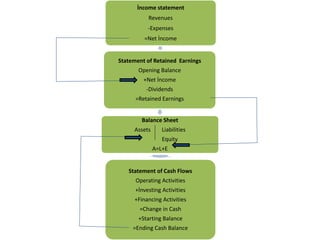
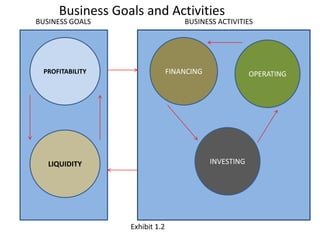
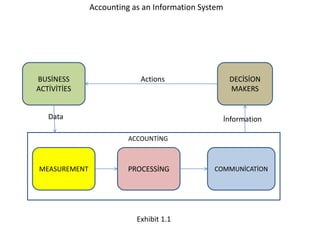
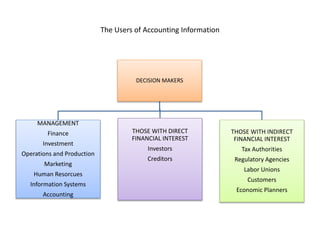
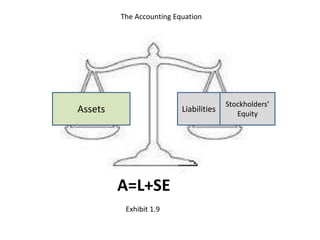
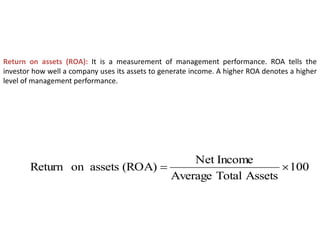
The document outlines key components of financial statements, which include the income statement, statement of retained earnings, balance sheet, and statement of cash flows, detailing how they contribute to understanding a business's profitability and liquidity. It emphasizes the role of accounting as an information system linking business activities with decision-makers and introduces various financial ratios to evaluate business performance. The document also categorizes users of accounting information based on their direct or indirect financial interests in a business.