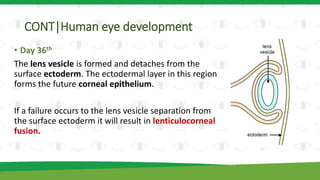
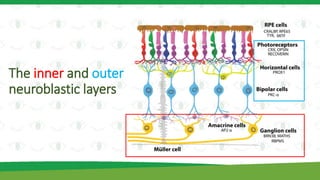
The document discusses the vital role of folate (vitamin B9) in human eye development and its connection to eye diseases related to folic acid deficiency. It highlights the importance of folate during pregnancy for preventing congenital abnormalities and outlines the various folate transport proteins present in the ocular structure. Additionally, it summarizes the consequences of folate deficiency, including nutritional amblyopia, retinal damage, and increased risk of cataracts, supported by findings from human and animal studies.