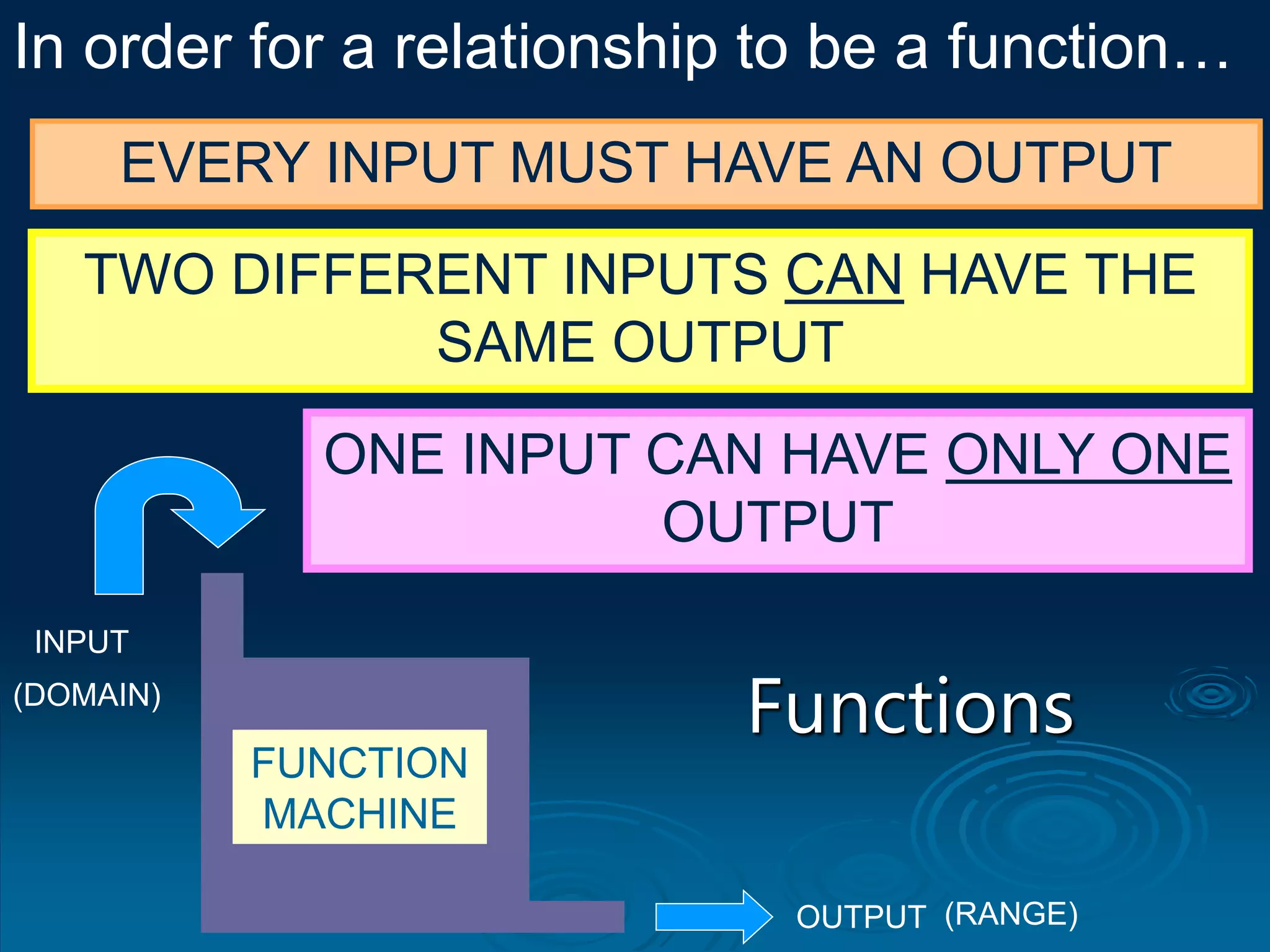
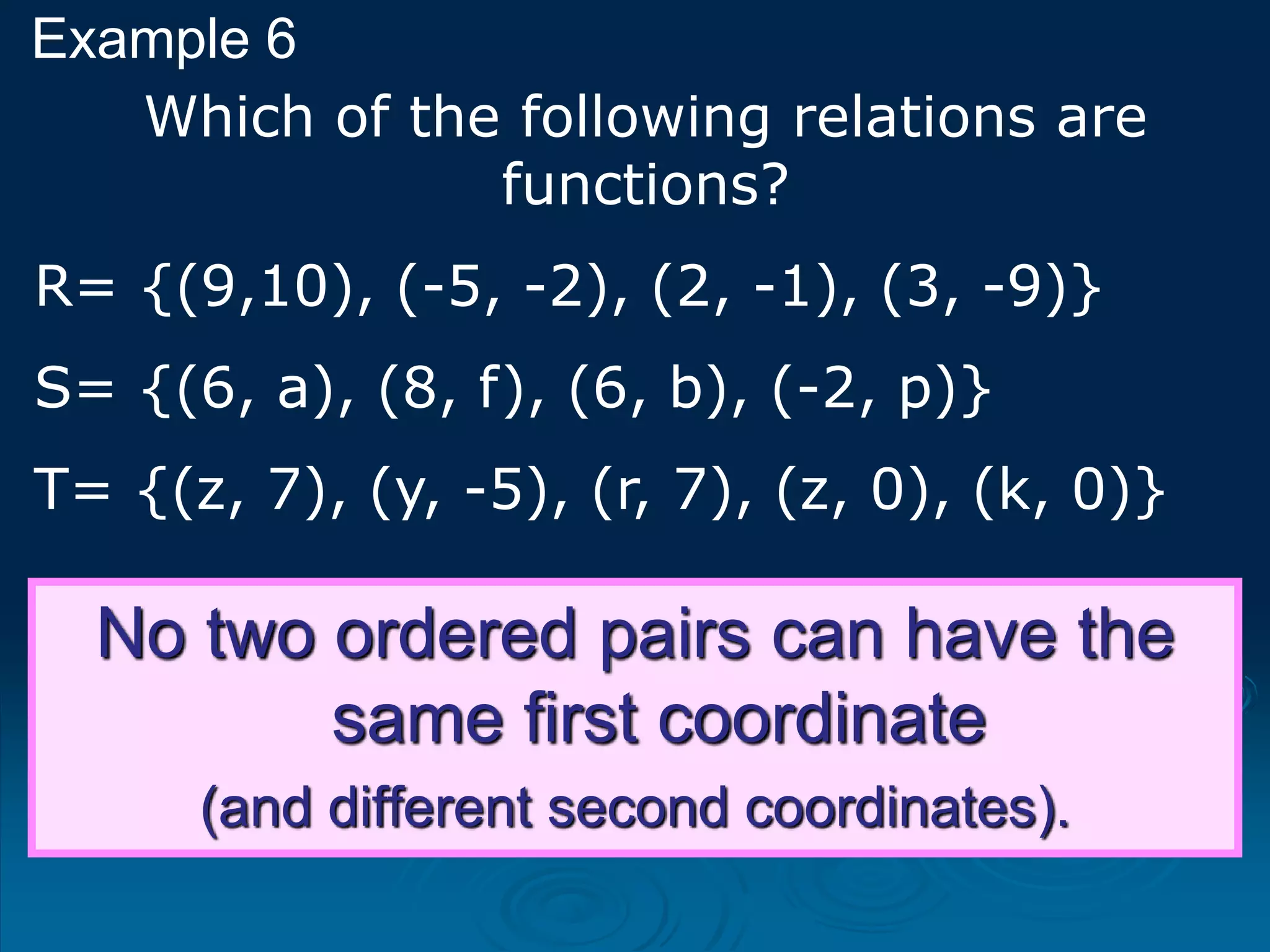
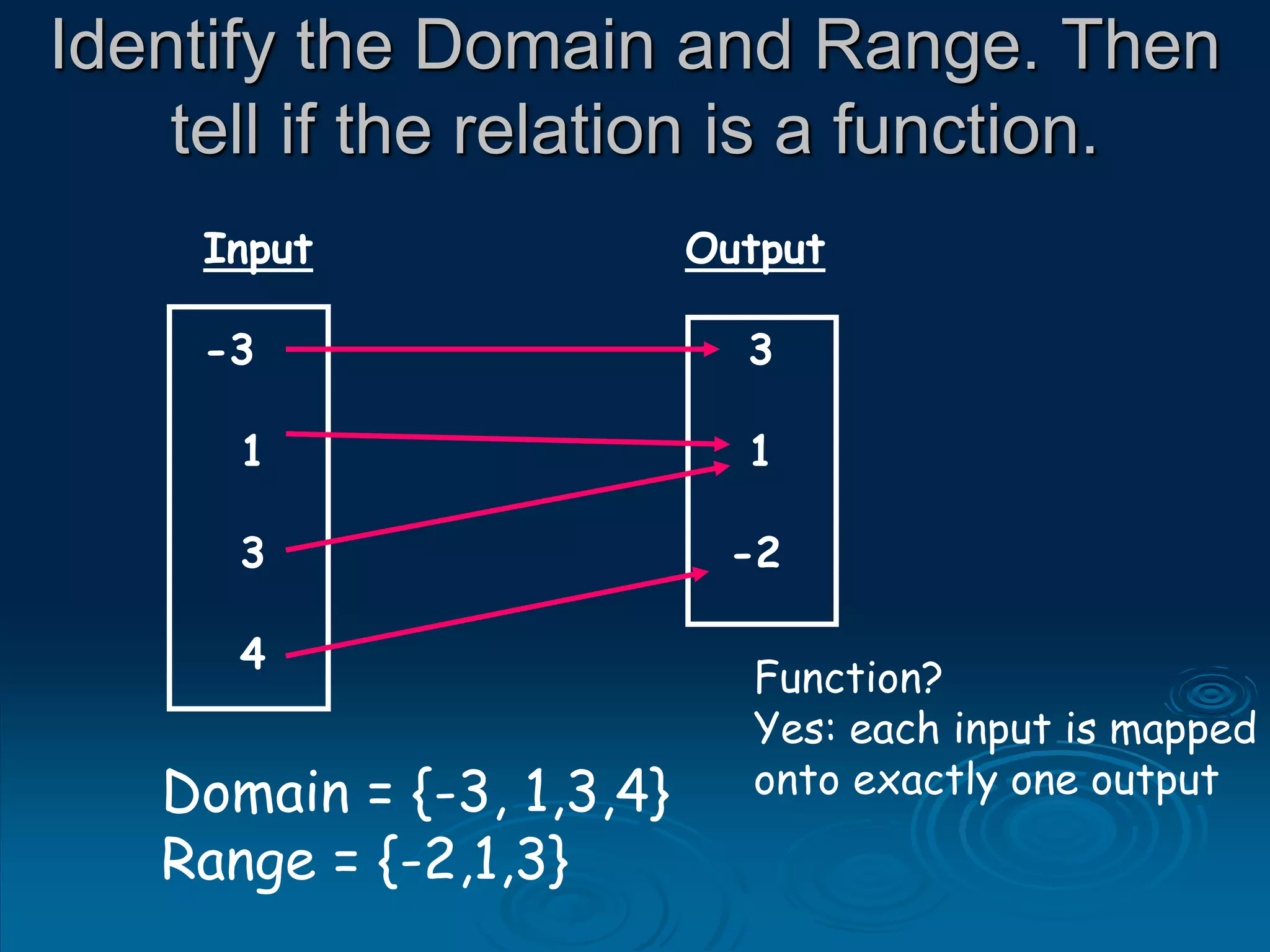
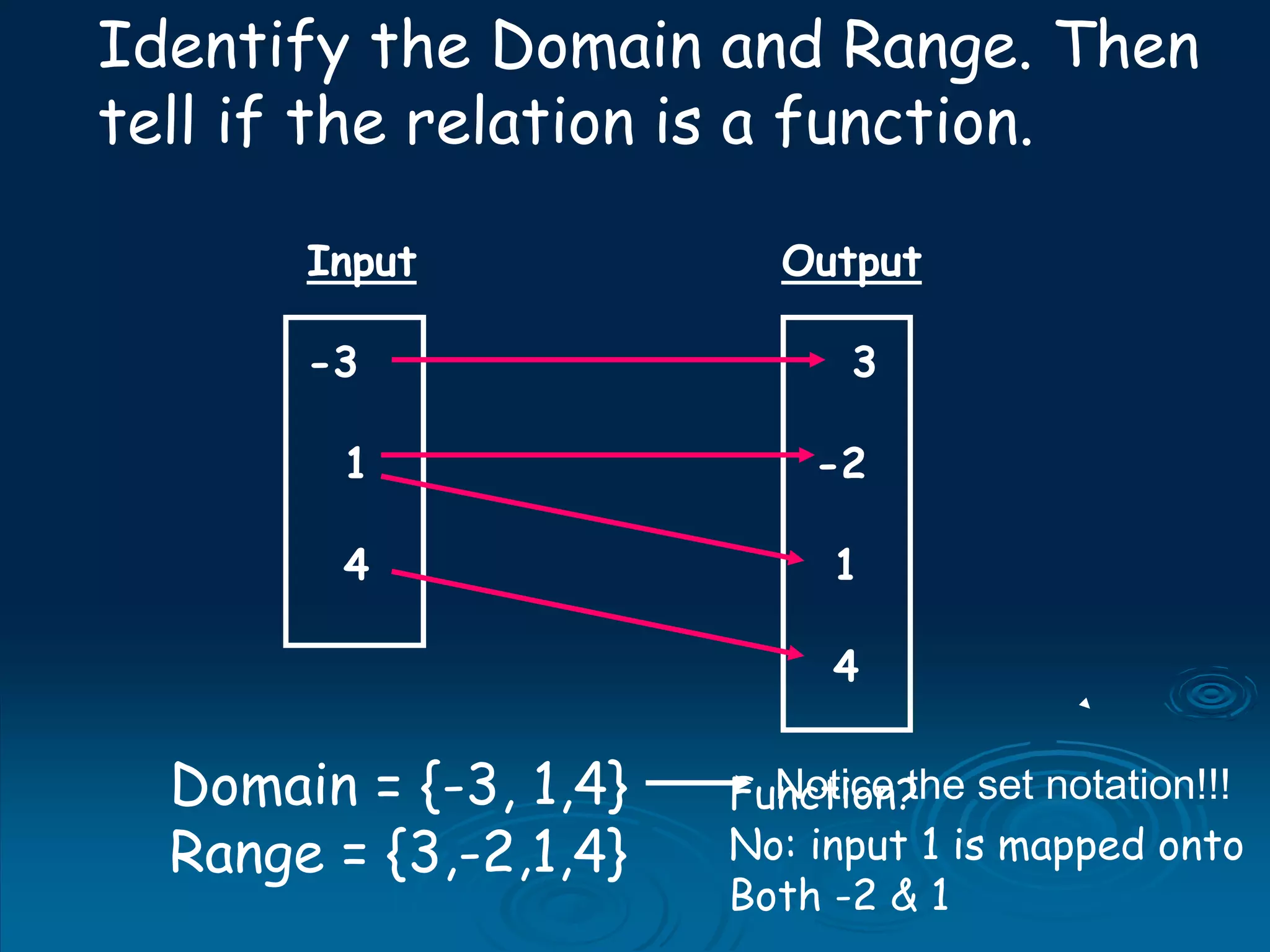
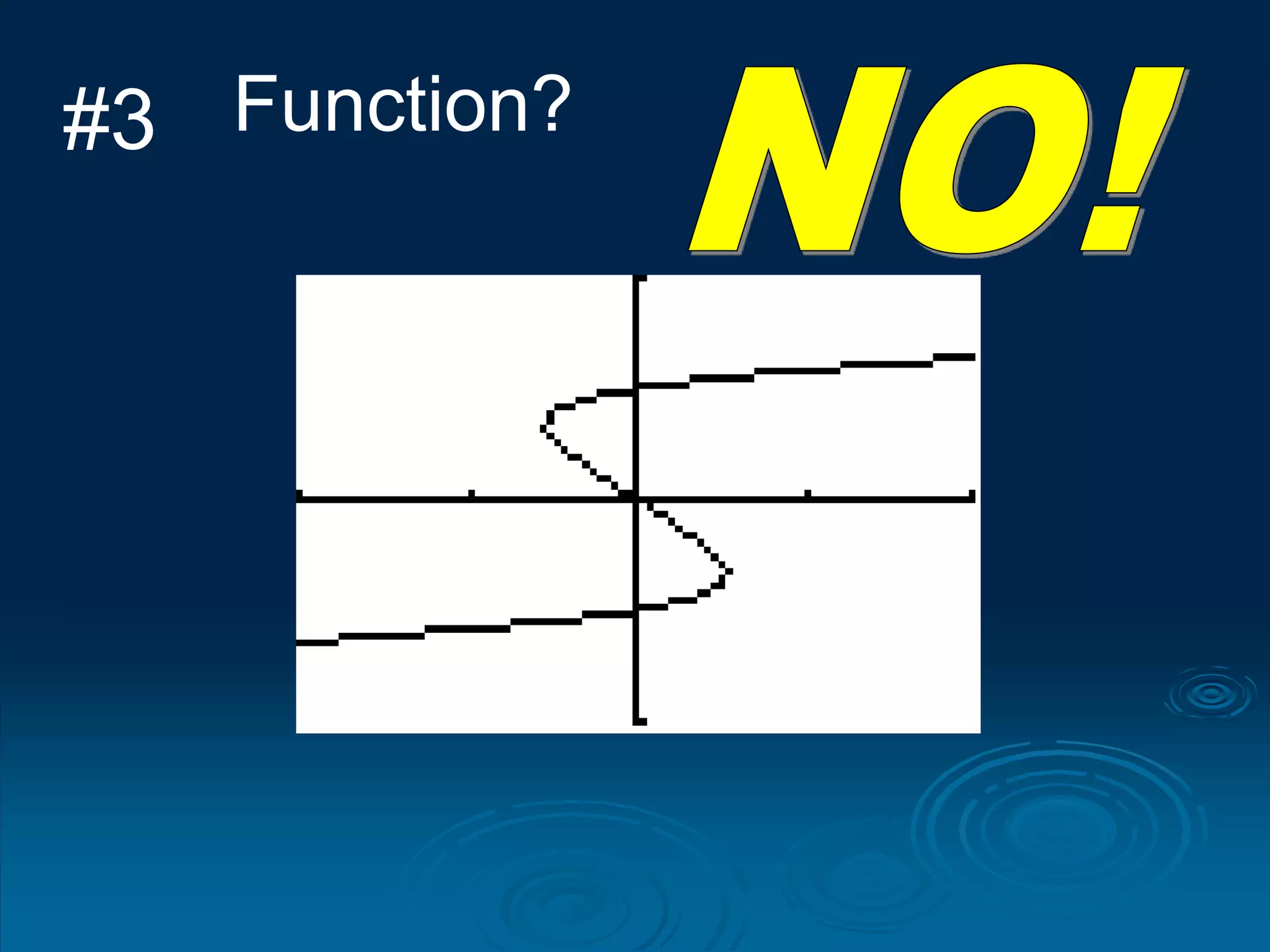
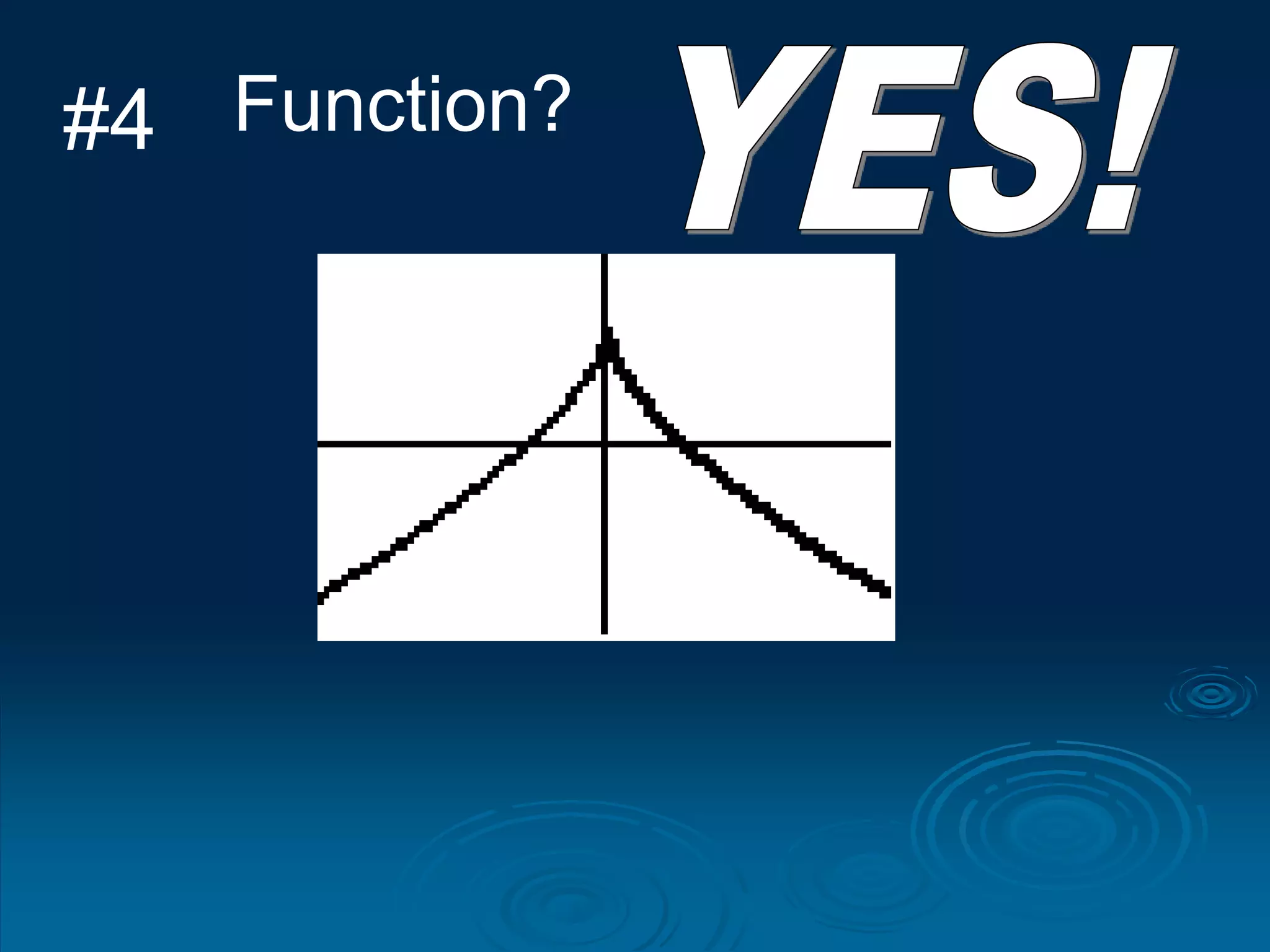
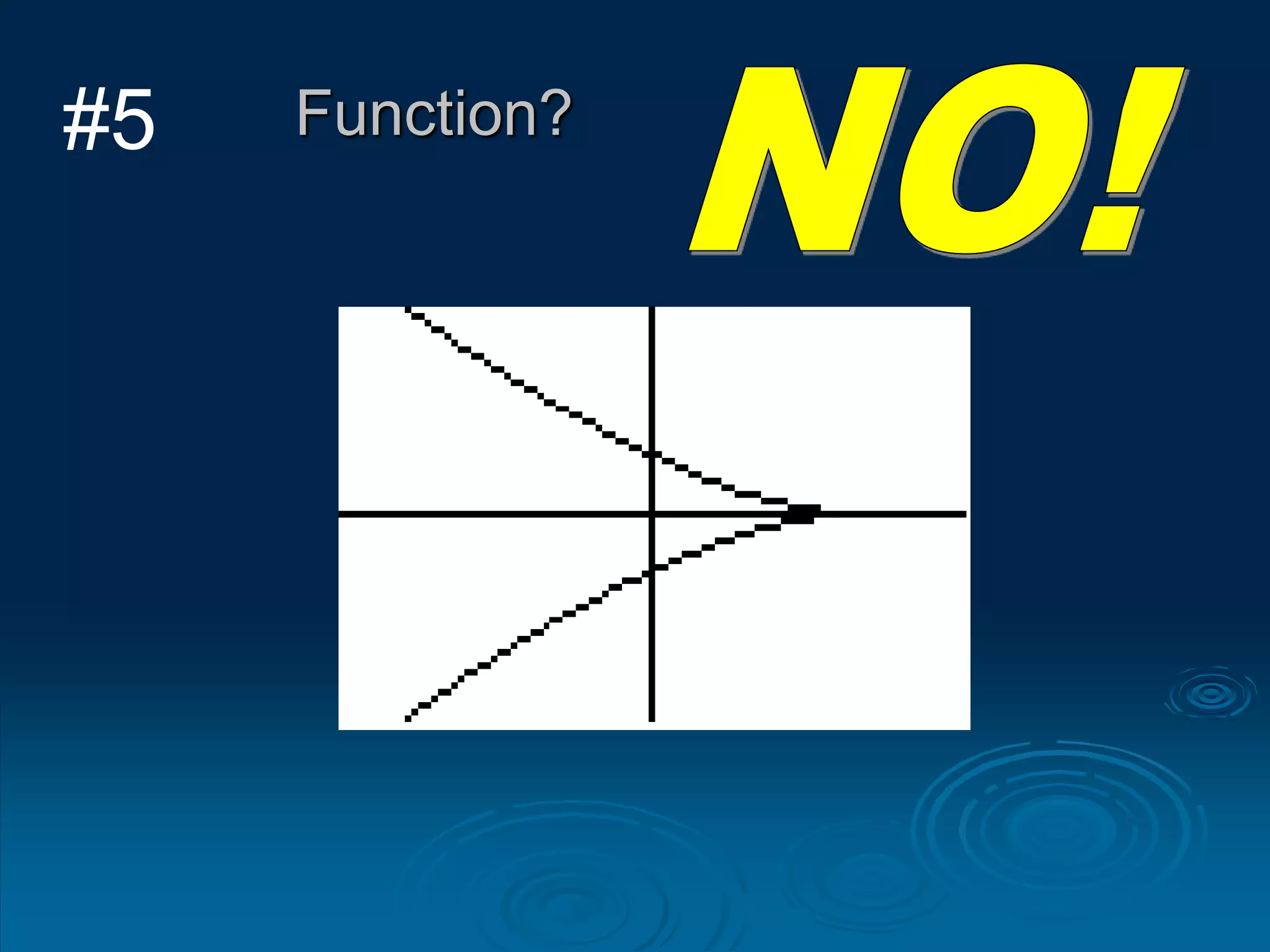
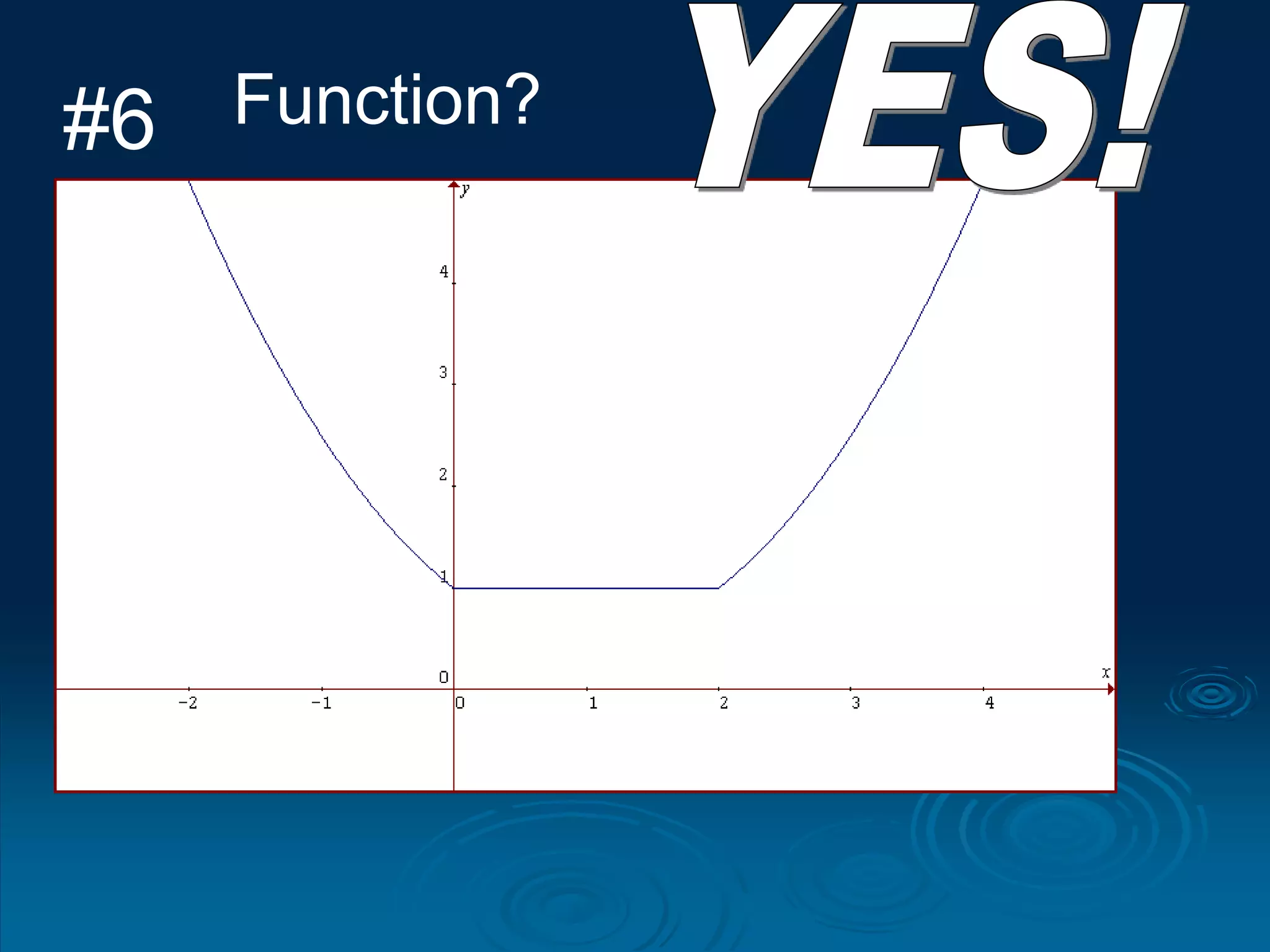
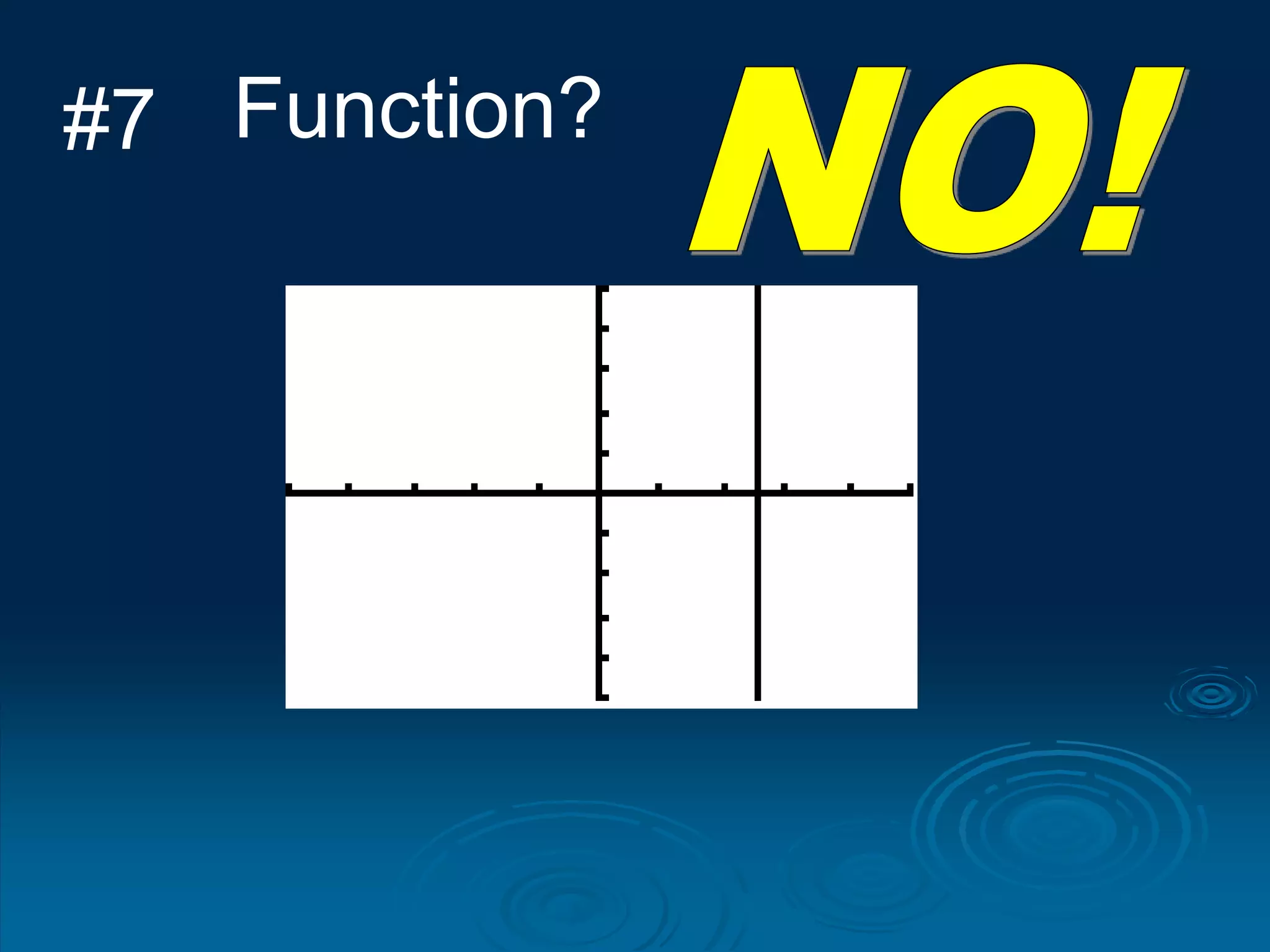
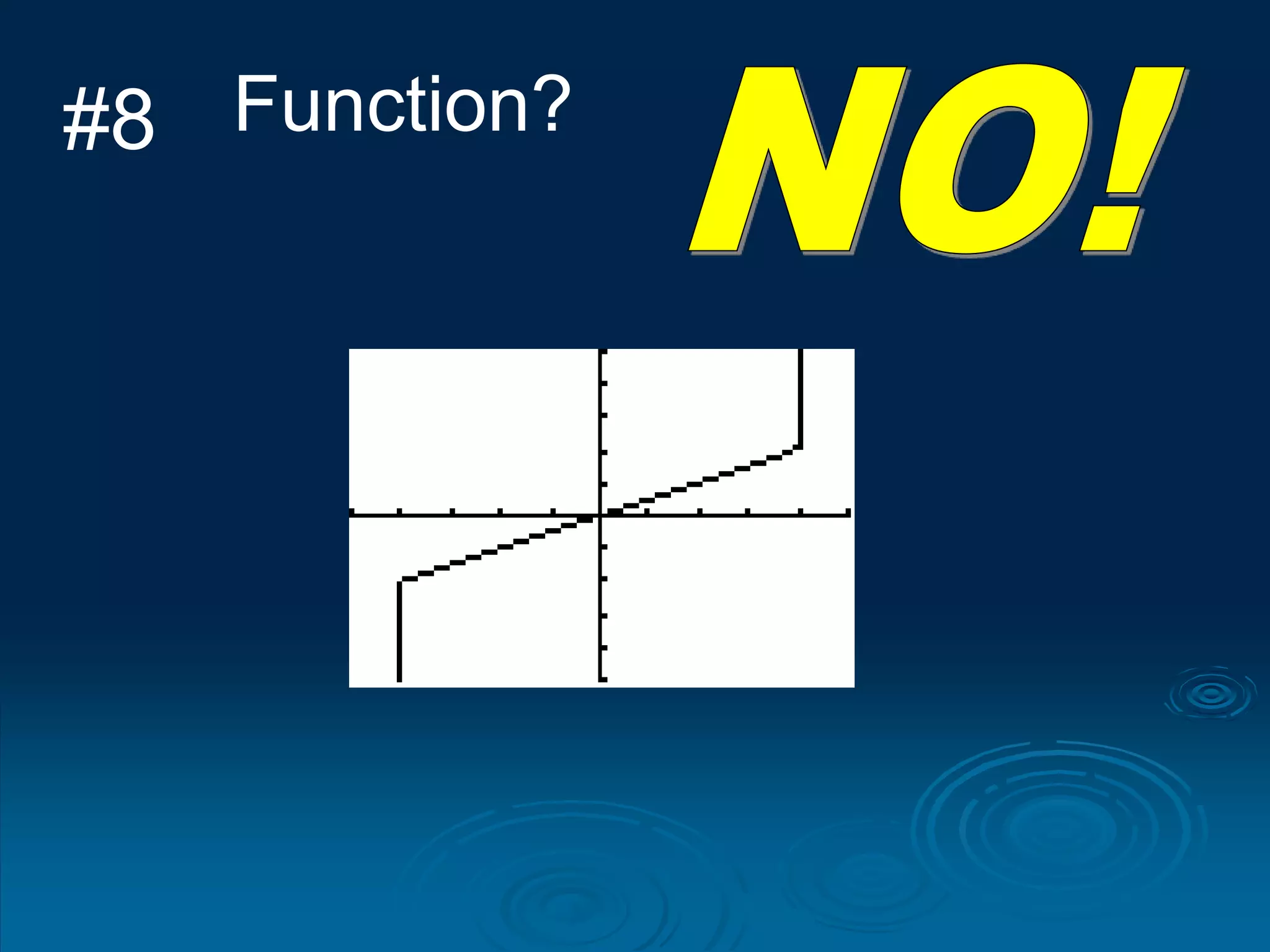
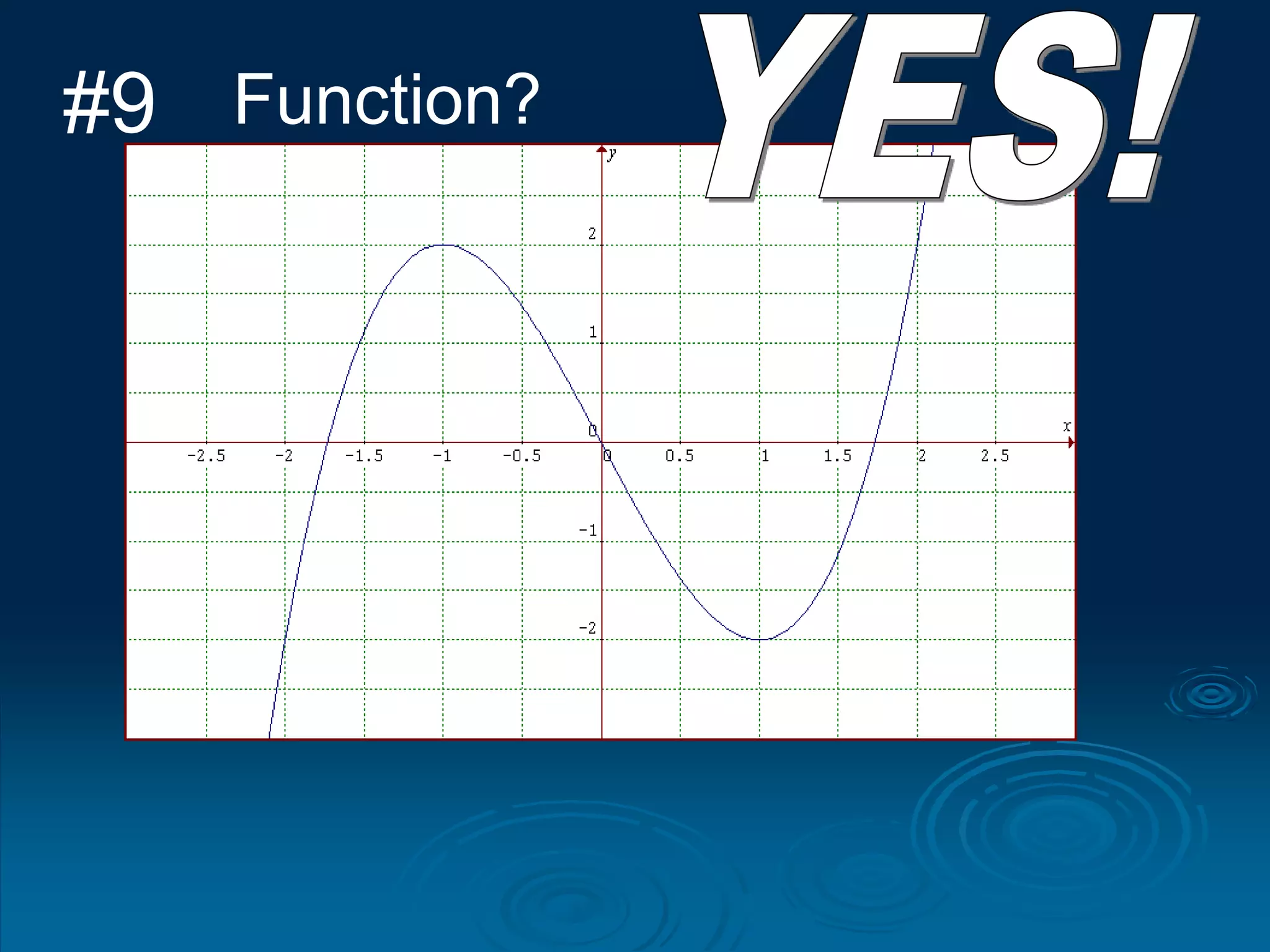
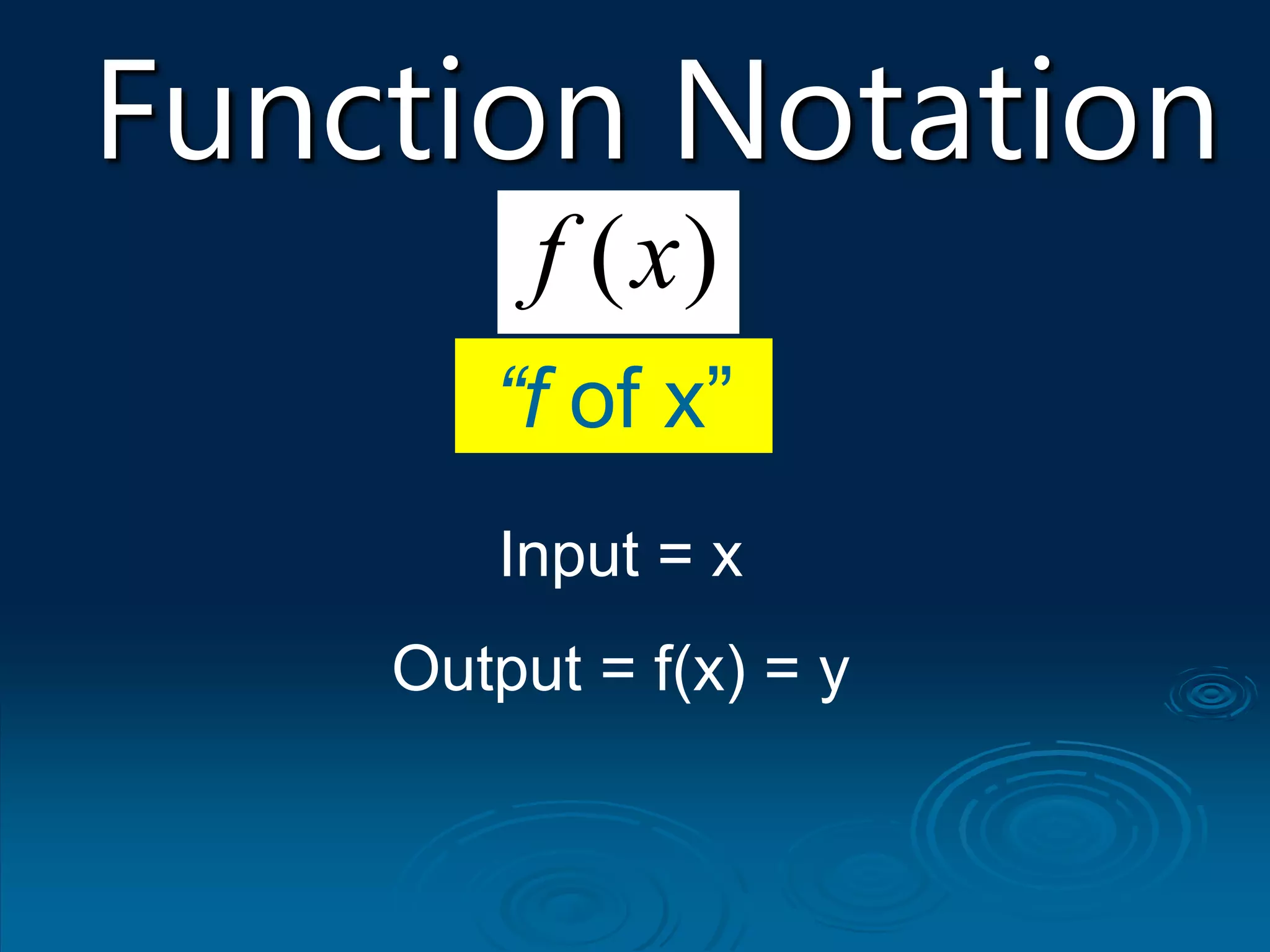
1. A function is a relation where each input is mapped to exactly one output. It is not a function if one input has more than one output.
2. For a relation to be a function, every input must have an output and two different inputs cannot have the same output. One input can only have one output.
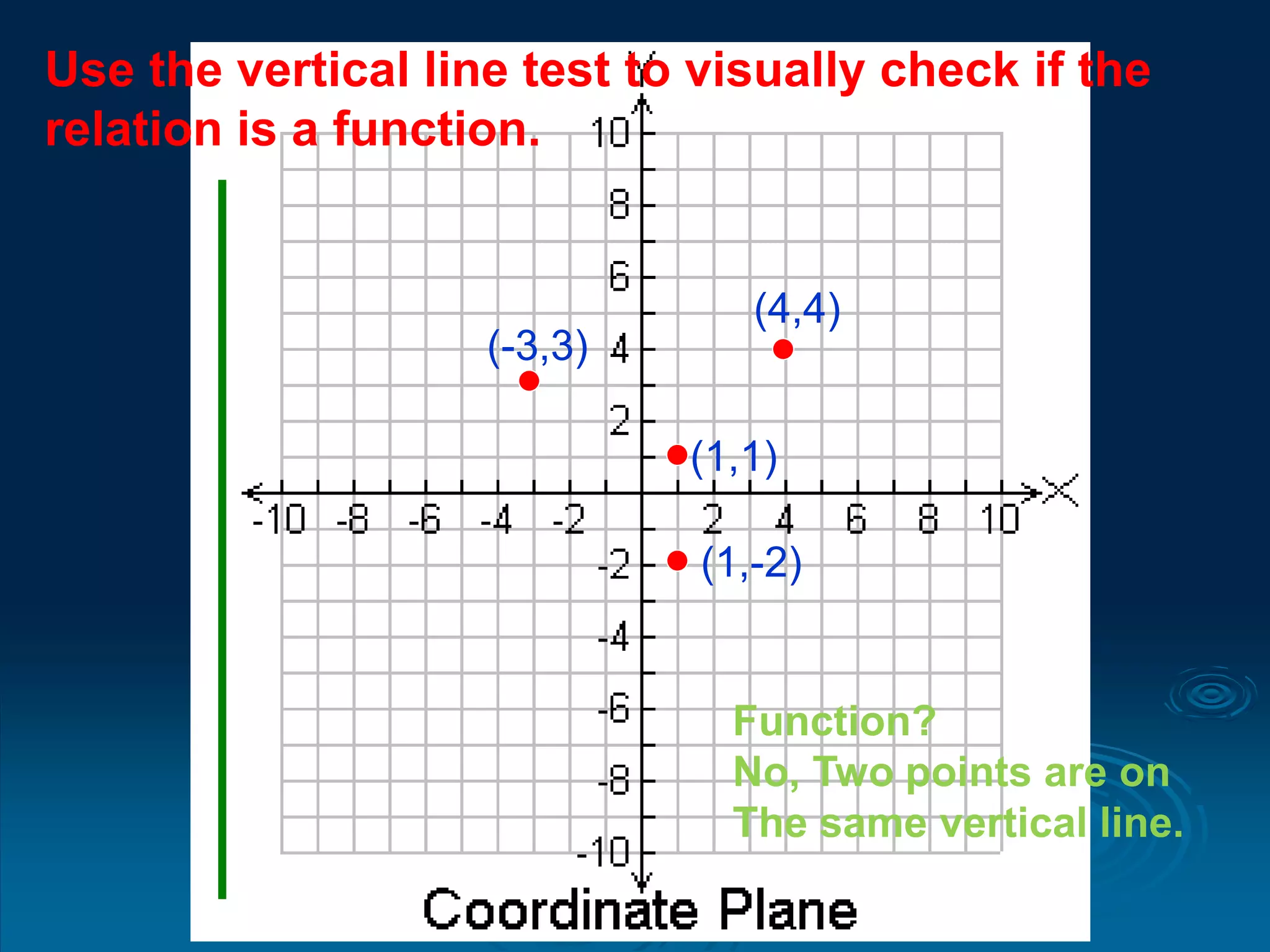
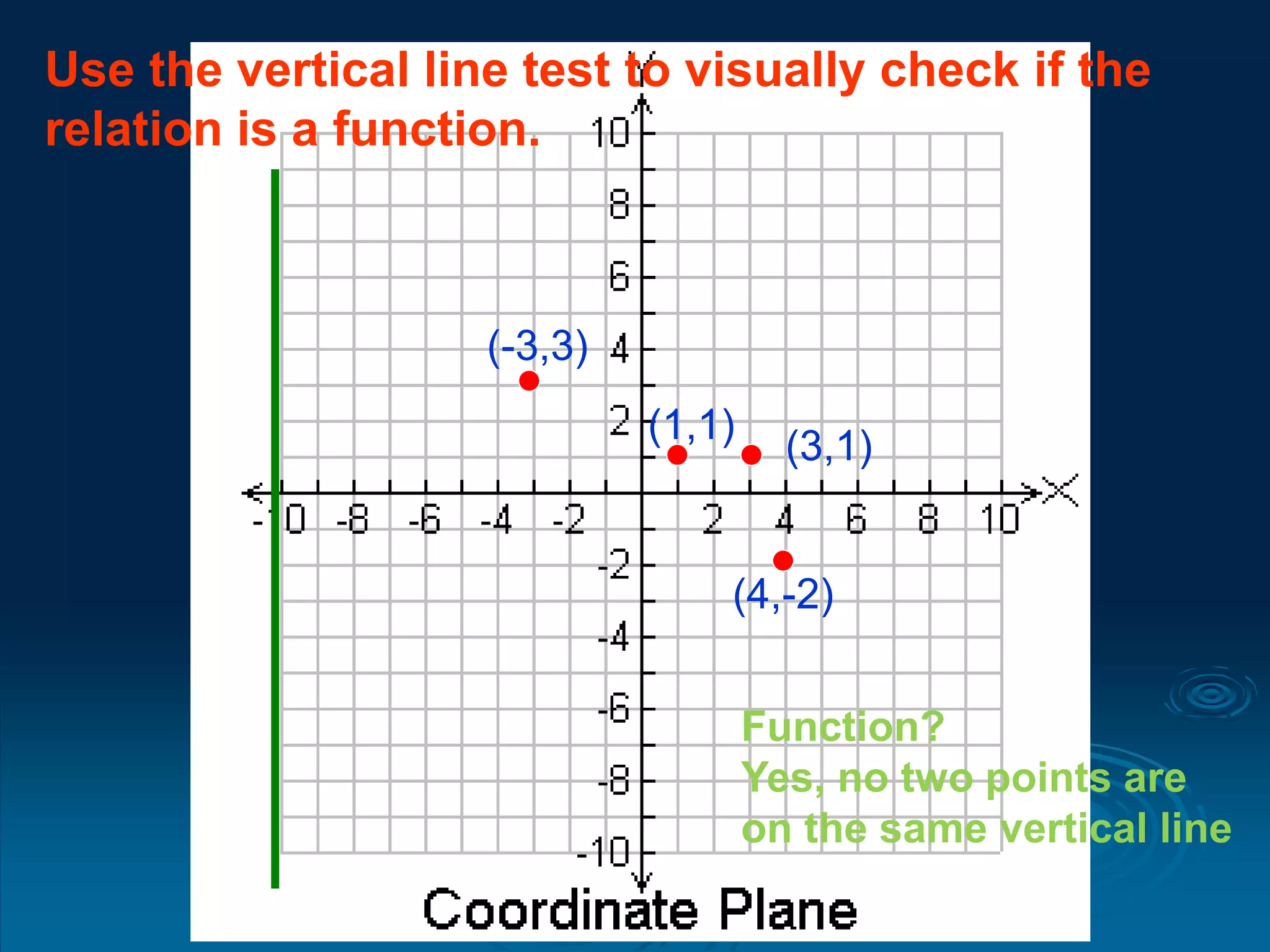
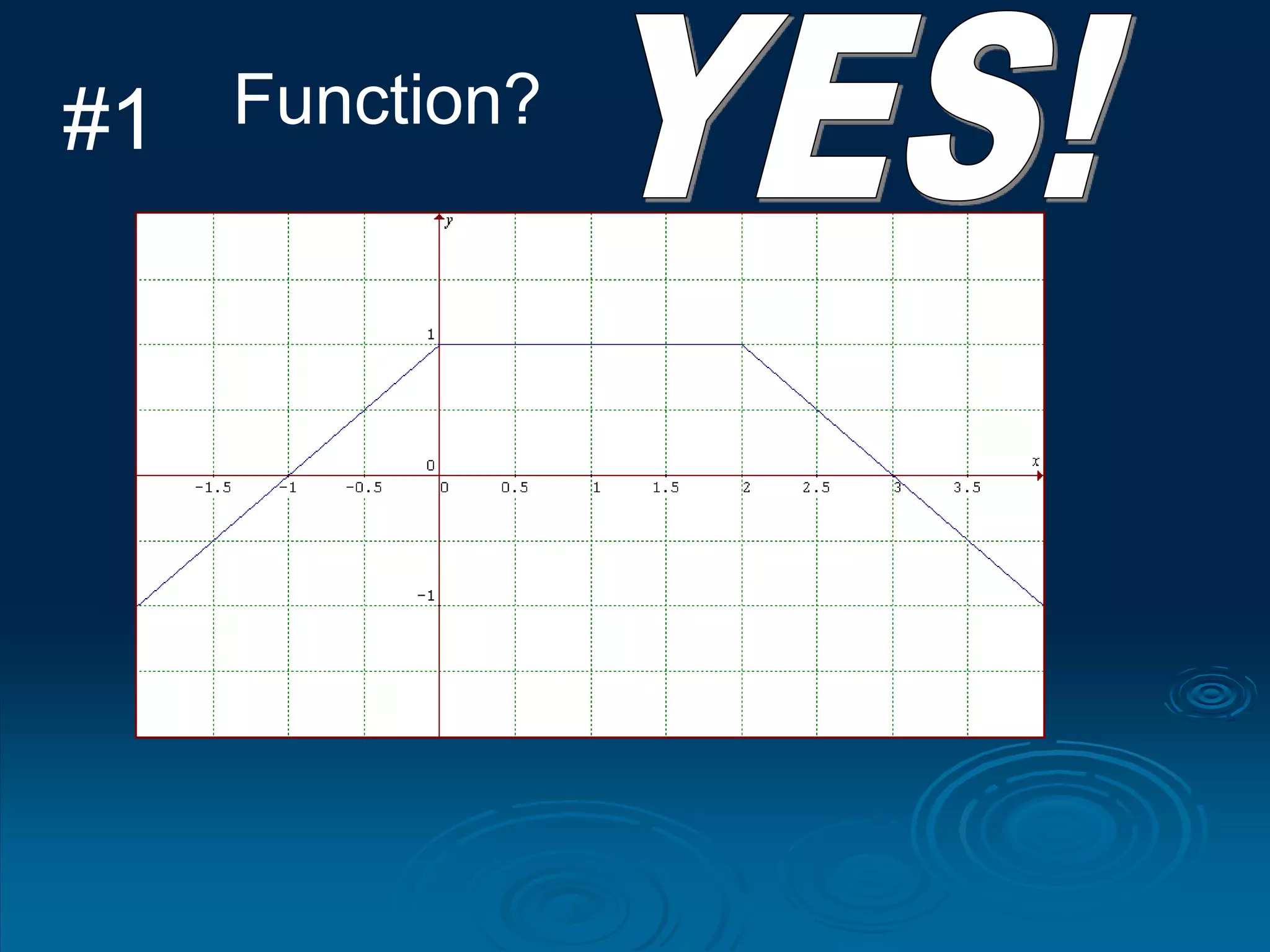
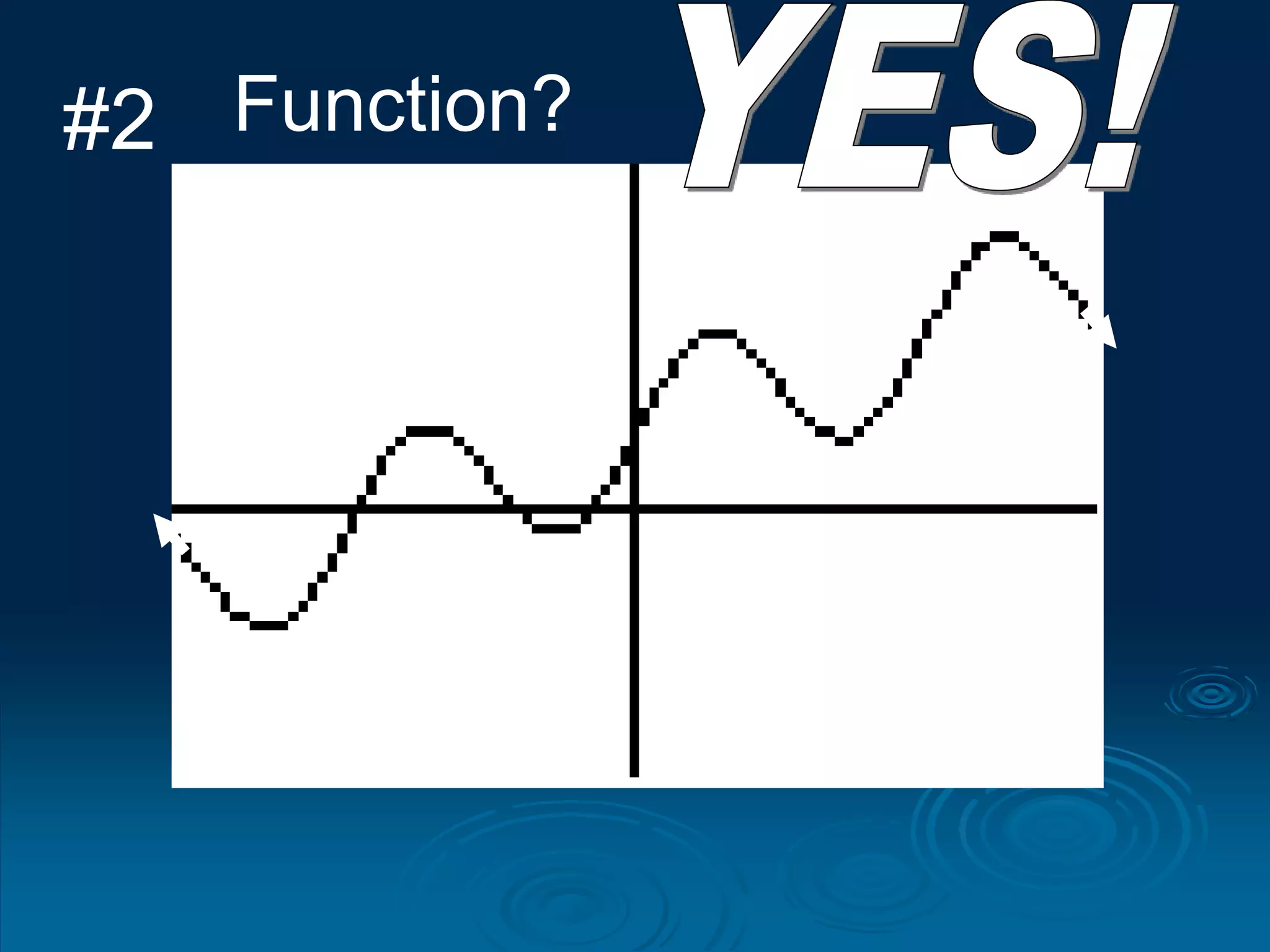
3. The vertical line test can be used to visually check if a relation is a function - if any vertical line intersects the graph at more than one point, it is not a function.