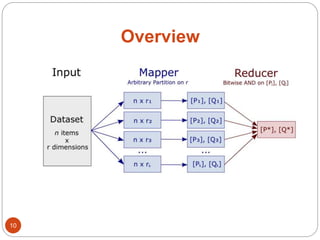
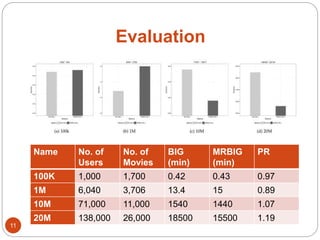
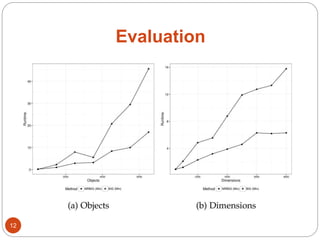
The document discusses a methodology for finding top-k dominance in incomplete big data using a MapReduce framework. It introduces algorithms like skyband-based and bitmap index guided algorithms to handle missing values and improve data evaluations. The paper includes technical definitions, evaluation metrics, and performance data across various user and movie datasets.





![References
13
Finding Top- k Dominance on Incomplete Big
Data Using MapReduce Framework [link]
Top-k dominating queries on incomplete data
[link]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/top-k-181223194810/85/Finding-Top-k-Dominance-on-Incomplete-Big-Data-Using-MapReduce-Framework-13-320.jpg)