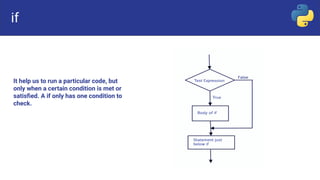
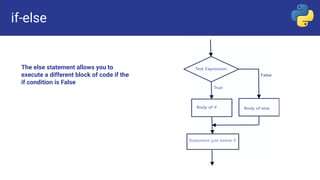
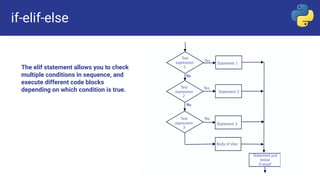
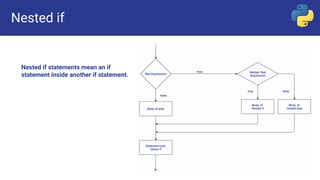
Control flow statements in programming include sequential, selection, and repetition statements. Selection statements, also called decision or branching statements, allow a program to test multiple conditions and execute code based on which conditions are true. Common selection statements include if, if-else, if-elif-else, and nested if statements. If statements run code when a single condition is met, if-else runs one code block if true and another if false, if-elif-else checks conditions sequentially, and nested if places an if inside another if.