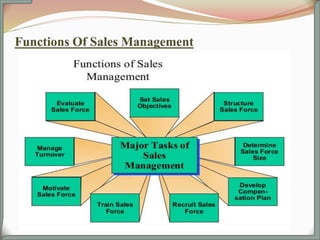
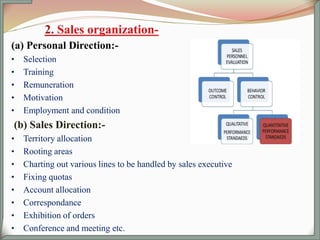
The document outlines the key functions and responsibilities of sales management. It discusses establishing sales objectives and strategies, structuring the sales force, determining size and managing the sales team. It also covers setting sales objectives and quotas, formulating sales plans, budgets and forecasts. Some of the general functions listed include preparing sales plans, recruiting and training salespeople, defining sales territories, quotas and compensation. It also discusses coordinating with marketing, sales policies/pricing, promotion, distribution channels, product development and customer relationships. Finally, it classifies sales management based on sales programming, organization, products and markets.