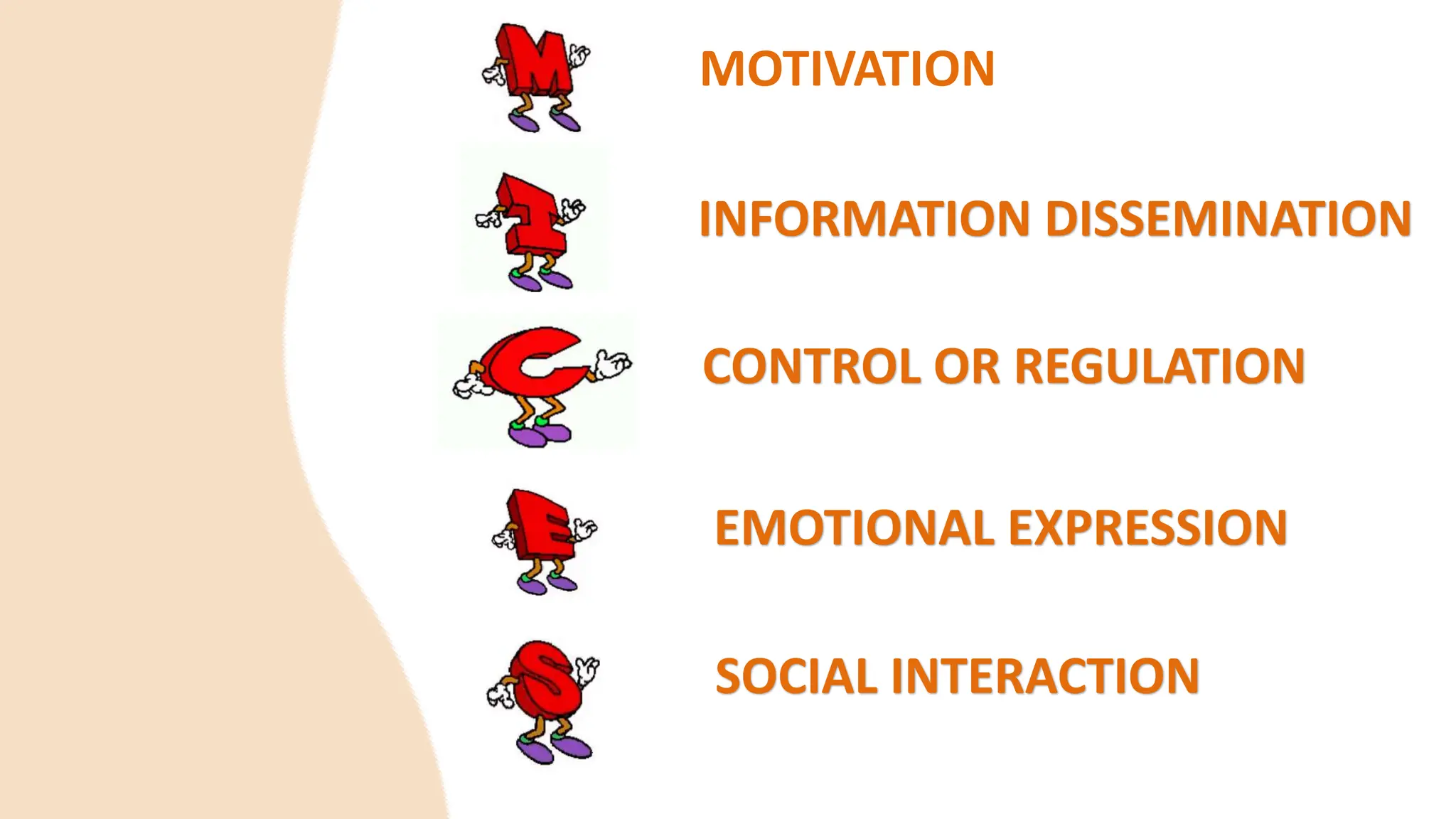
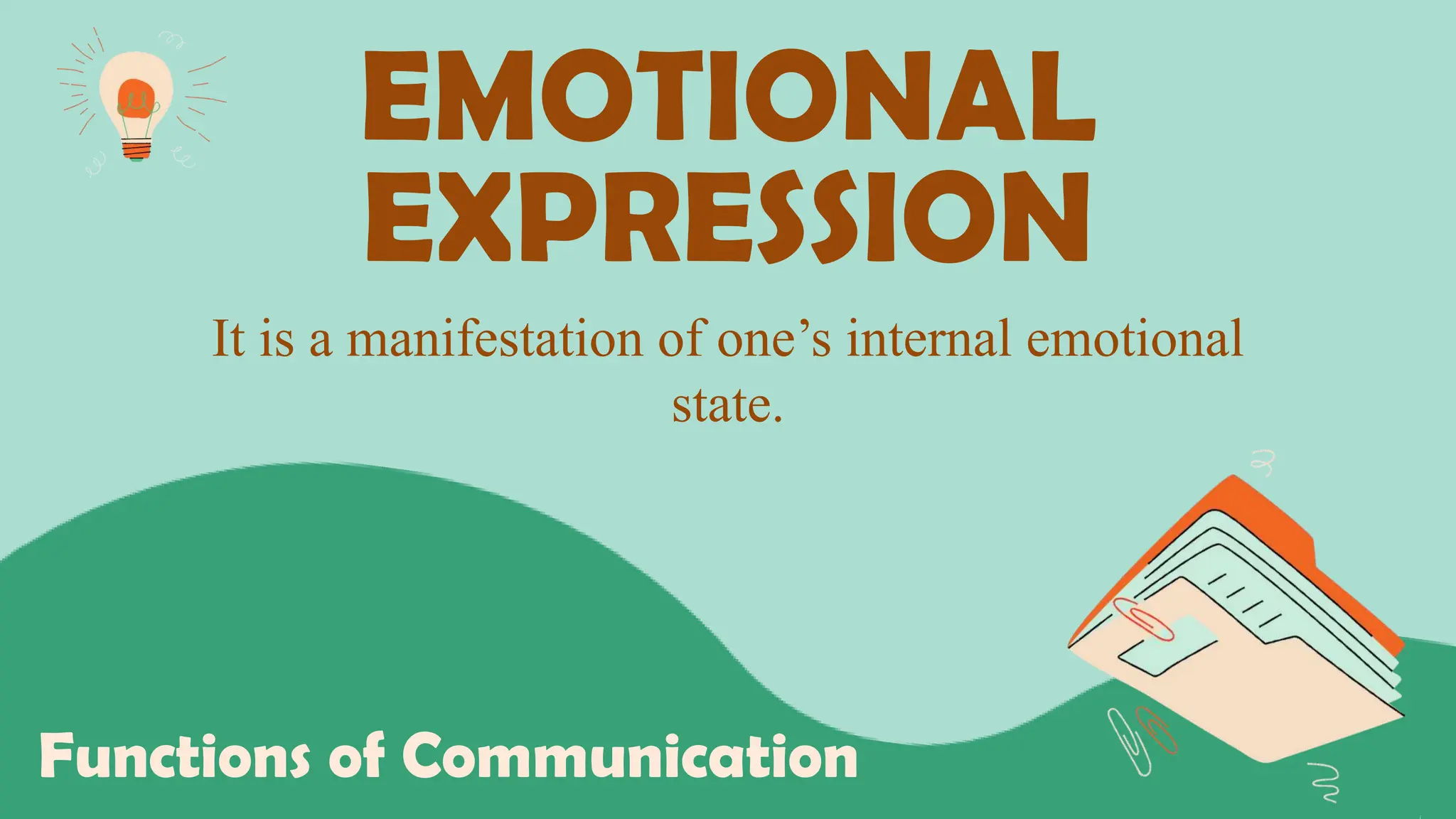
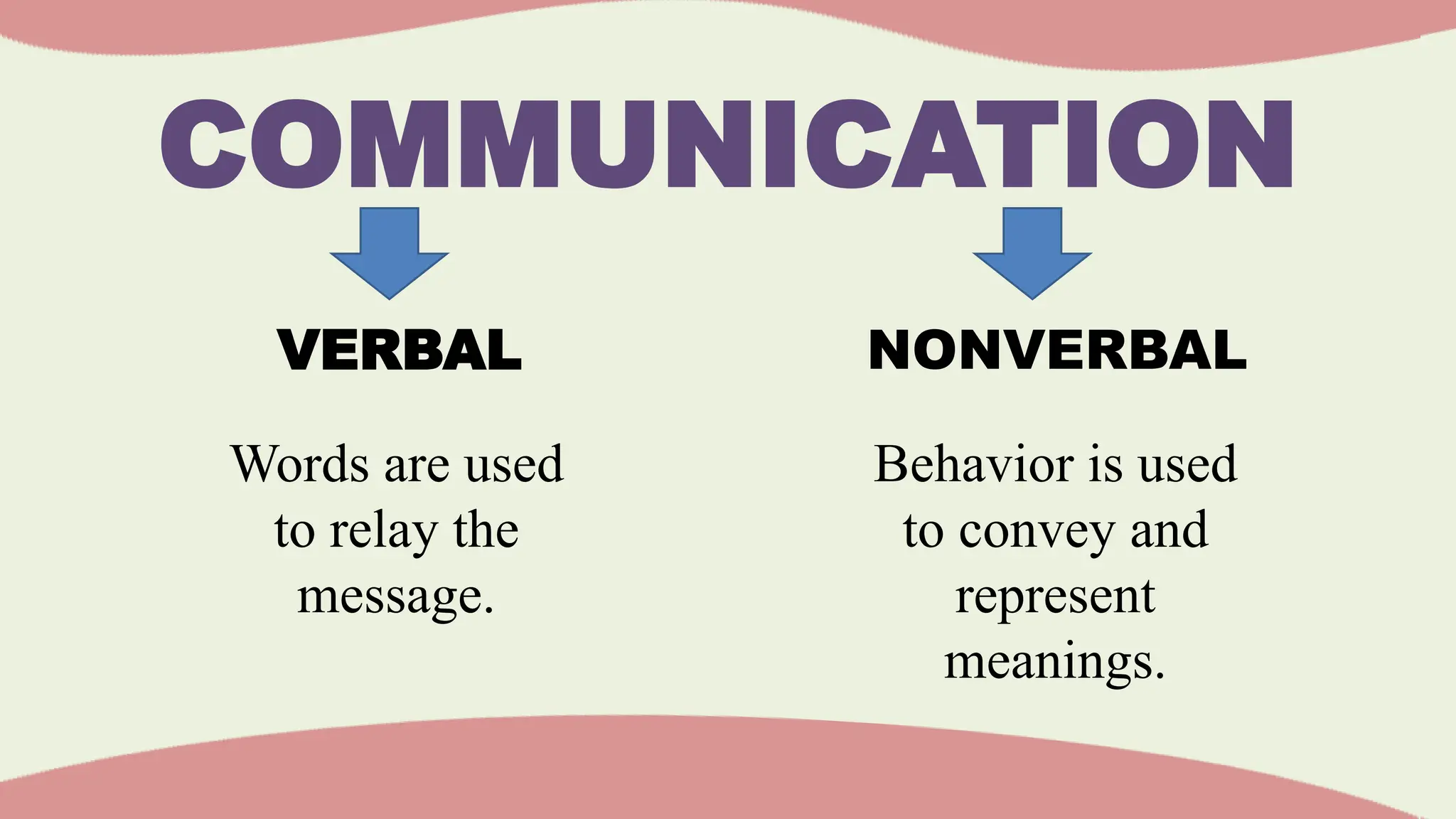
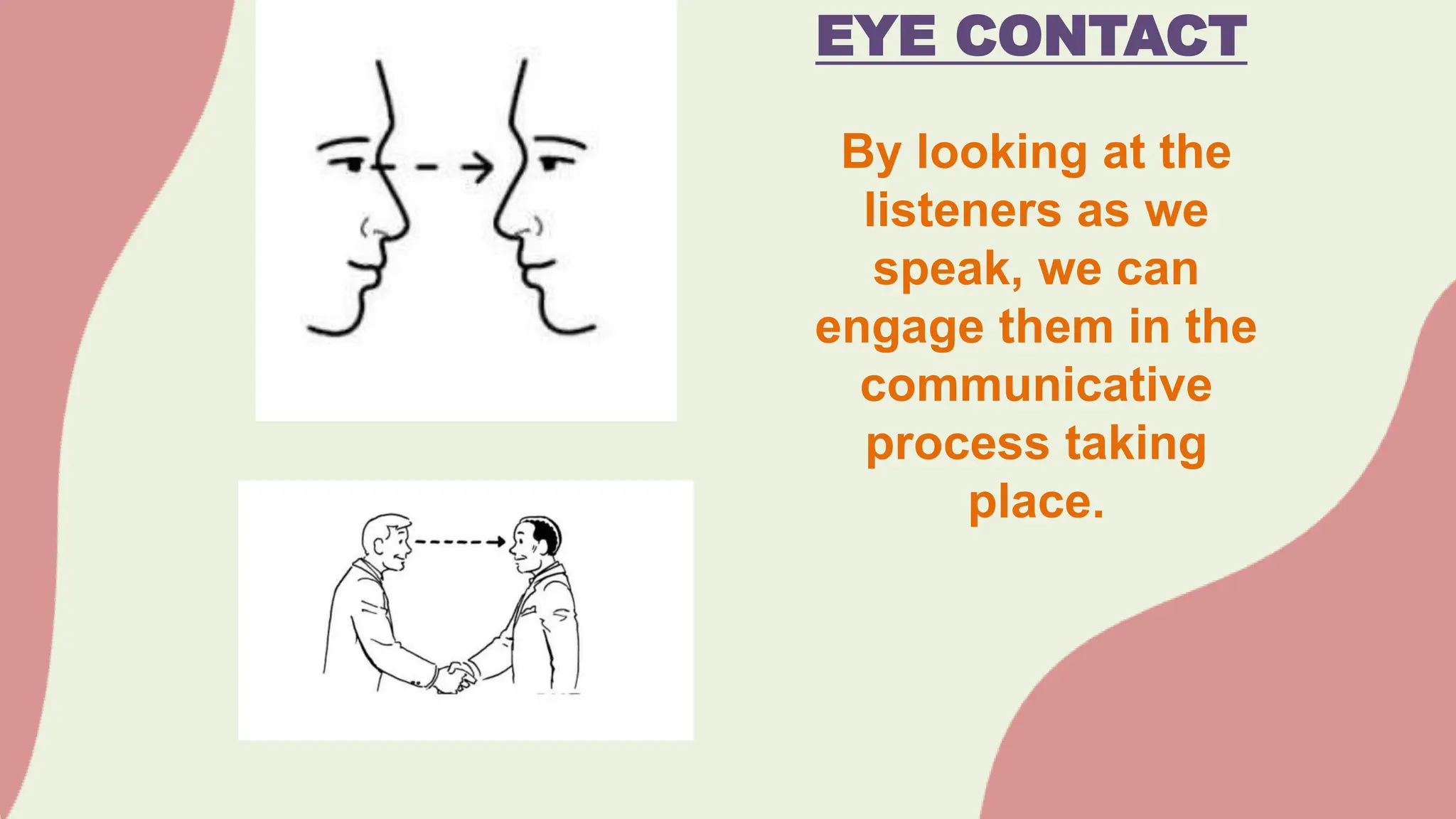
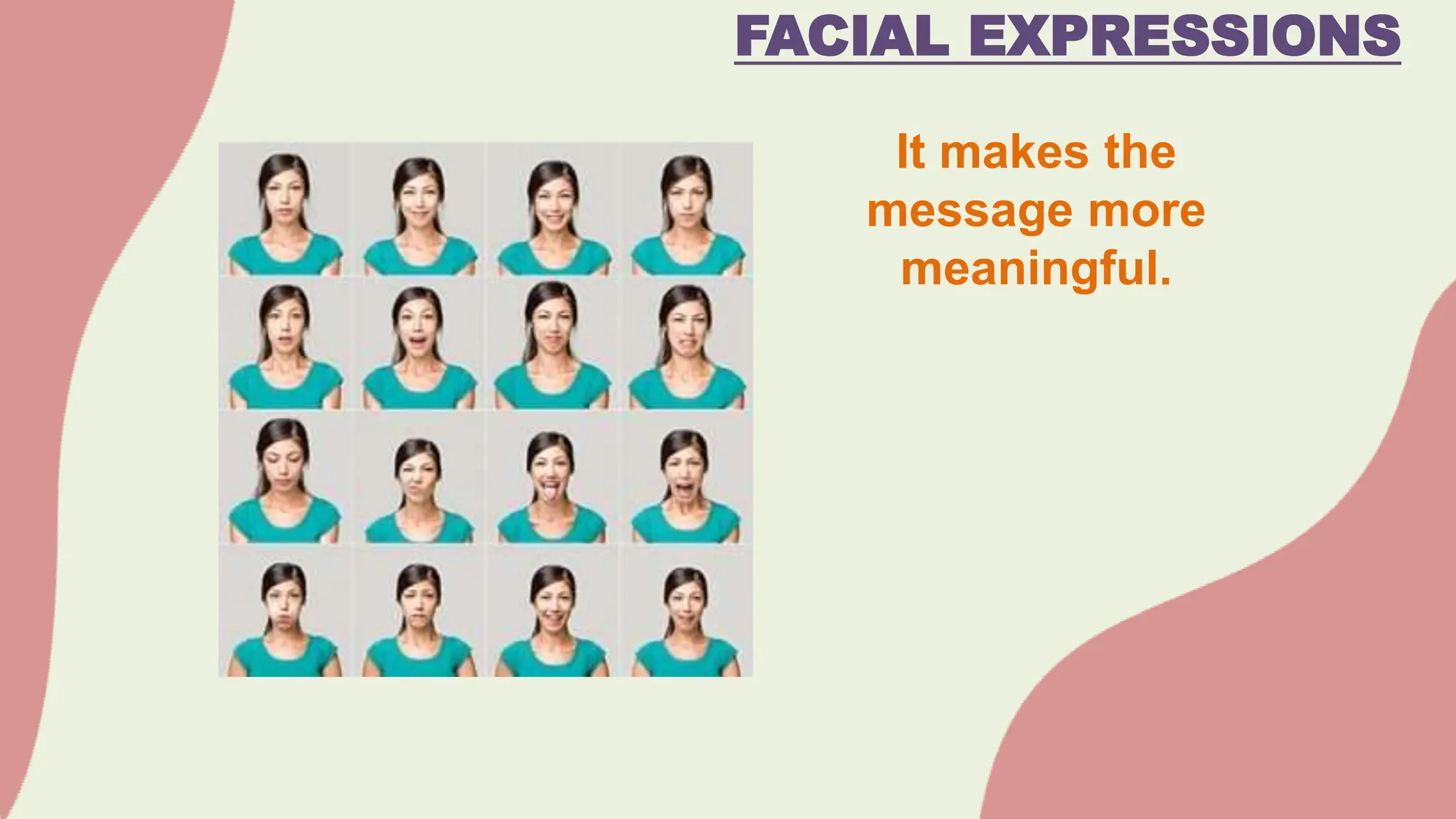
The document discusses various barriers to effective oral communication and the functions of communication. It identifies 6 main barriers: language barriers which occur when technical terms are misunderstood, physical barriers caused by external noises or equipment issues, psychological barriers due to distraction or preoccupation, physiological barriers from issues like dyslexia that interfere with speech or hearing, cultural barriers from lack of shared understanding across cultures, and semantic noise which distorts the message sent. It also outlines 5 main functions of communication: motivation, information dissemination, control/regulation, emotional expression, and social interaction. The document provides further explanation of verbal and nonverbal communication aspects.