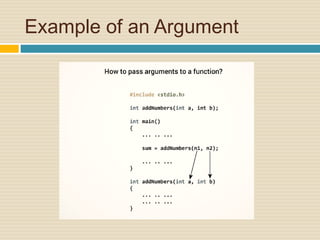
The document presents an overview of functions in C programming, including function definition, declaration, arguments, and return values. It emphasizes the importance of functions for task execution and demonstrates how to declare and use functions with an example program that adds two numbers. Additionally, it mentions built-in functions from the C standard library to avoid code duplication.