1. Free monads allow defining monadic interpreters for domain-specific languages (DSLs) by representing the DSL's abstract syntax tree as a recursive data type and making it an instance of the Functor typeclass.
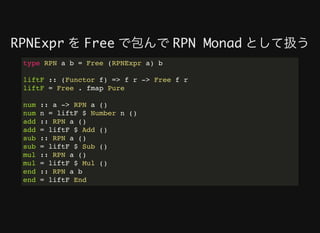
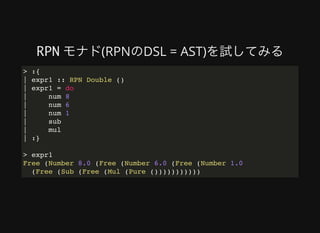
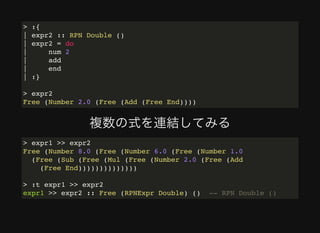
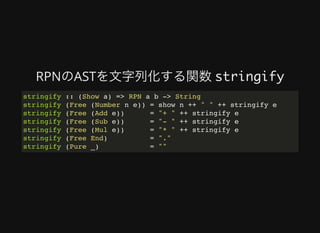
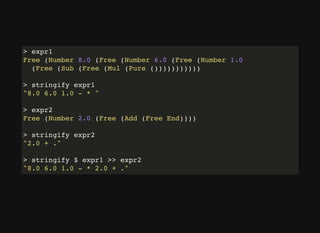
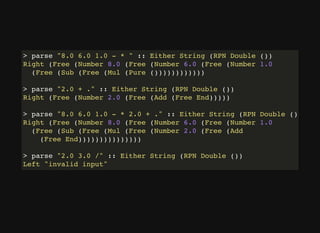
2. The document provides an example of defining a DSL for reverse polish notation (RPN) expressions using a Free monad. This includes defining the RPNExpr data type, making it a Functor, lifting it into a Free monad, and writing functions for evaluation, parsing, and pretty-printing RPN expressions.
3. By defining the interpreter as a monad, the RPN expressions can be combined in a composable manner while retaining the ability to run,

![Self-introduction
/laʒenɔʁɛ̃k/ カマイルカlagénorhynque
(defprofile lagénorhynque
:name "Kent OHASHI"
:account @lagenorhynque
:company "Opt, Inc."
:languages [Clojure Haskell Python Scala
English français Deutsch русский]
:interests [programming language-learning mathematics]
:contributing [github.com/japan-clojurians/clojure-site-ja])](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/free-monads-getting-started-170526071638/85/Free-Monads-Getting-Started-2-320.jpg)



![return
値 a をモナド m に⼊れる
Haskell: return
Scalaz: point
a -> m a
A => M[A]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/free-monads-getting-started-170526071638/85/Free-Monads-Getting-Started-6-320.jpg)
![bind
値 m a に 関数 a -> m b を適⽤して m b にする
Haskell: >>=
Scalaz: bind (cf. flatMap)
m a -> (a -> m b) -> m b
M[A] => (A => M[B]) => M[B]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/free-monads-getting-started-170526071638/85/Free-Monads-Getting-Started-7-320.jpg)



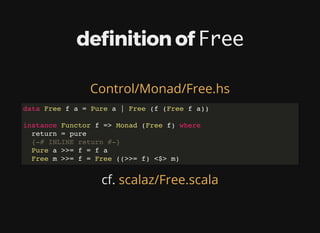
![リストのような再帰的データ構造
data [] a = [] | a : [a]
f が Functor ⇒ Free f は Monad
→ Functor のインスタンスを Free で包めば
Monad として扱える
※ GHC拡張で Functor を⾃動導出することも:
DeriveFunctor](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/free-monads-getting-started-170526071638/85/Free-Monads-Getting-Started-12-320.jpg)



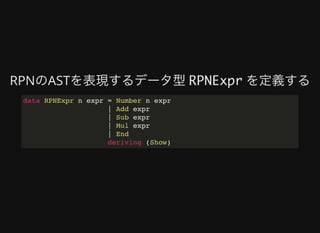

![⽂字列をRPNのASTに変換する関数 parse
parse :: (Read a) => String -> Either String (RPN a ())
parse = foldM rpn (Pure ()) . reverse . words
where
rpn e "+" = Right . Free $ Add e
rpn e "-" = Right . Free $ Sub e
rpn e "*" = Right . Free $ Mul e
rpn _ "." = Right $ Free End
rpn e n = case reads n of
[(v,_)] -> Right . Free $ Number v e
_ -> Left "invalid input"](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/free-monads-getting-started-170526071638/85/Free-Monads-Getting-Started-24-320.jpg)
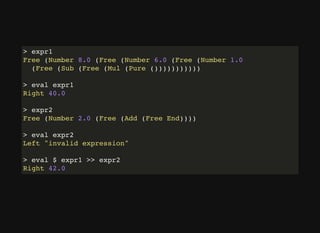
![RPNのASTを評価する関数 eval
eval :: (Num a) => RPN a b -> Either String a
eval = calc []
where
calc stack (Free (Number n e)) = calc (n : stack) e
calc (n1:n2:ns) (Free (Add e)) = calc (n2 + n1 : ns) e
calc (n1:n2:ns) (Free (Sub e)) = calc (n2 - n1 : ns) e
calc (n1:n2:ns) (Free (Mul e)) = calc (n2 * n1 : ns) e
calc (n:_) (Free End) = Right n
calc (n:_) (Pure _) = Right n
calc _ _ = Left "invalid expression"](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/free-monads-getting-started-170526071638/85/Free-Monads-Getting-Started-26-320.jpg)