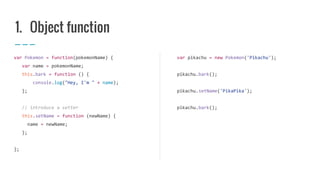
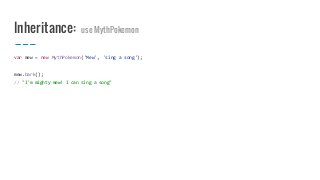
The document provides an introduction to Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) in JavaScript, explaining key concepts such as classes, properties, and methods through the example of a Pokémon class. It covers how to define a class, create instances, encapsulate properties, and implement inheritance. Various coding patterns are demonstrated, including the use of prototypes, object literals, and immediately invoked function expressions (IIFEs) to manage private data and behavior.