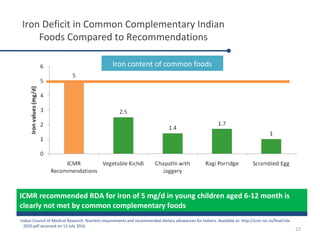
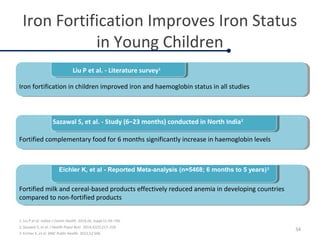
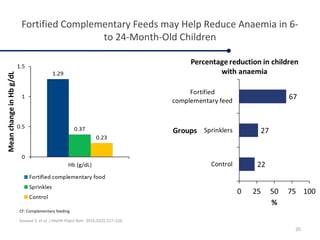
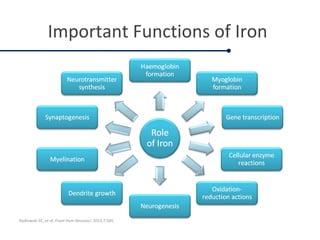
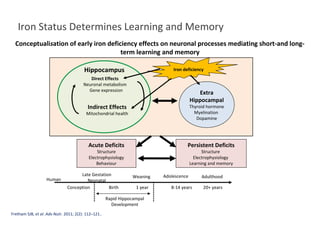
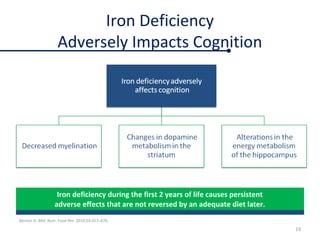
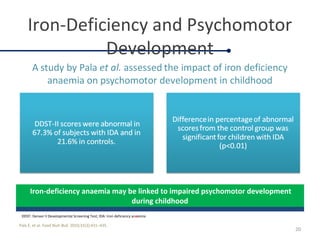
Fortified complementary foods can help address hidden hunger and nutrient deficiencies in children under 2 years of age. Iron deficiency is a particular problem, with prevalence of anemia estimated to affect over 50% of Indian children. While breastmilk is important, it does not provide all nutrients needed during complementary feeding. Common local foods are also low in critical nutrients like iron. Fortifying complementary foods with micronutrients is a promising strategy, as it has been shown in multiple studies to improve iron and hemoglobin status in young children. Fortification may help bridge the nutrient gaps more effectively than oral supplements alone. Widespread use of fortified complementary foods has the potential to reduce anemia and its cognitive impacts on young, developing children.











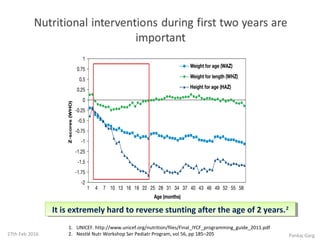

![Complementary Feeding: A Critical
Window for Improving Iron Status
Krebs N, et al. Nutr Today. 2014;49(6):271–277. 24
1000 days critical window
PREGNANCY Exclusive
Breast Feeding
COMPLEMENTARY FEEDING OUTCOMES
↓ Iron stores
↑ Postnatal requirement
Low Fe intake from milk
↓ Milk [Zn] & ↓ Zn intake
Growth requirement
Human Milk
Dependence on CF:
Fe & Zn Rich Foods
(meats) &/or
Fortified Foods
Improved Fe
& Zn Status
Improved Neuro
cognitive Development
& Immune Function
↑LAZ
↑↓ Stunting
↑ Maternal growth & nutritional status
↑ Maternal Education
↓ Enteric infection & inflammation
+
+
CF: Complementary foods; LAZ: Length-for-age Z score; Fe: iron; Zn: zinc .
After 6 months](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fortifiedcomplementaryfoods-170526131116/85/Fortified-complementary-foods-Dr-M-Sucindar-24-320.jpg)
![Nutrient Gap for Iron is the widest
World Health Organization. Complementary feeding: Report of the global consultation [Internet]. 2001.
25
94% of Iron
Requirements
Need to be
Fulfilled by
Complementar
y foods
Nutrient Gaps to be filled by complementary foods
for a breastfed child 12–23 months](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fortifiedcomplementaryfoods-170526131116/85/Fortified-complementary-foods-Dr-M-Sucindar-25-320.jpg)