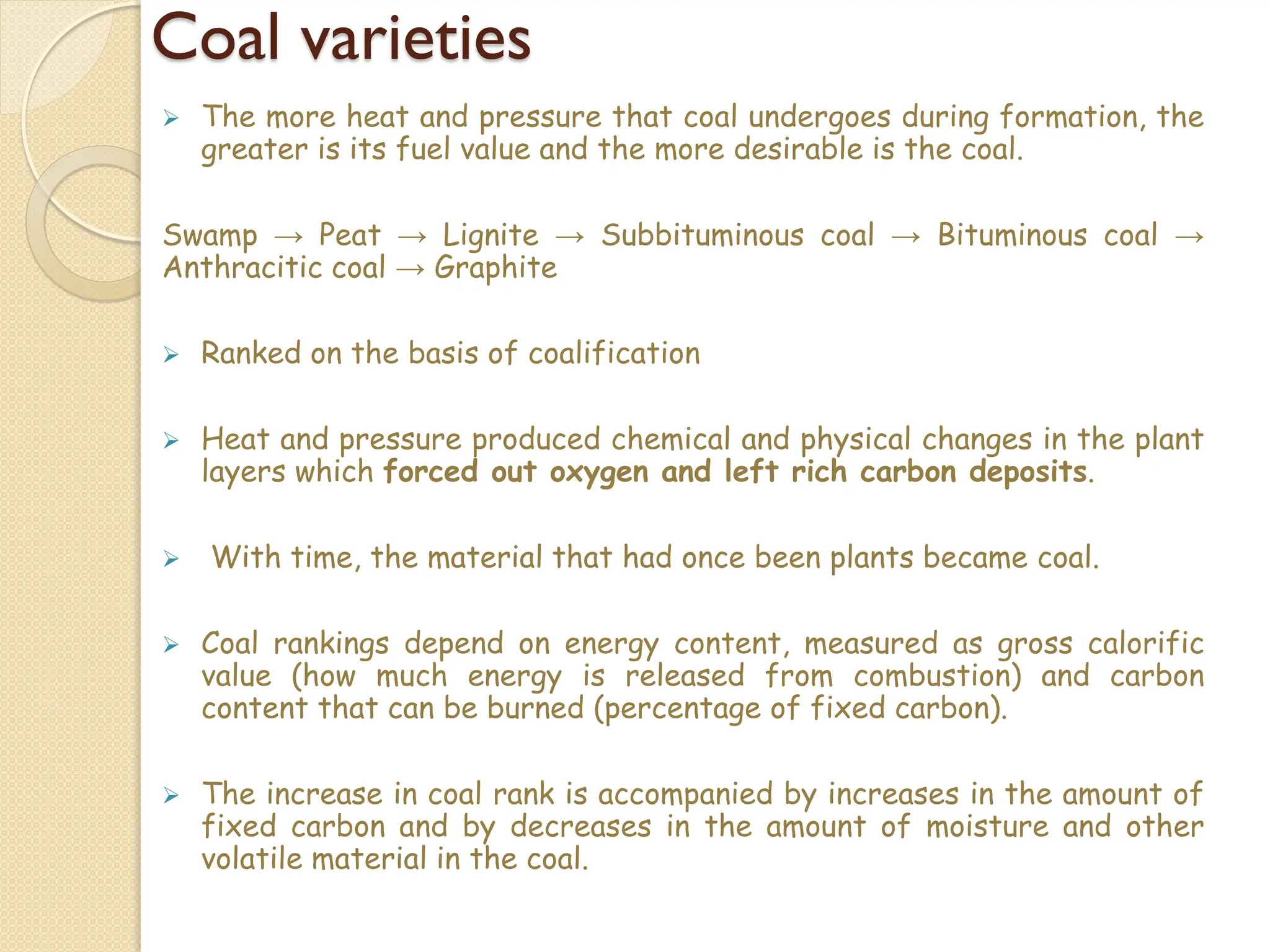
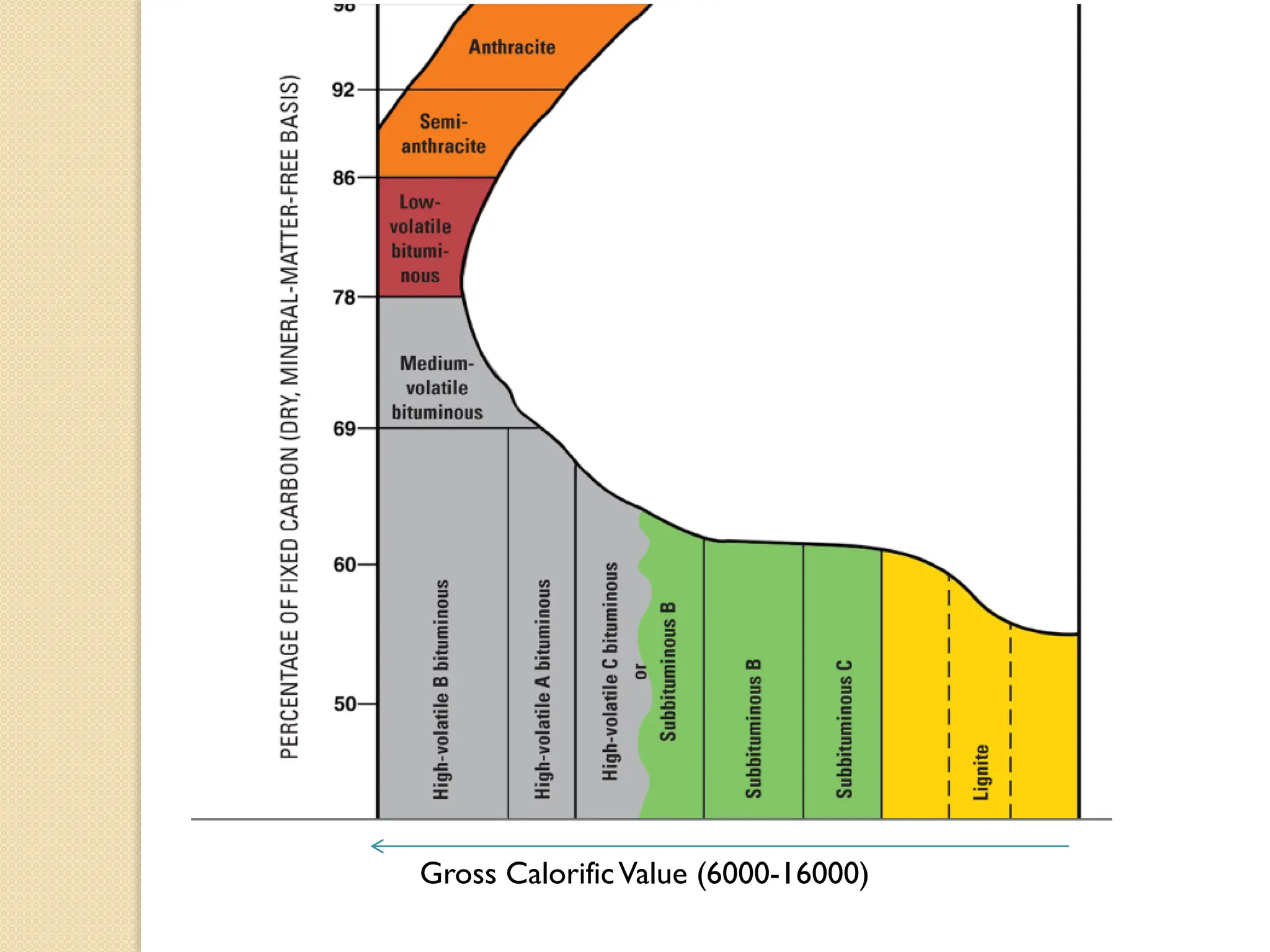
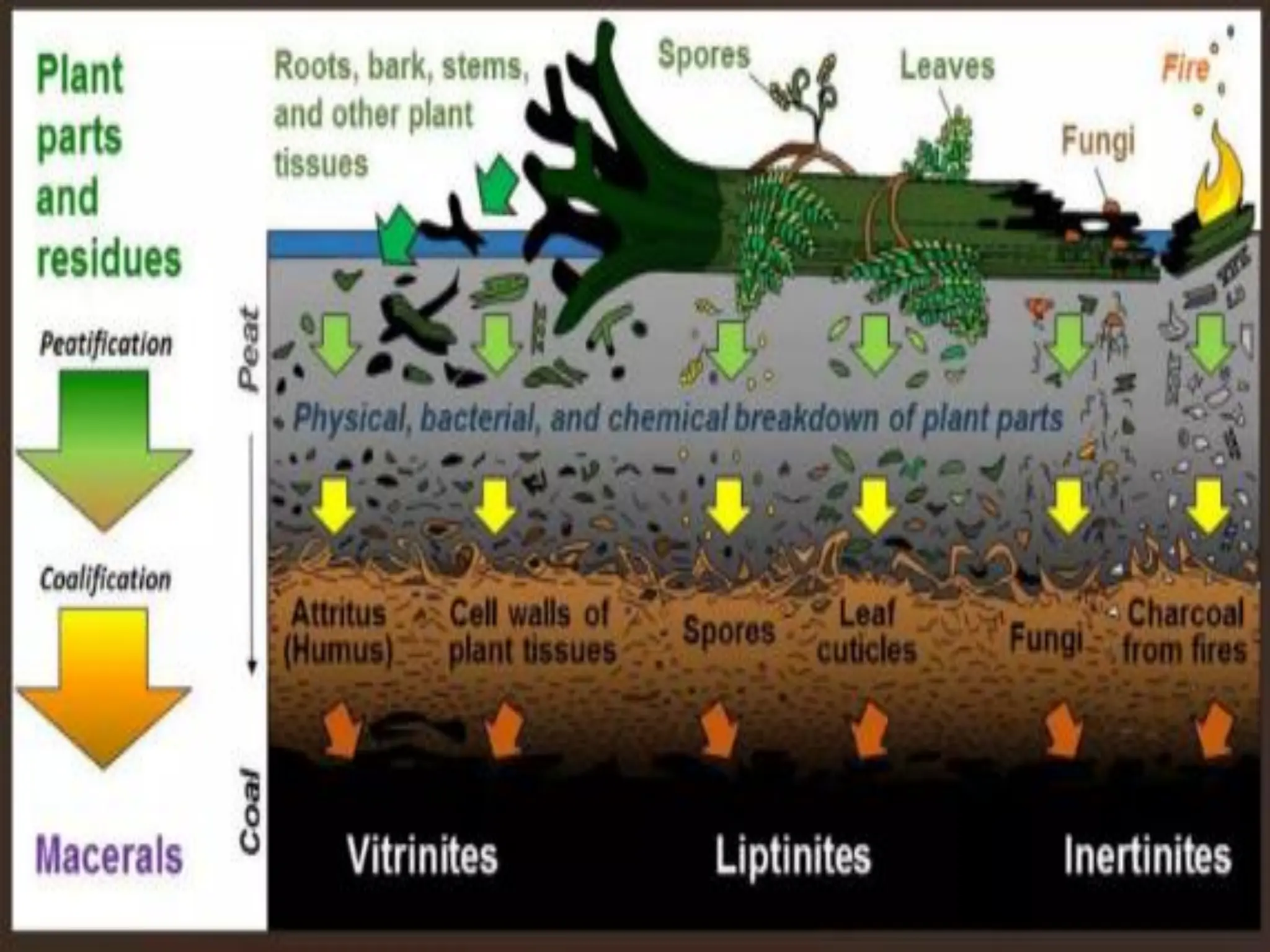
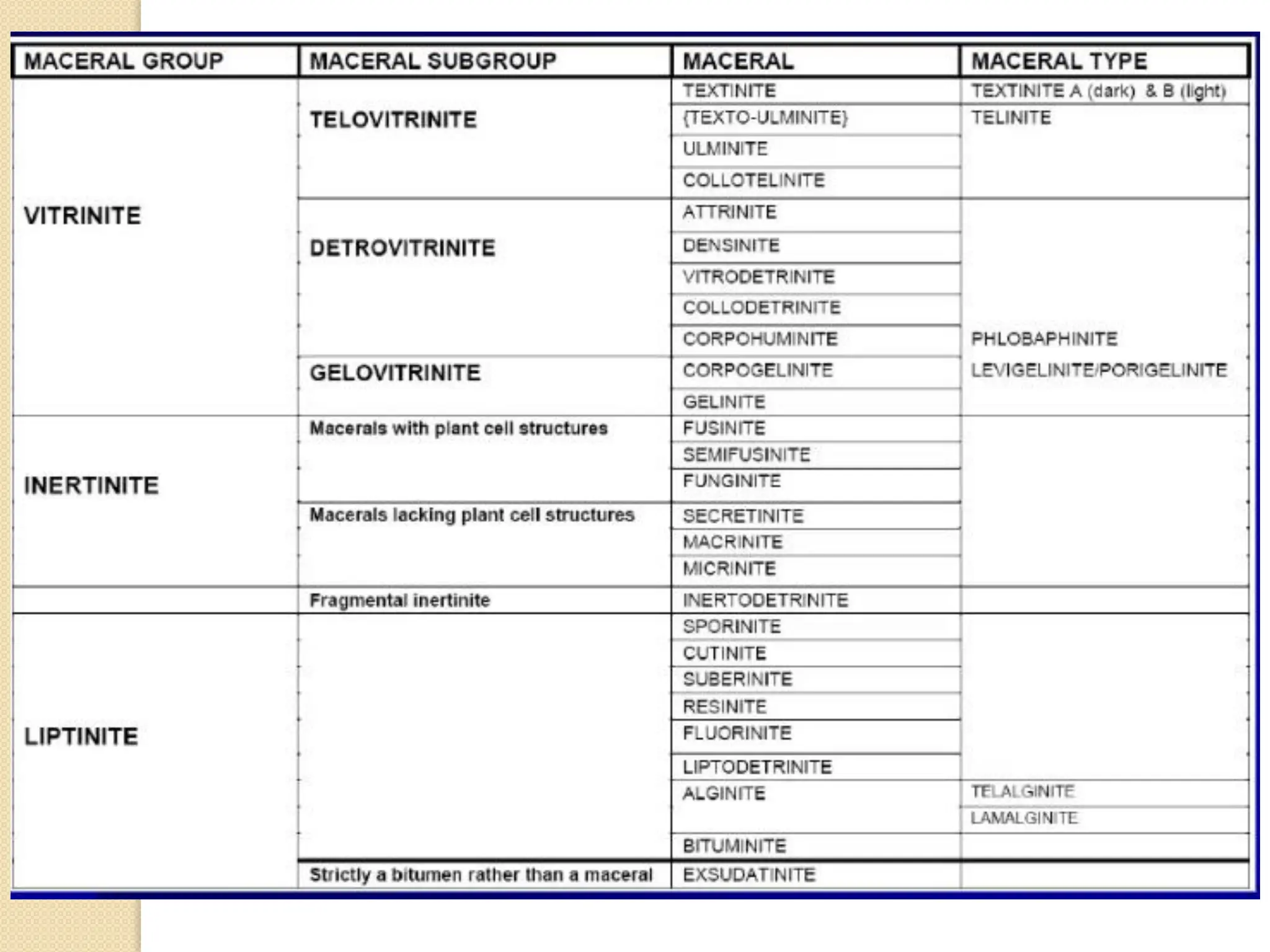
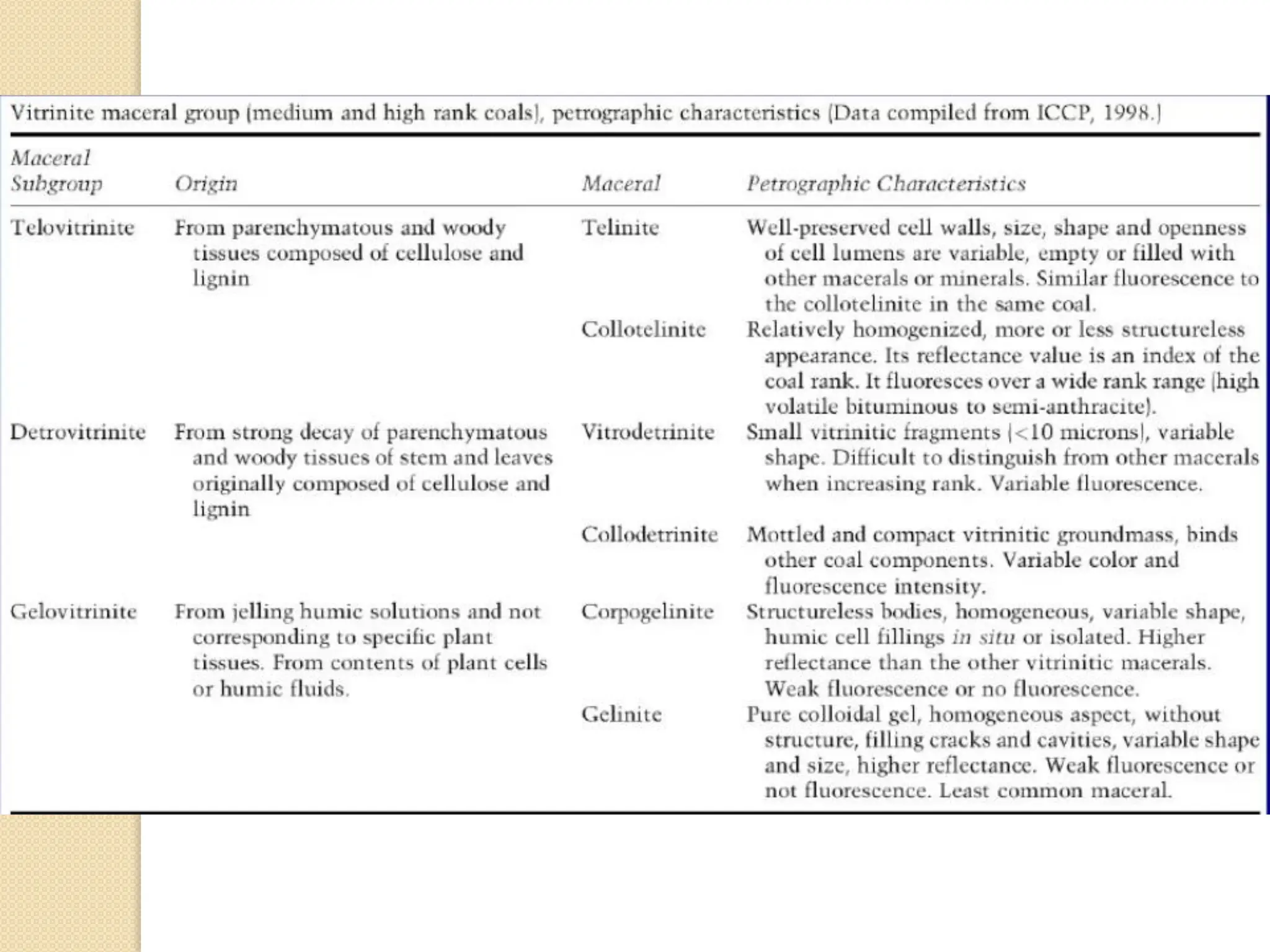
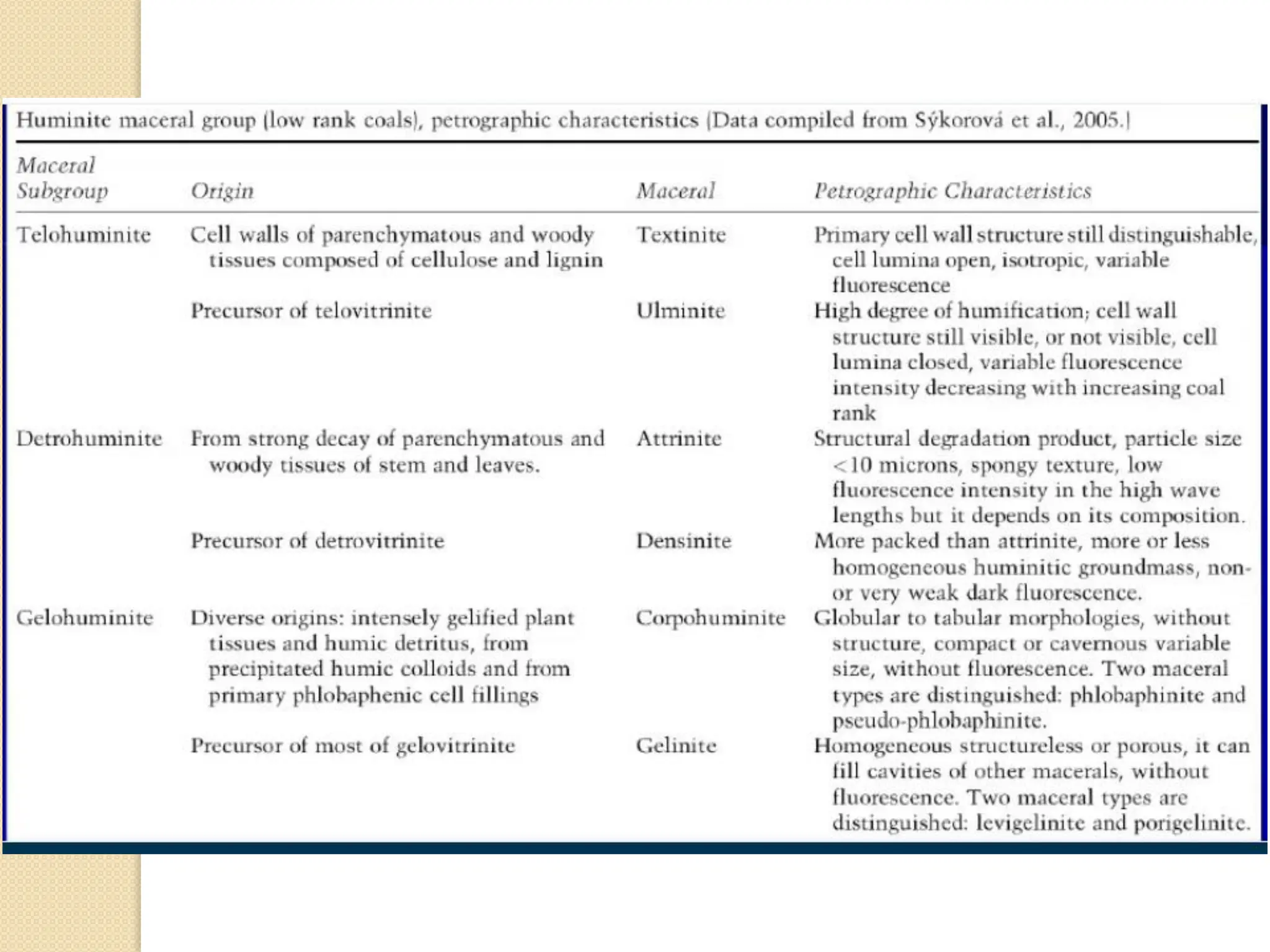
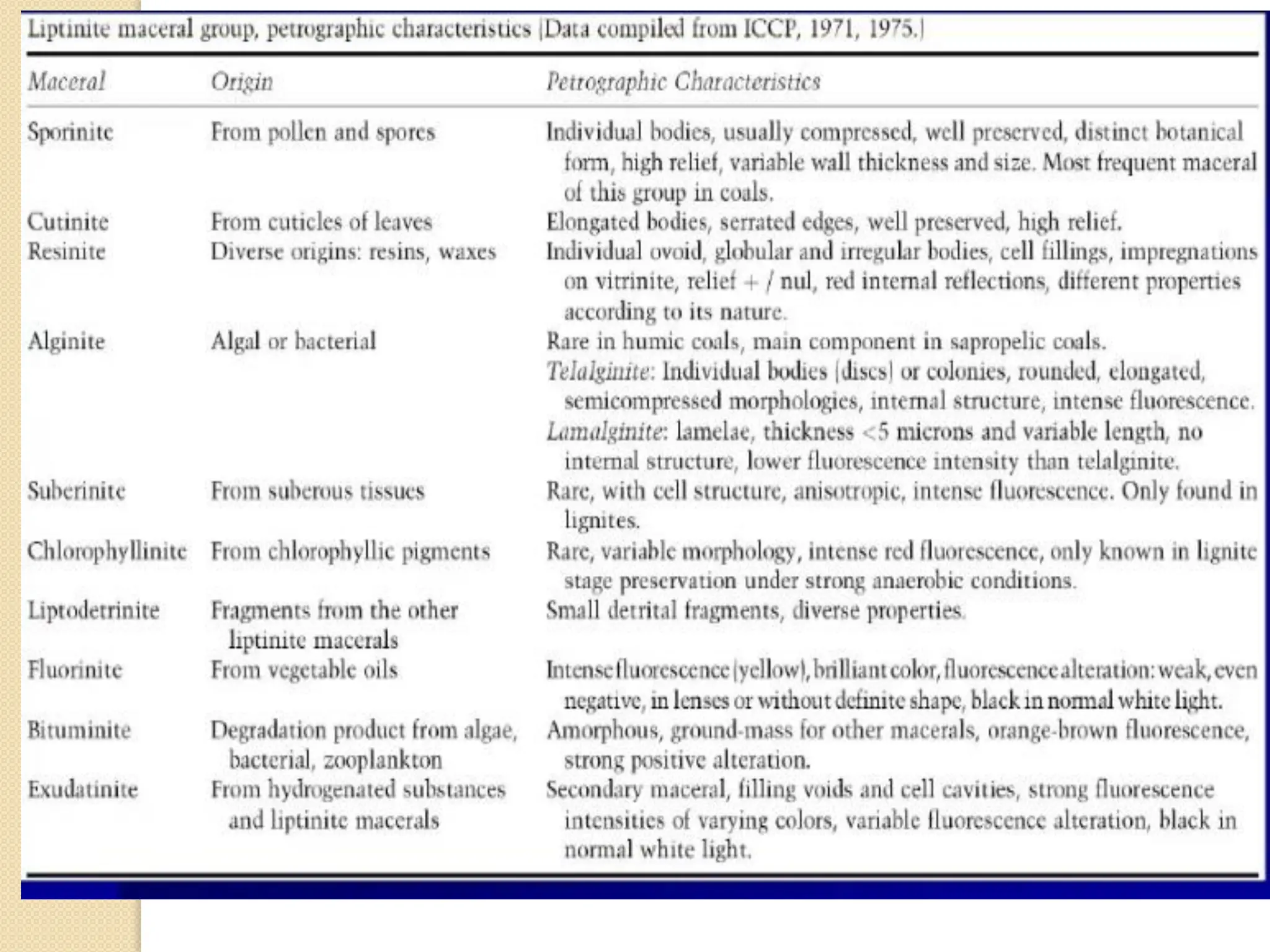
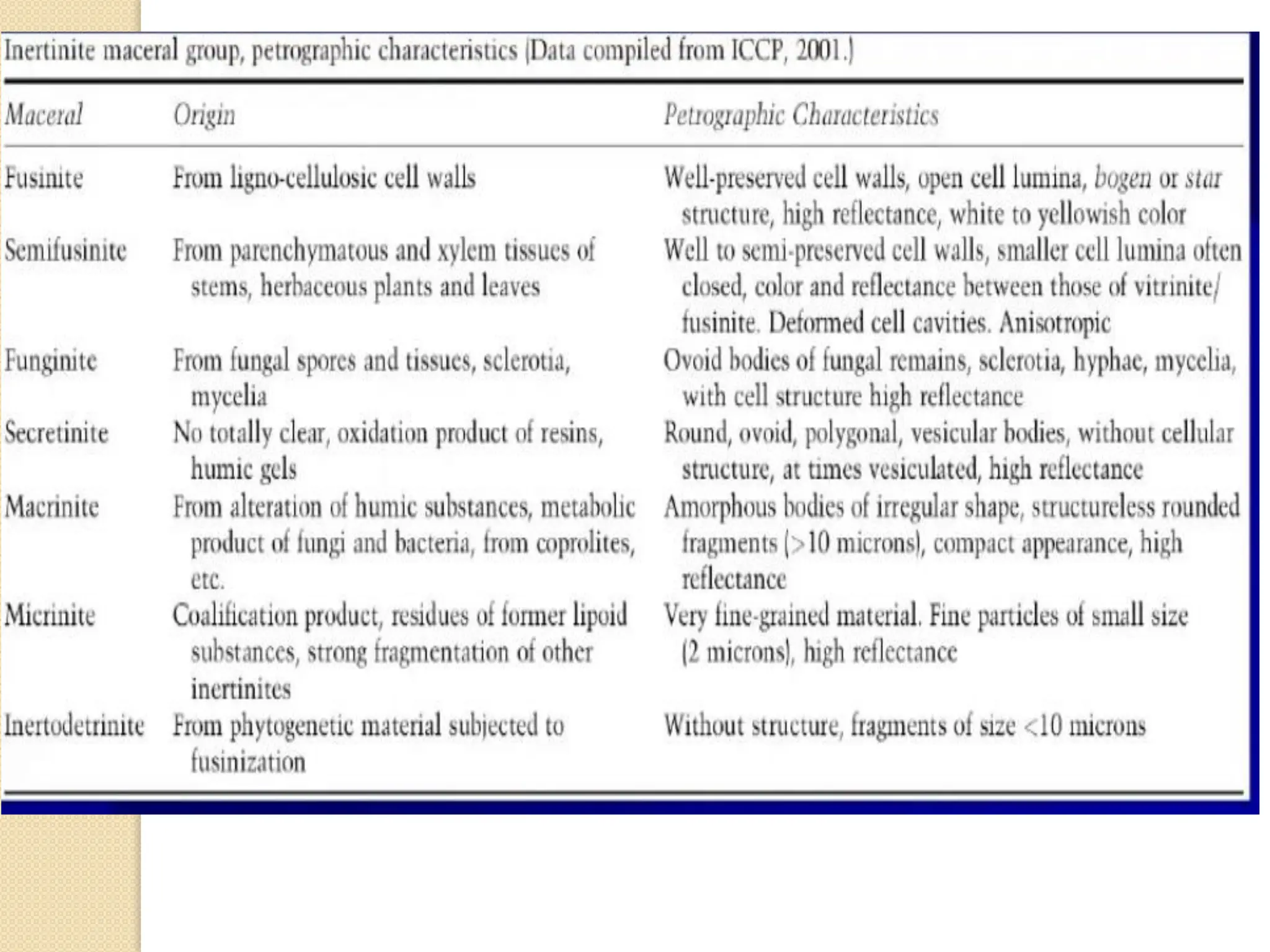
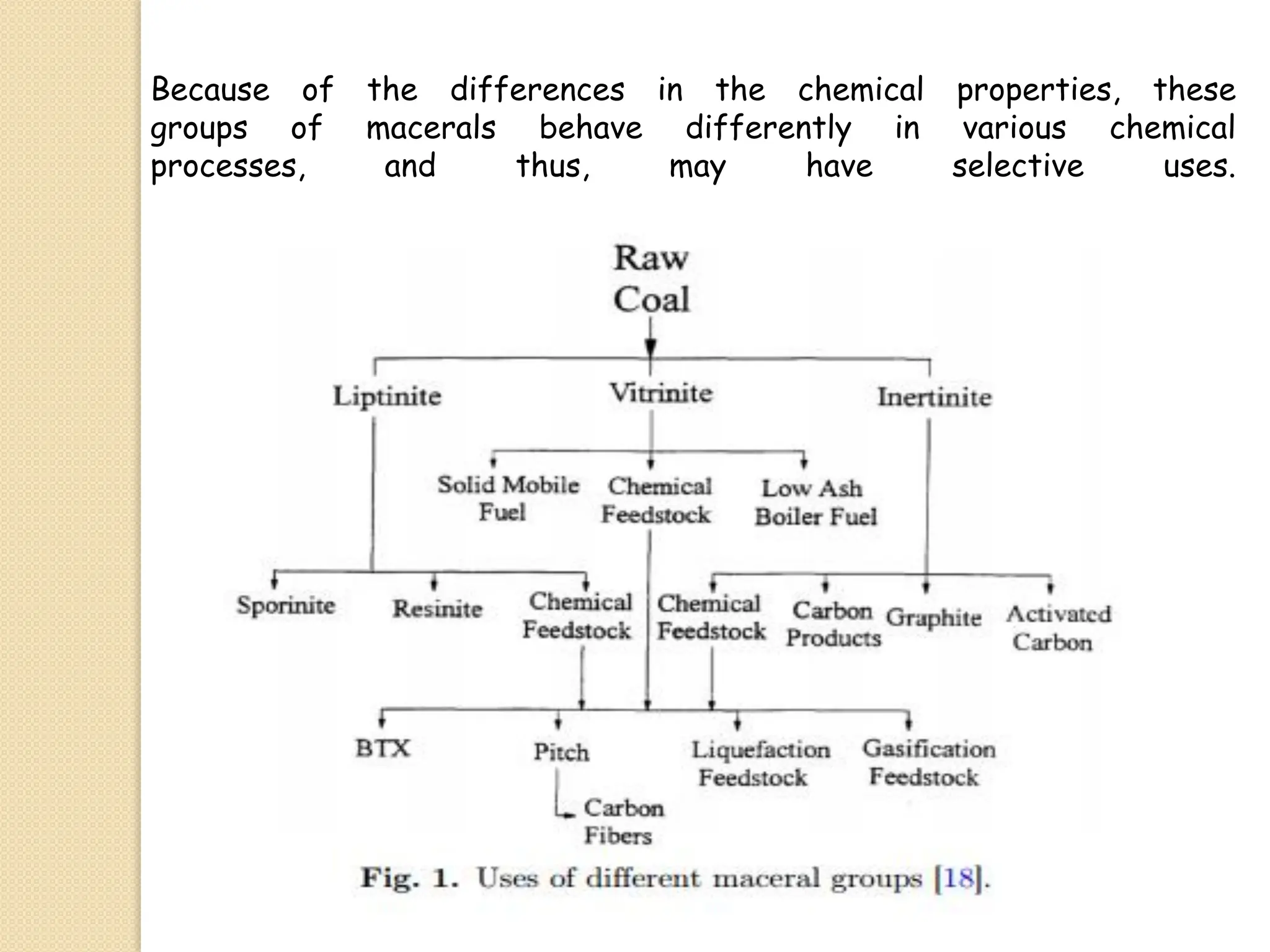
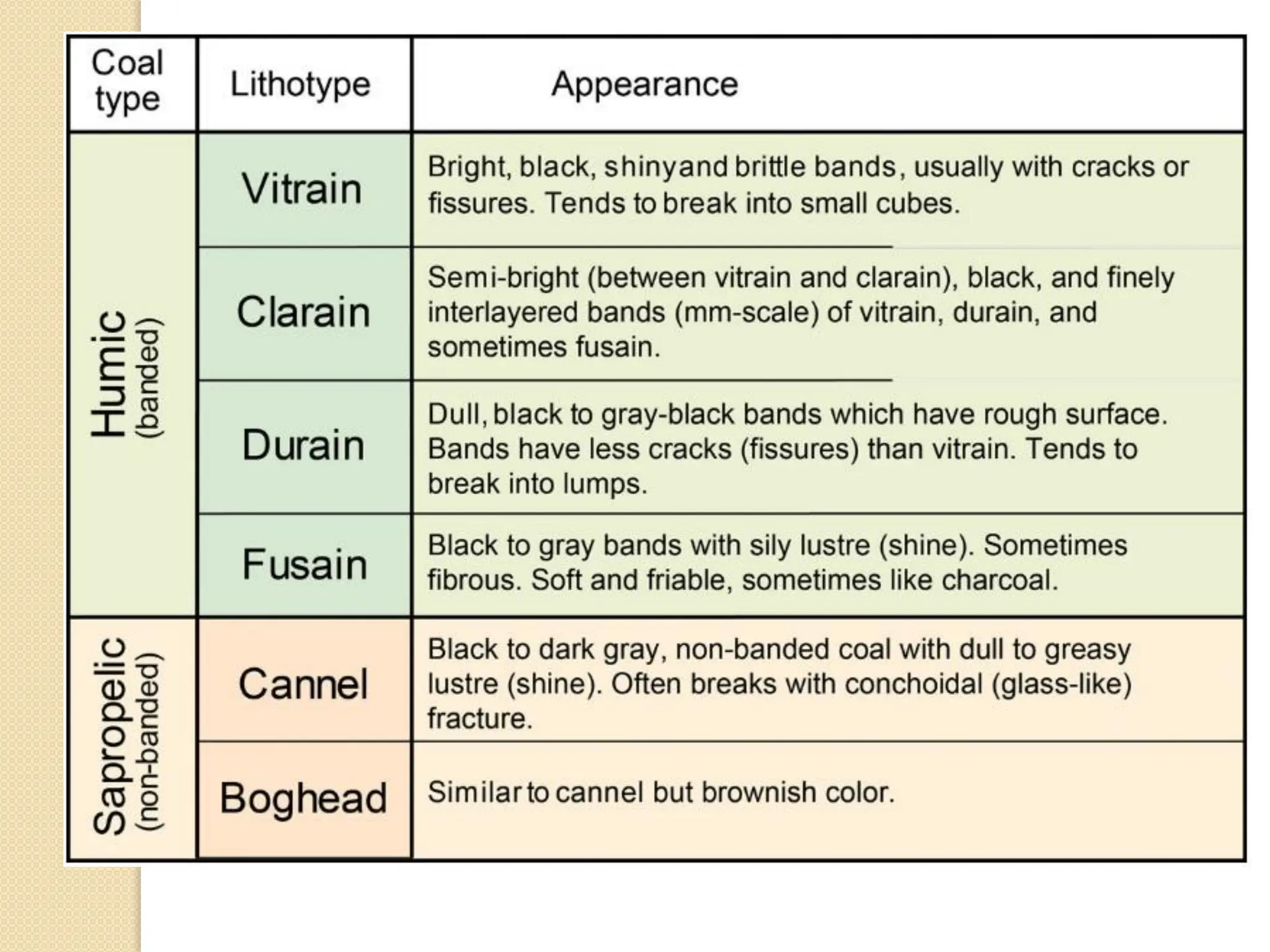
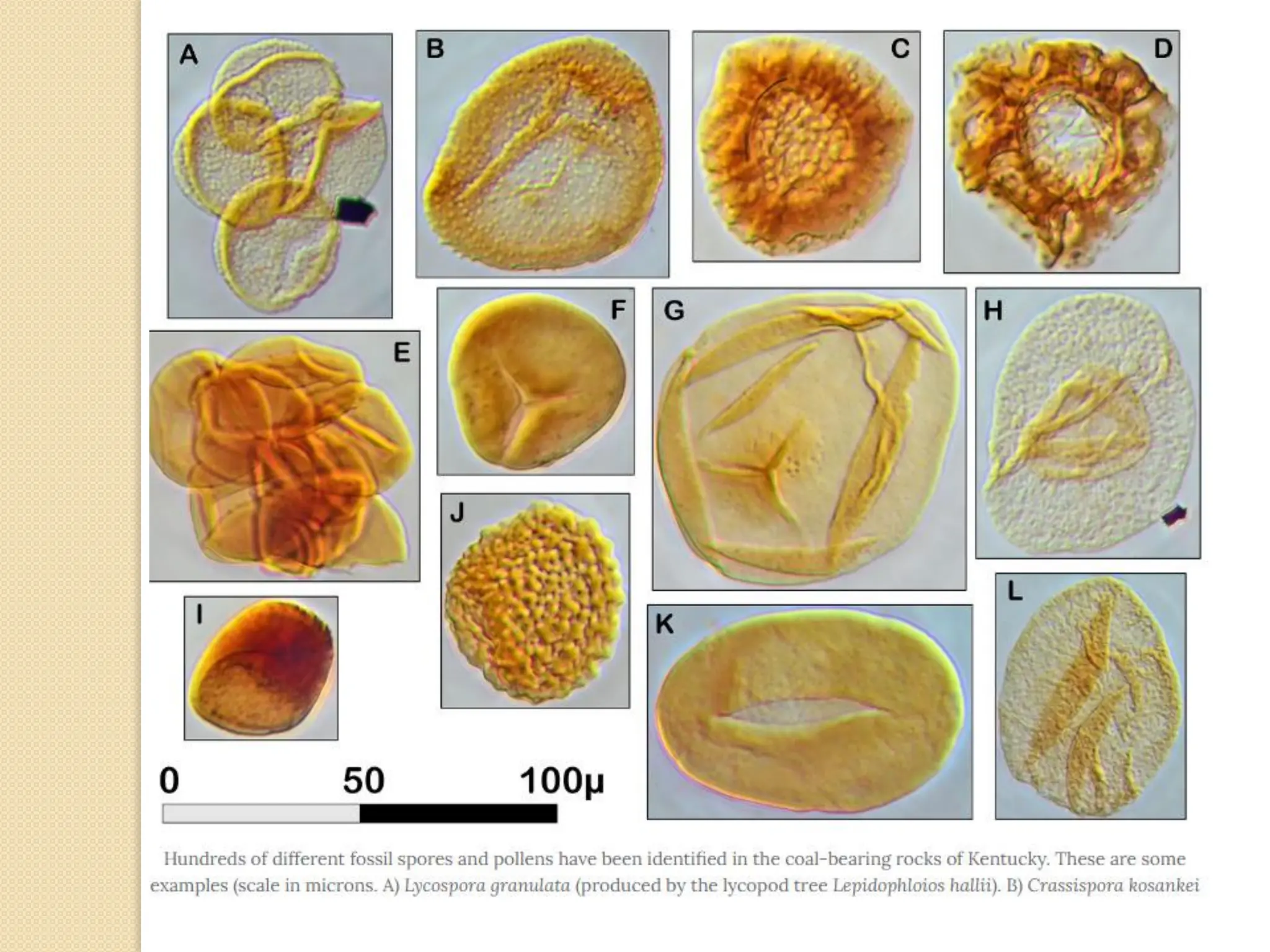
Fossil fuels, including coal, petroleum, and natural gas, are nonrenewable energy sources formed from the remains of ancient organisms through geological processes over millions of years. They release carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases upon combustion, significantly contributing to global warming, while peatlands, which sequester carbon, represent critical ecosystems that require monitoring to prevent emissions from their degradation. The document details the formation, extraction, and thermal processing of fossil fuels, as well as the ecological and economic importance of peat and its role in climate regulation.