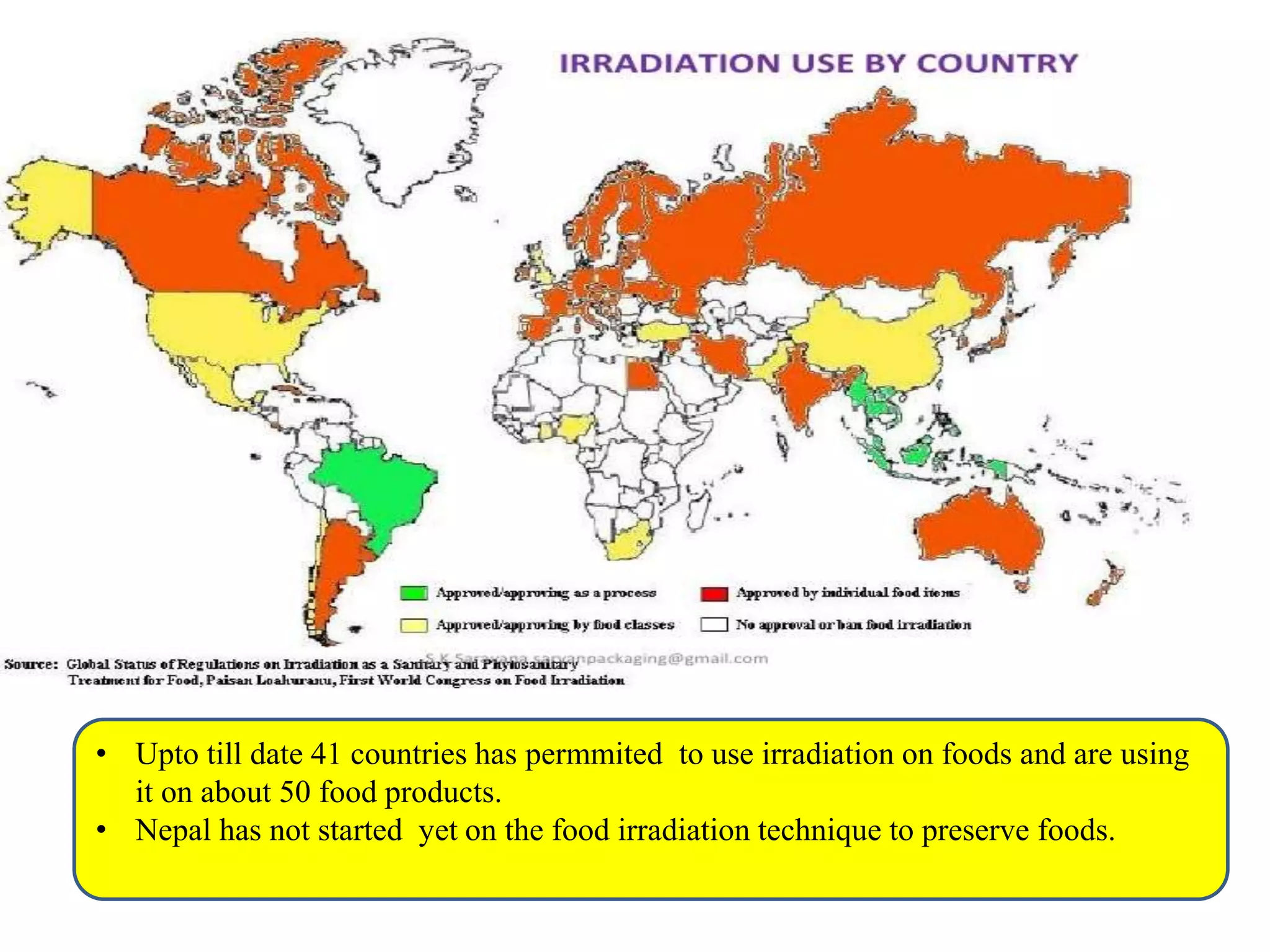
The document presents information on food irradiation, including what it is, how it works, its history and origins, advantages, and disadvantages. Specifically, it explains that food irradiation uses ionizing radiation to kill bacteria, parasites, and microbes in food in order to eliminate foodborne illness. It notes several countries that permit and use food irradiation and lists organizations that support its use. However, it also outlines some disadvantages like high costs and potential vitamin loss.