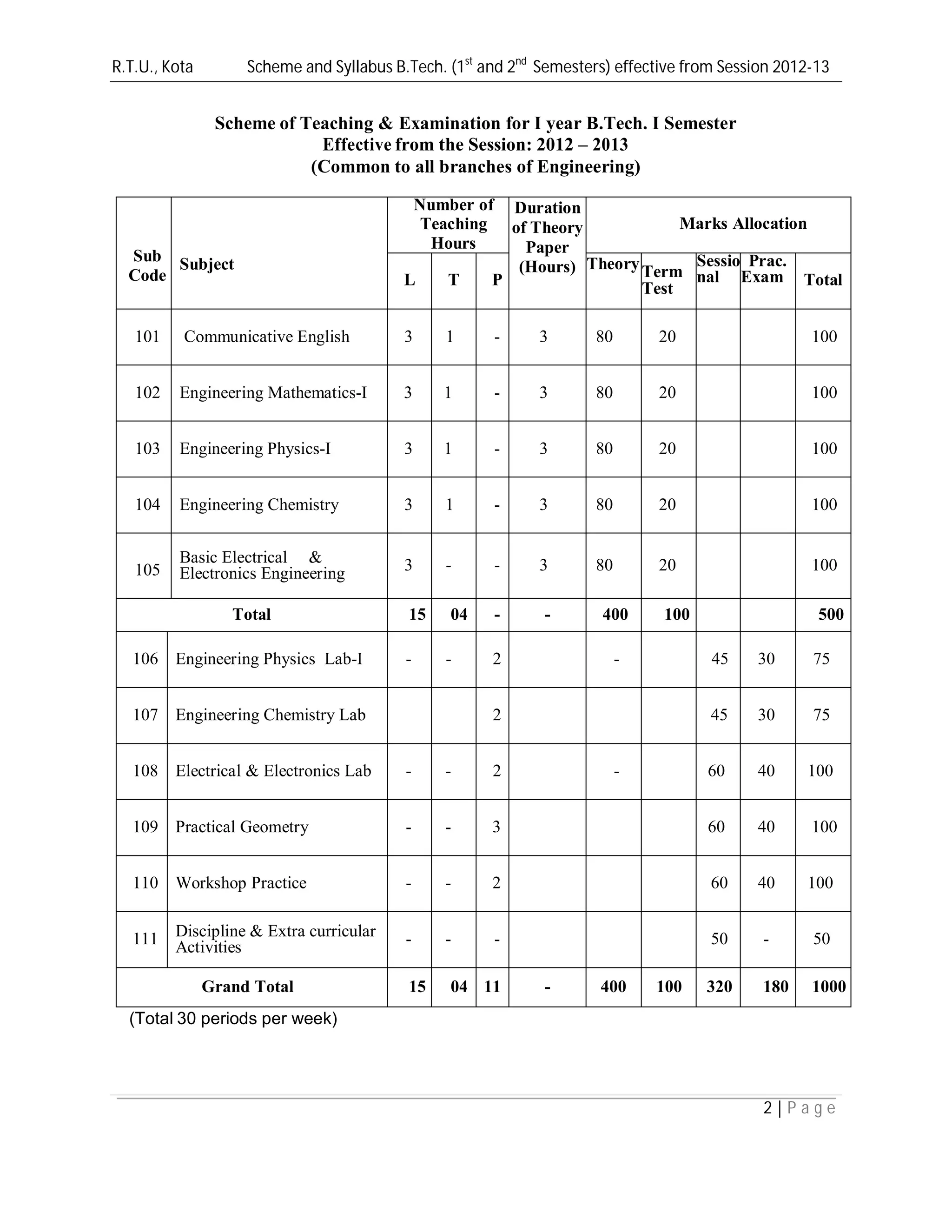
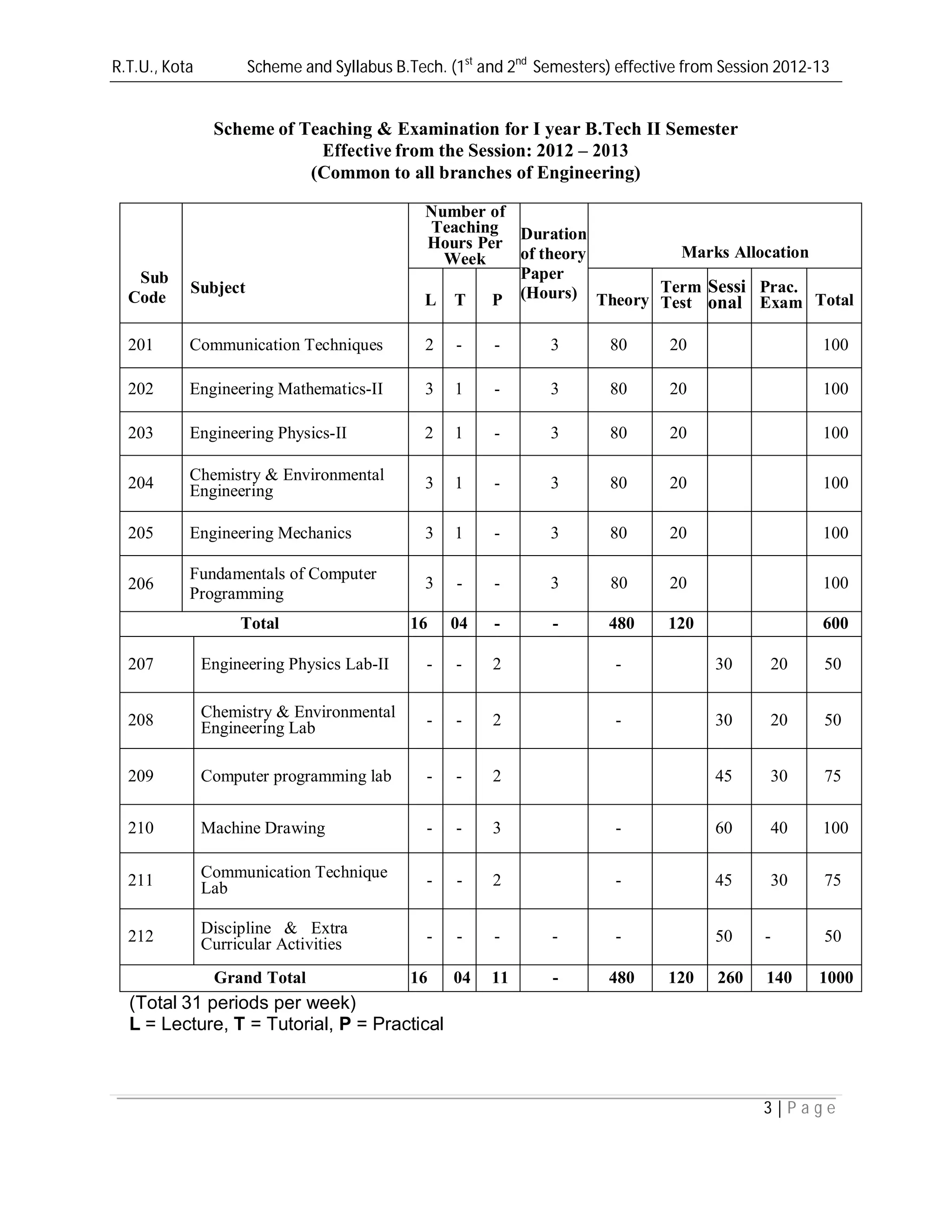
This document provides the scheme and syllabus for the first and second semesters of the B.Tech program at R.T.U., Kota effective from the 2012-2013 session. It includes:
1) The list of subjects for each semester, number of teaching hours for each, exam duration and marks allocation.
2) The detailed syllabus for the core subjects of the first semester like Communicative English, Engineering Mathematics, Engineering Physics, Engineering Chemistry, and Basic Electrical and Electronics Engineering.
3) The scheme of examinations for labs and other subjects in the first and second semesters.