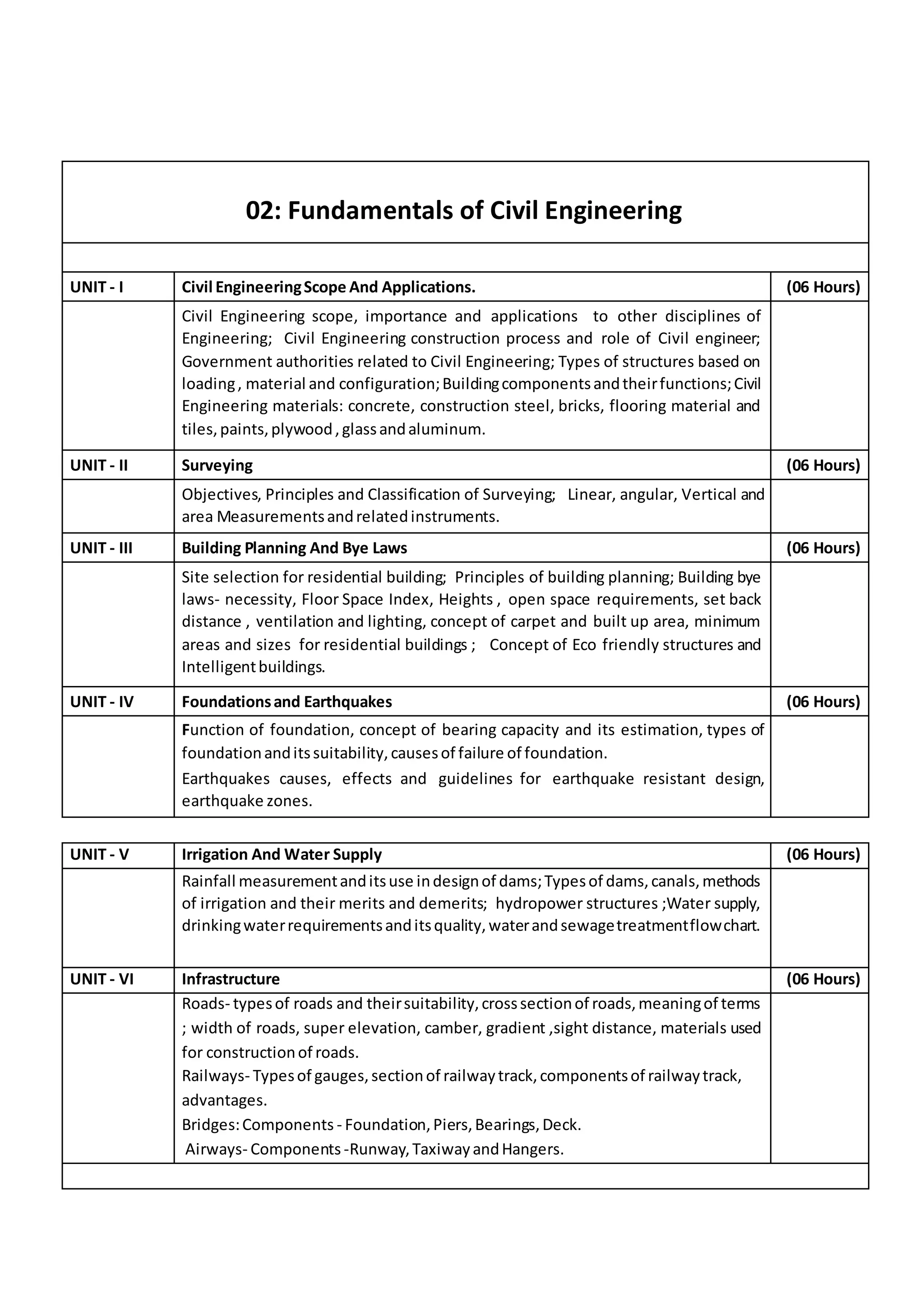
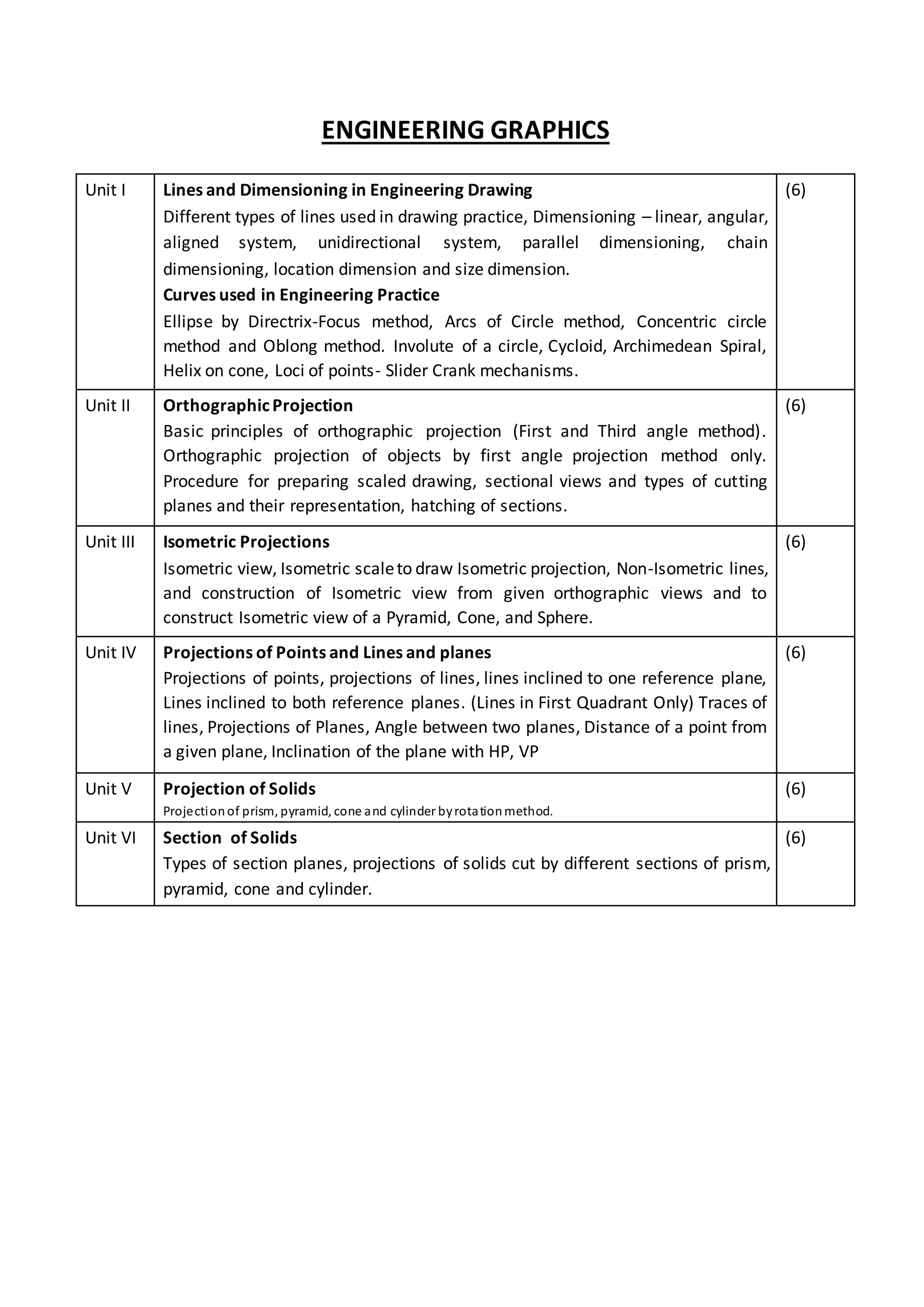
The document provides an overview of the topics covered in the Engineering Mathematics-I course. The course covers six units: (1) matrices, linear transformations, and eigenvalues; (2) complex numbers and applications; (3) differential calculus; (4) infinite series; (5) partial differentiation and applications; and (6) Jacobians and maxima/minima problems. It also outlines the key concepts taught in each unit, such as rank, normal form, Taylor/Maclaurin series, L'Hospital's rule, and Lagrange's method of undetermined multipliers.